Overview
You can configure the portal to enable default auditing. The system will then audit transactions involving all entities, such as folders, assets, and tasks.
Users can view an audit Report by selecting an entity and viewing the audit history.
To enable system-level auditing, navigate to the System > Settings folder, select Default Auditing Settings and click the Edit Settings option in the bottom right.
Example
In the example, configure the portal to enable auditing.
Begin by navigating to the folder System > Settings. In the folder data panel in the Entity Name list, click Default Auditing Settings. In the Entity Actions menu in the lower right, select Edit.
.png)
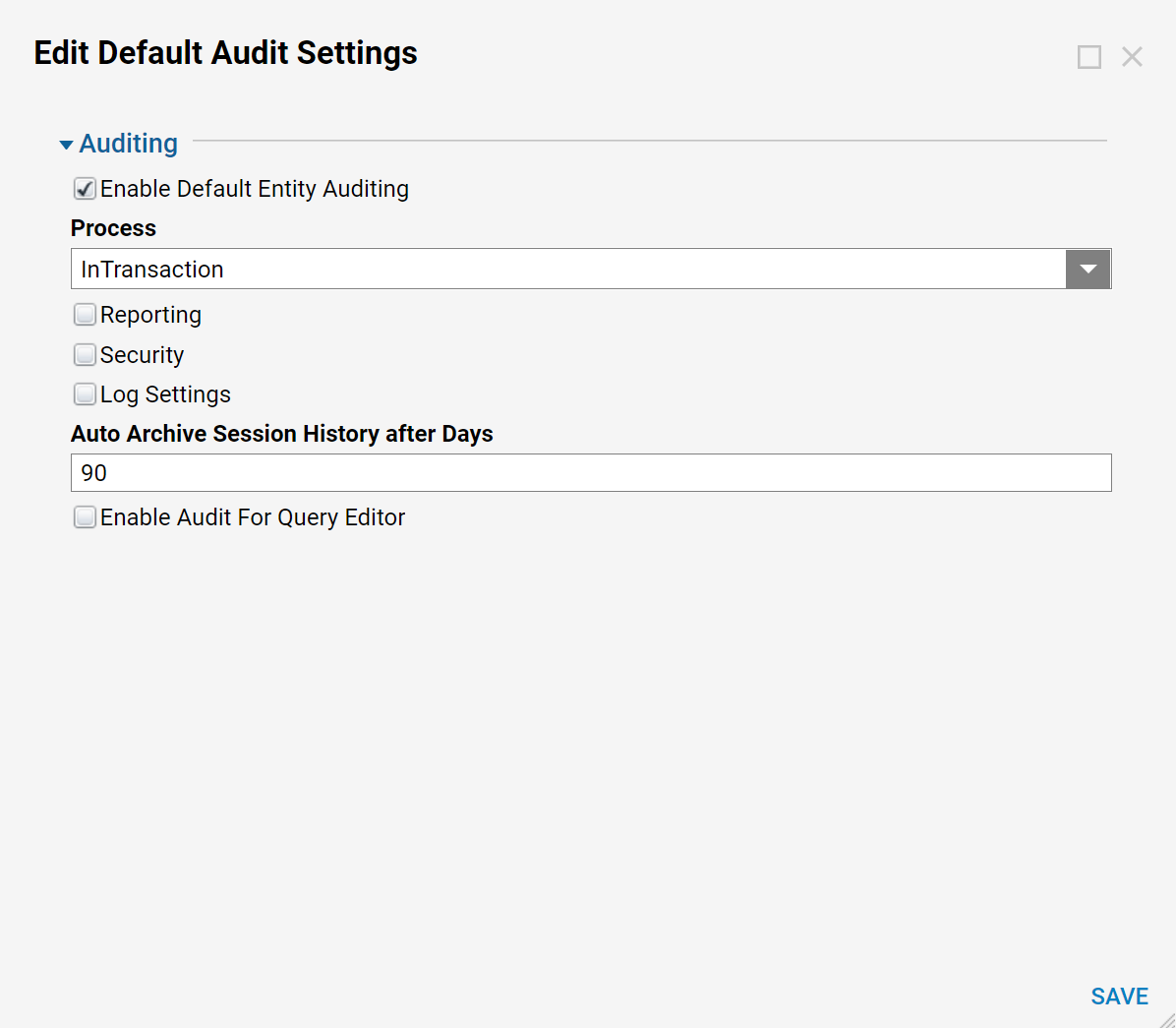
In the Edit Default Audit Settings pop-up, select the Enabled checkbox. Determine the desired Process setting:
InTransaction - all the updates are stored in the same transaction.
Queued - The updates do not share transactions of the main update; they are updated very quickly but in a different transaction. (If data integrity is primary, then doing InTransaction is best.)
The Reporting checkbox, when enabled, will capture who ran a Report and the Report name. The Security checkbox, when enabled, will capture user logins.
Select Save. The system will now audit all entity transactions automatically. To see the data introduced, create a new Report and select the Audited Entities data source.
Enabling Auditing Within Custom Data Structures
Custom Data Structures can also be configured for auditing. To enable it, select the Structure Type Name, navigate to the Advanced category, and select Audit Changes.
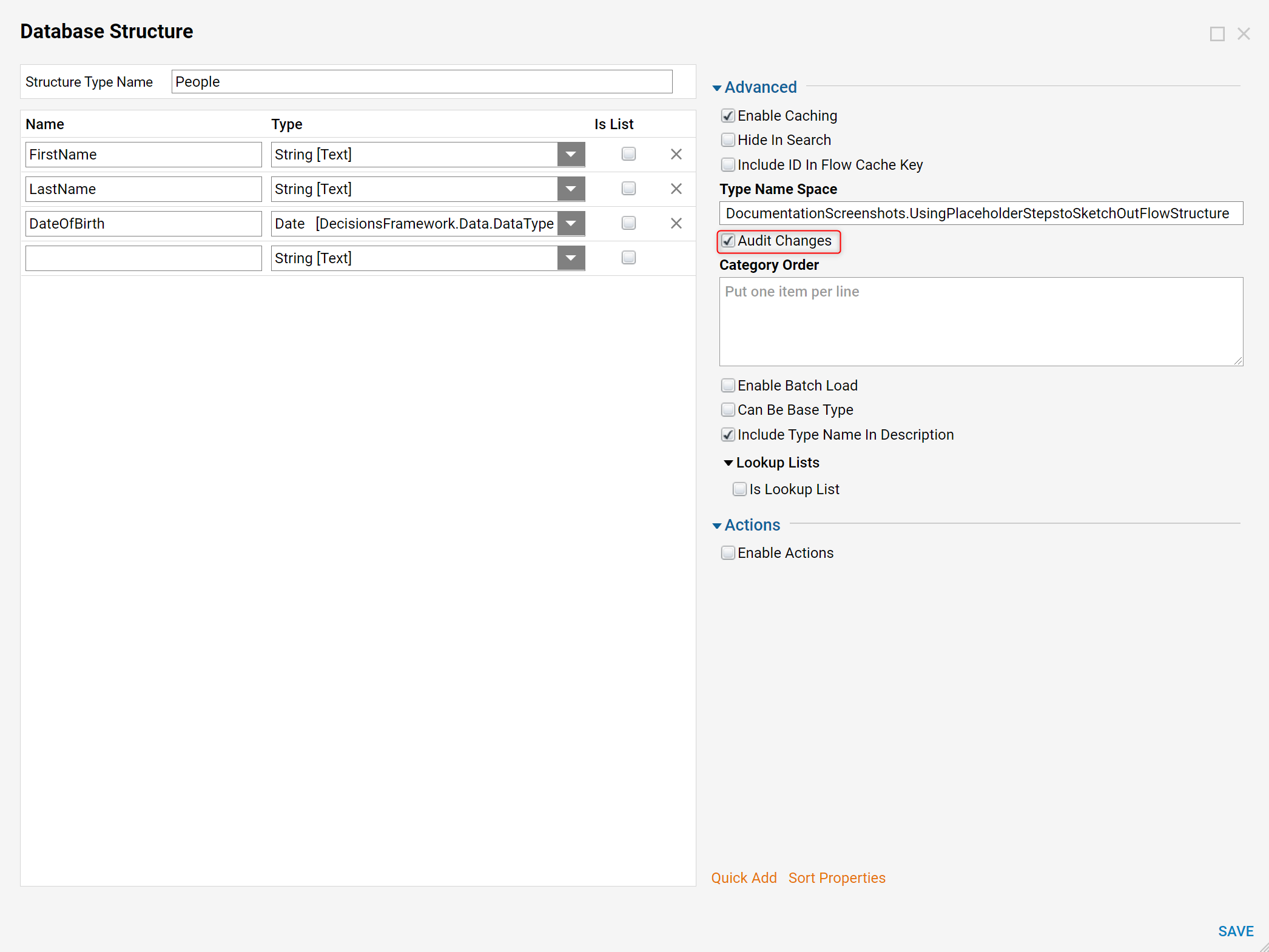
Any create, update, or delete action taken against this data structure will be recorded. A default audit Report is made available to users under System > Administration > Auditing Report. The same information can be accessed by querying the audit_entity table on the Decisions database.
.png)