Overview
Creating custom data sources for Reports is useful when knowing what all of the data sources will be. When the list of data sources can only be known at runtime, it's useful to create a data source factory that can create the necessary list of data sources at runtime.
Example
The following example will demonstrate a case where each data source reads its information from a database table.
TableDataSource
The class below is a Data Source that takes a database table name as a parameter in its constructor. Based on that, the class returns the columns it wants to provide Reports in the ReportFields property and the Report data from the GetData() method.
using System.Data;
using DecisionsFramework.Design.ConfigurationStorage.Attributes;
using DecisionsFramework.Design.Report;
namespace MyNamespace
{
[Writable]
public class TableDataSource : AbstractCustomDataSource, ISpecifiedCategoryReportFilter
{
public string TableName { get; set; }
public TableDataSource(string tableName)
{
TableName = tableName;
}
public override bool Applies(ReportDefinition definition)
{
return definition.HasDataSourcesOrFilters() == false;
}
public override ReportFieldData[] ReportFields
{
get
{
// Here, the class could access the database to discover what the columns are.
// To simplify this example, we will return two columns of data.
return new ReportFieldData[] { new ReportFieldData(TableName, "Column1", typeof(int)),
new ReportFieldData(TableName, "Column2", typeof(string))};
}
}
public override DataTable GetData(DataTable table, IReportFilter[] filters, int? limitCount, int pageIndex)
{
// create the DataTable if it doesn't exist yet
if (table == null) table = new DataTable();
// set up the columns in the DataTable based on the ReportFields
table.Columns.AddRange(GetColumnsFromReportFields(ReportFields));
// At this point, the class would read the rows from the database and fill the DataTable
// [CODE OMITTED]
return table;
}
// This property implemented as part of ISpecifiedCategoryReportFilter,
// allows the class to specify which category it belongs in.
public string[] Category
{
// For this example, specify a sample category name.
get { return new string[] { "My Database Table Sources" }; }
}
// When used with a Data Source Factory, Data Sources have their names pulled from the ToString() method.
public override string ToString()
{
return TableName;
}
}
}
TableDataSourceFactory
A data source factory can be created which creates objects of the TableDataSource class and returns them:
using System.Collections.Generic;
using DecisionsFramework.Data.ORMapper;
using DecisionsFramework.Design.Report;
namespace MyNamespace
{
[AutoRegisterReportElementFactory("My Database Table Sources", "Sample Factory")]
class TableDataSourceFactory : IFilterFactory
{
// This method returns the data sources that Decisions should use.
public IReportFilter[] GetFilters(CompositeSelectStatement compositeSelectStatement, IReportFilter[] currentFilters)
{
List<ireportfilter> results = new List<ireportfilter>();
// Here, the class would determine which database tables should be made available as data sources
// based on whatever logic is required.
// As an example, two tables are used as parameters for TableDataSource objects.
results.Add(new TableDataSource("dog"));
results.Add(new TableDataSource("cat"));
return results.ToArray();
}
// This method is part of the IFilterFactory interface, but not necessary for this example.
// DataSources that implement the ICustomFilter also implement an IncludeRow(DataRow row) method,
// which allows them to filter out individual rows from the report.
public ICustomFilter[] GetCustomFilters(ReportDefinition def, IReportFilter[] currentFilters)
{
return null;
}
}
}
</ireportfilter></ireportfilter>
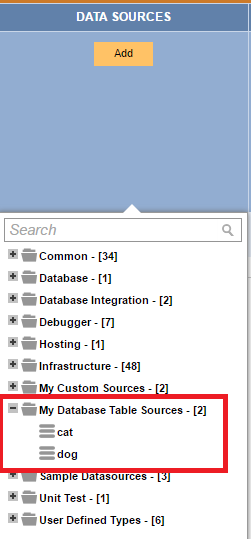
After building these two classes in a project with the Decisions SDK and installing it, the two TableDataSources will appear in the Report Designer: