Overview
A Pie Chart is a graphical demonstration of "parts per whole" relationships through division of a circle (pie) into separate slices for an at-a-glance comparison between the pieces. When added to Diagram Tiles, Reports, and Pages, Pie Charts provide data visually while reducing verbiage.
Similarly, Ring Charts serve the same purpose but display the data in the form of a ring, providing a more side-by-side view of the data.
The example below demonstrates how to create and use a Pie chart applied to a Diagram Tile on a Page in Decisions.
Pie Charts
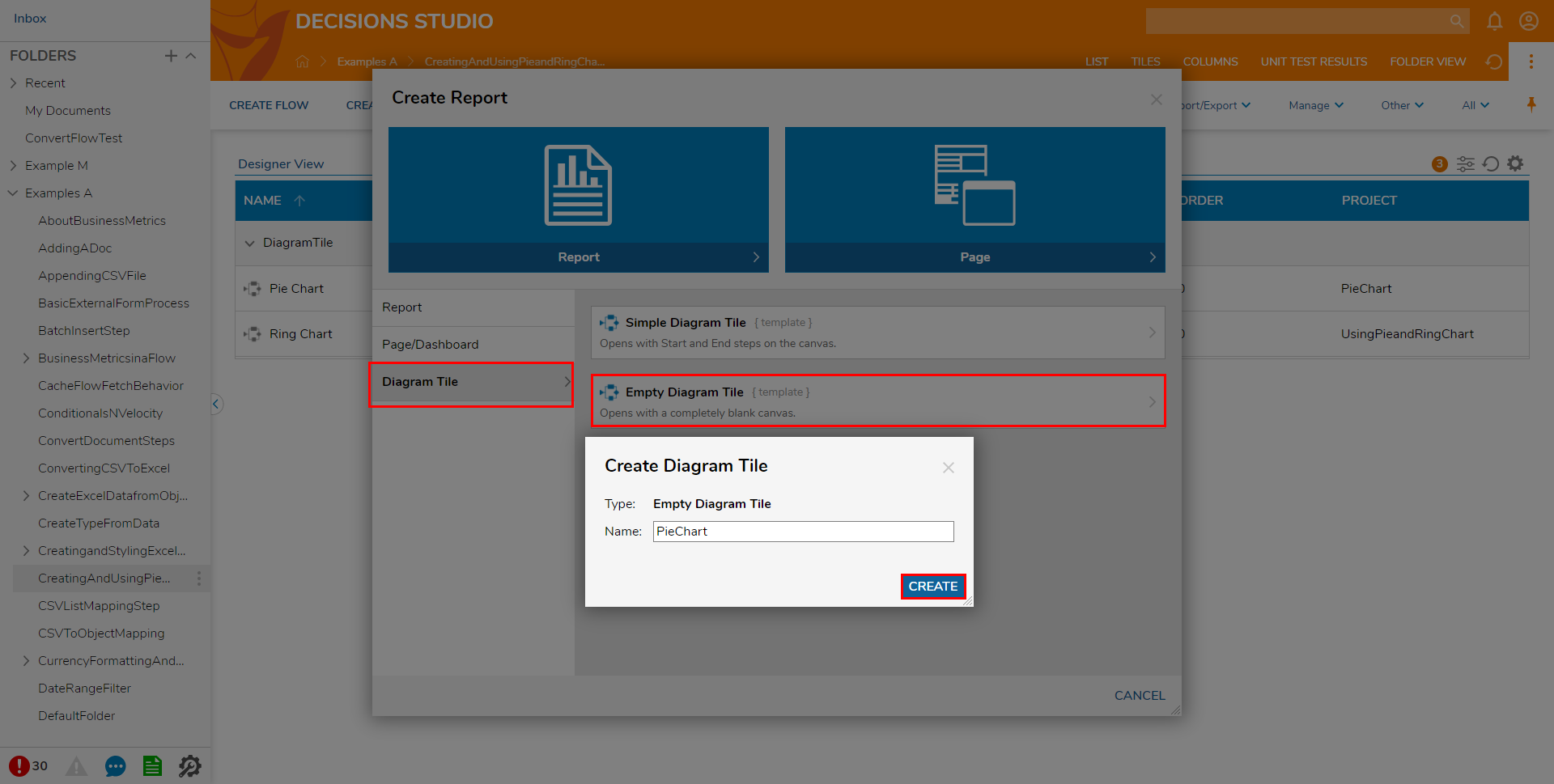
- To create one, navigate to a Designer Project, and select the CREATE REPORT button on the Global Action Bar; select Diagram Tile > Empty Diagram, provide a Name, then click CREATE.
- From the Toolbox tab under CHARTS, add a Pie chart to the design space.
- Navigate to the Properties tab; under CHART SETUP > ChartType, click the drop down arrow for ChartType and select Multiple Values. This ChartType allows the ability to input more than three values on the chart. Under SeparatorColor, select the Edit icon then PICK the desired Color.
Once a color has been selected, set both ShowLabel and ShowValue to OnSlice. If desired, change the Color for the Label on slice via Label Color on Slice.The Advanced properties drop-down of the Pick Color panel allows users to adjust the separator's opacity. This is adjusted via a slider that alters the amount of opacity.
The OnSlice option will display the configured value on the Pie chart slice rather than beside it. This helps reduce ambiguity about the amount of each value on the chart.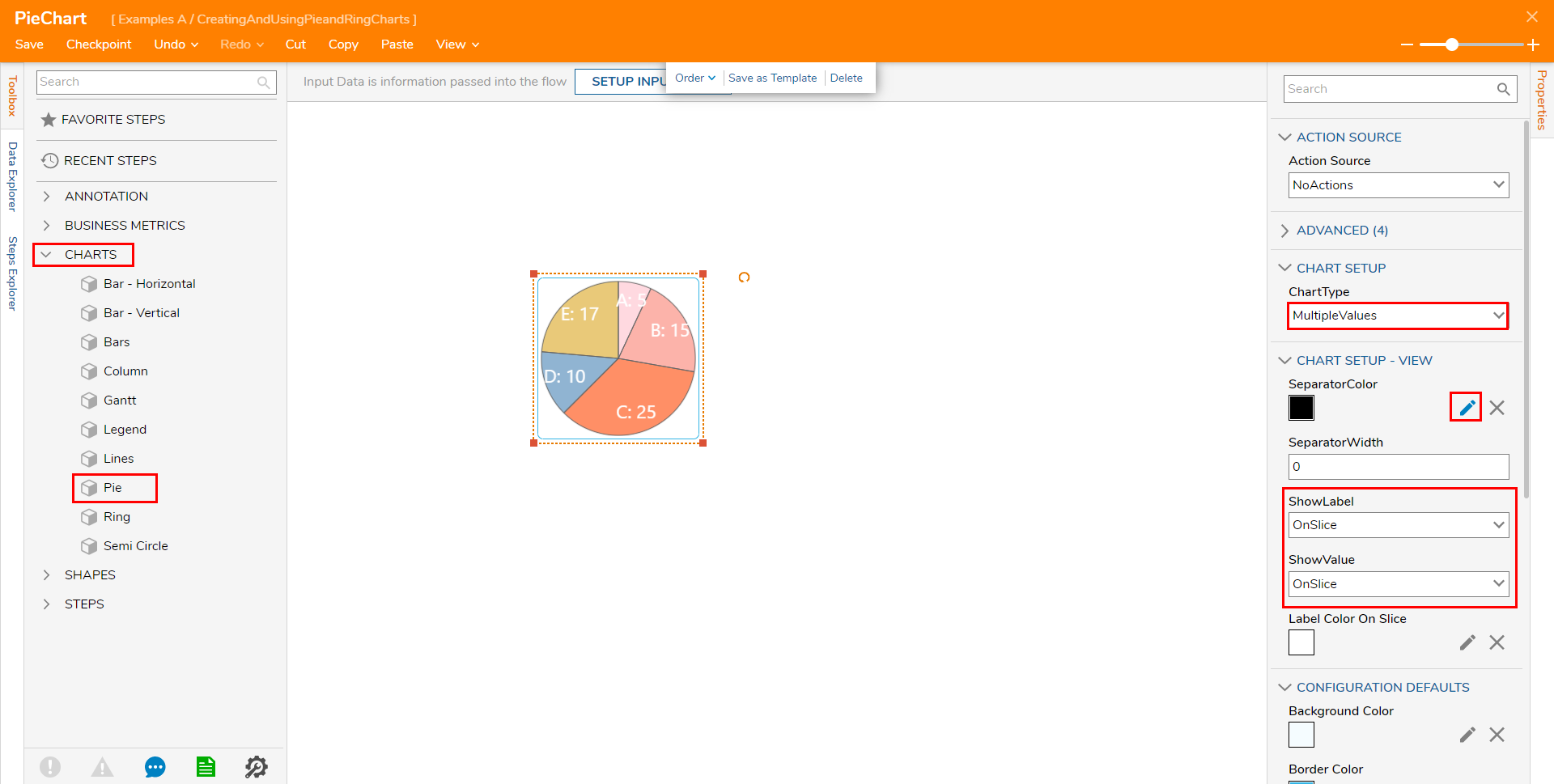
Scroll down to INPUTS > Chart Data; change the mapping to Constant then click ADD. From the Add Value screen, PICK the desired slice Color. Provide the Label "Employee A"; under Value, input the corresponding numerical value. For this example, input "5". Once configured, click OK.
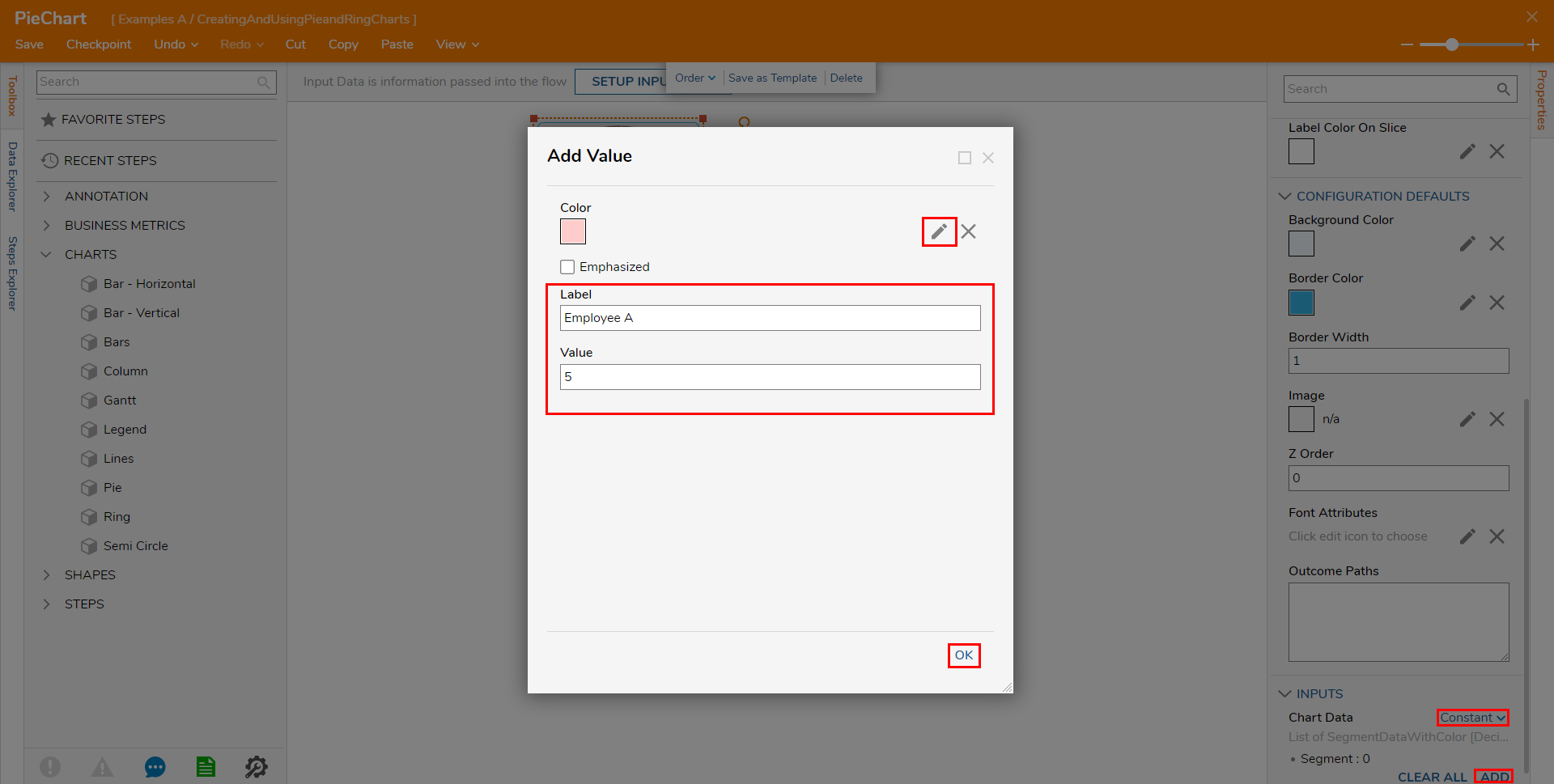
Repeat the process 3 more times for Employee B, C, D. Set their respective Values as "12, 8, and 9."
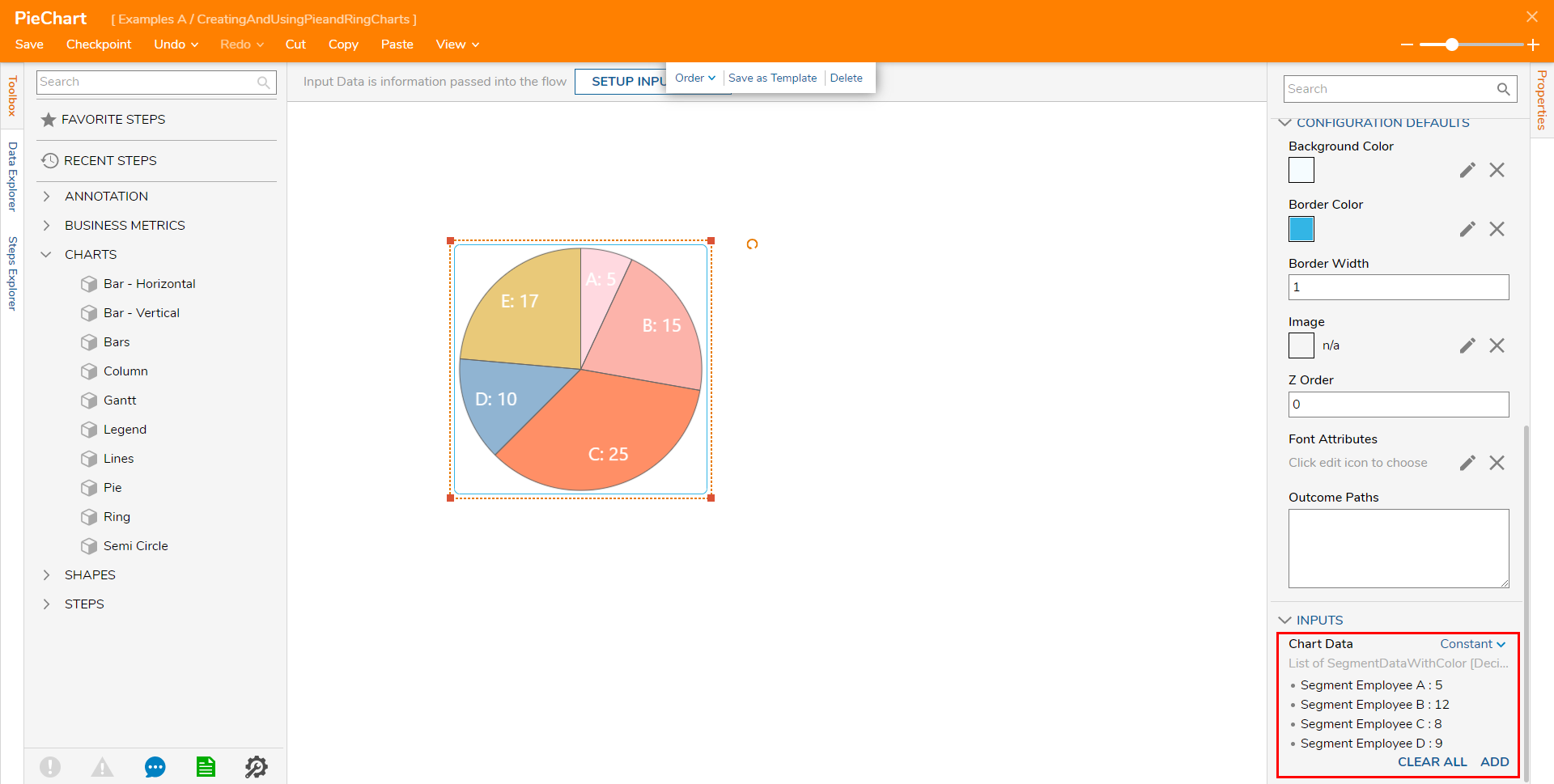
Once configured, Save the Diagram Tile, then close via X.
Either open the associated Dashboard Page, or create a new one.
For more information regarding Dashboard Pages, see Create a Page and Dashboard.From the Page Designer, navigate to Toolbox > TILES > [SELECT TILES] > [CURRENT FOLDER], and drag the Diagram Tile onto the Page.
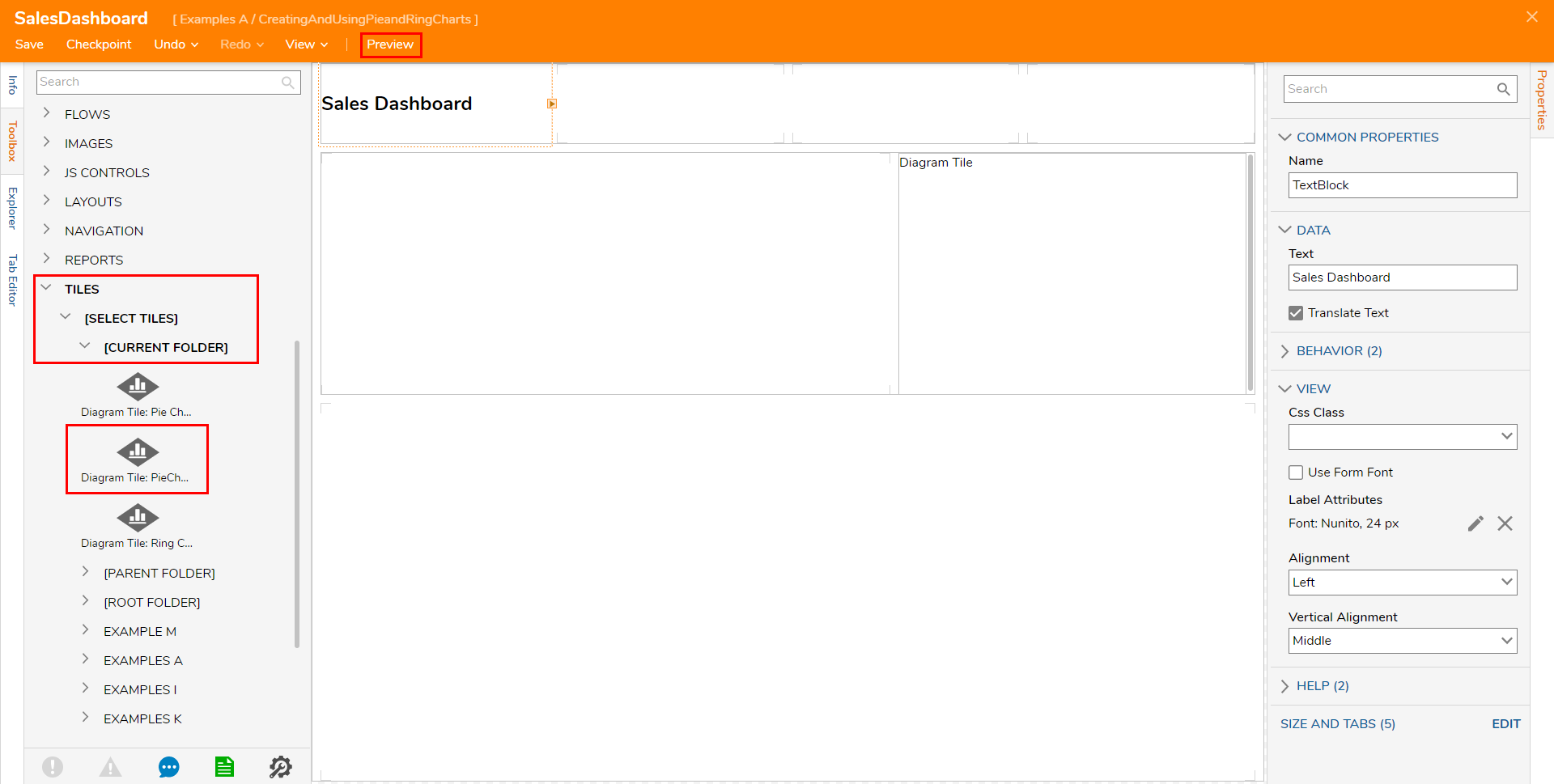
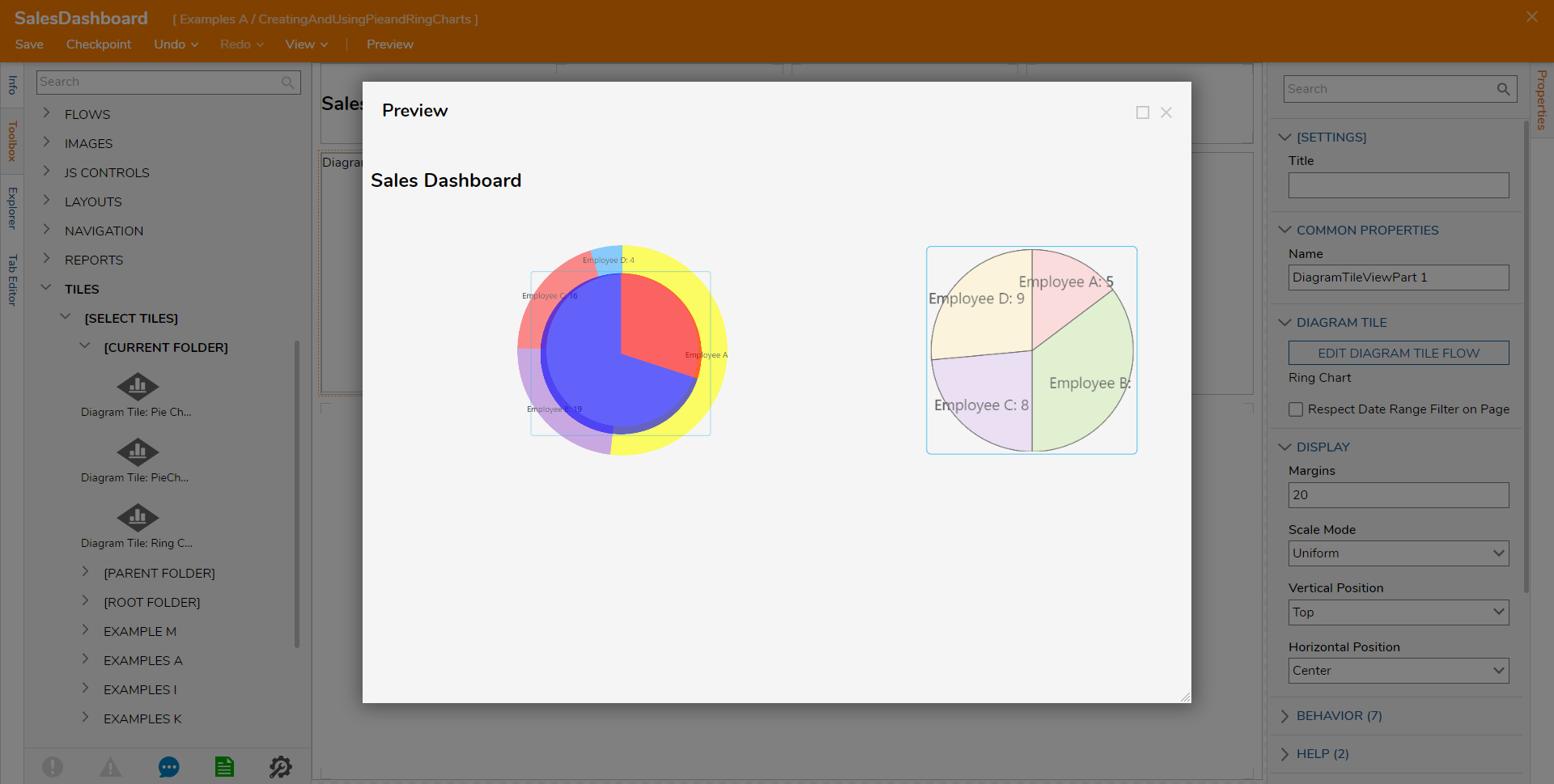
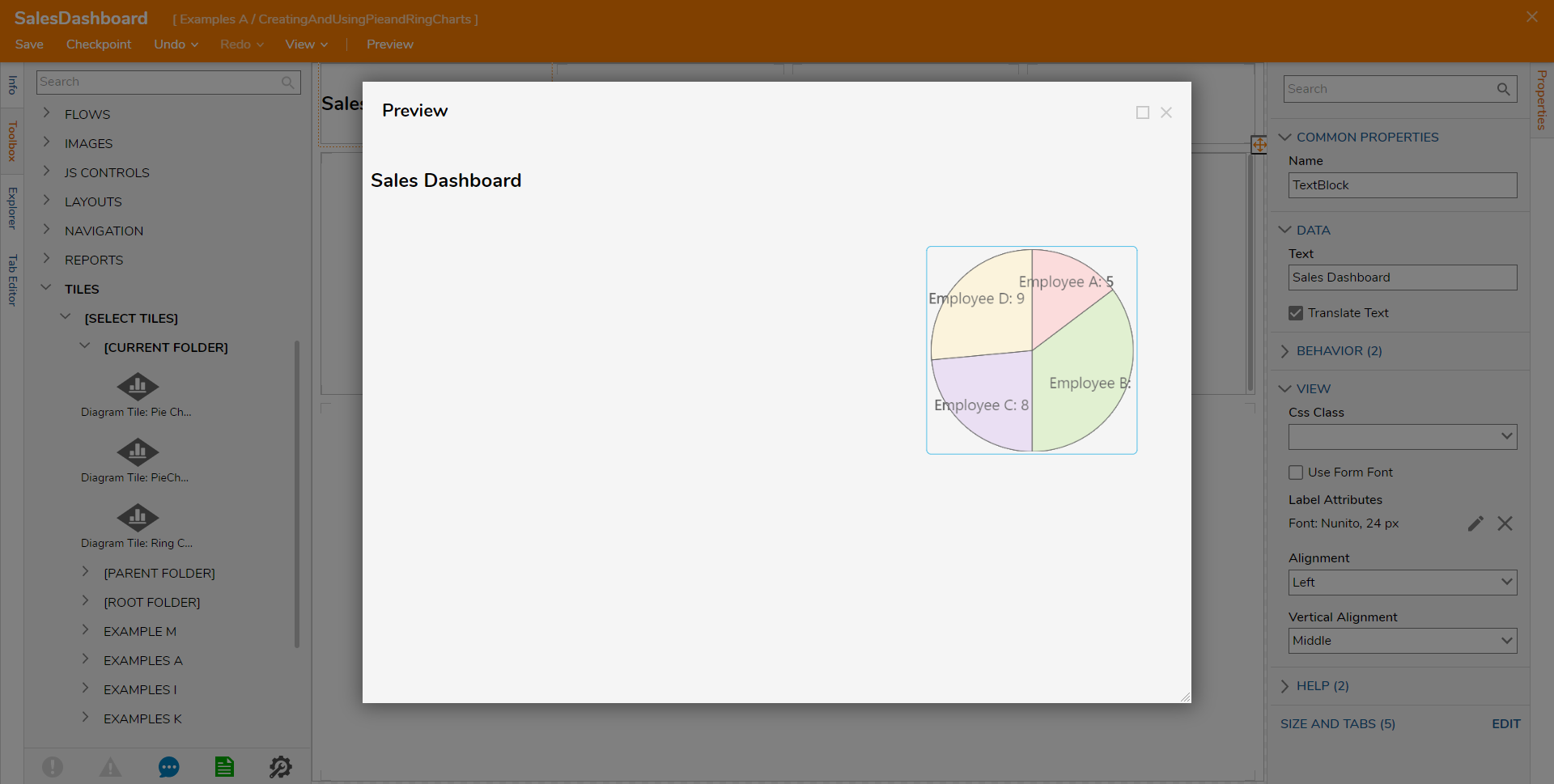
Once the Tile is added and the Page is configured as desired, Save the Page, then click Preview to view the Page and the Pie Chart.
Ring Charts
If a user wishes to display similar types of data on a Report or Dashboard Page, they may opt to use a Ring Chart instead.
Ring Charts are used the same way as Pie Charts, but display the data side by side rather than in a Pie shape. This can be beneficial as it allows the chart to take up less space, displays percentages in terms of parts of the whole circle. and allows for additional information (such as labels) to be added to the center of the circle.
Ring Charts contain the additional property RingWidth, which is used to adjust the width of each ring segment.
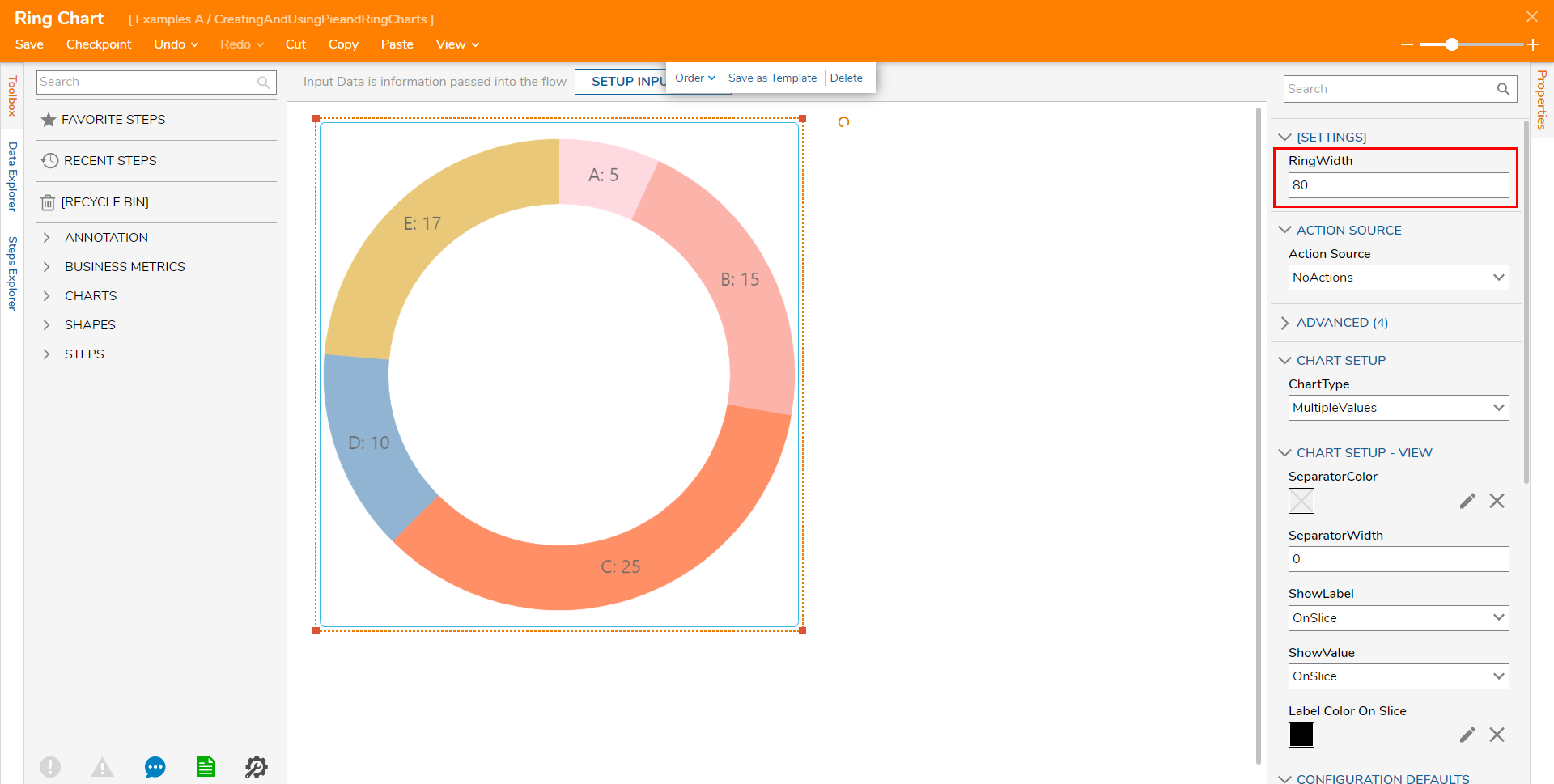
Using More Than One Chart
Charts may be displayed alongside one another within the Tile: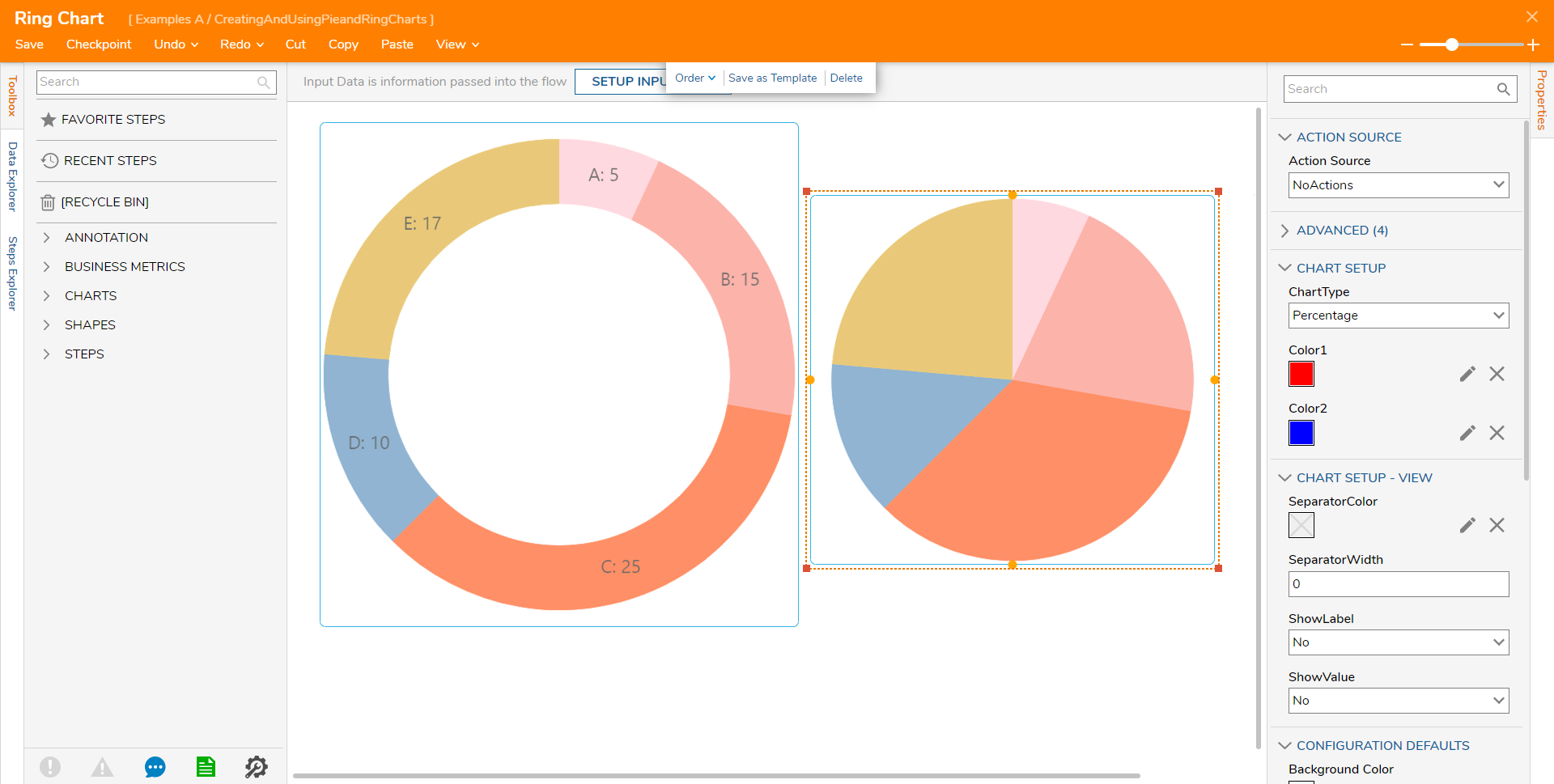
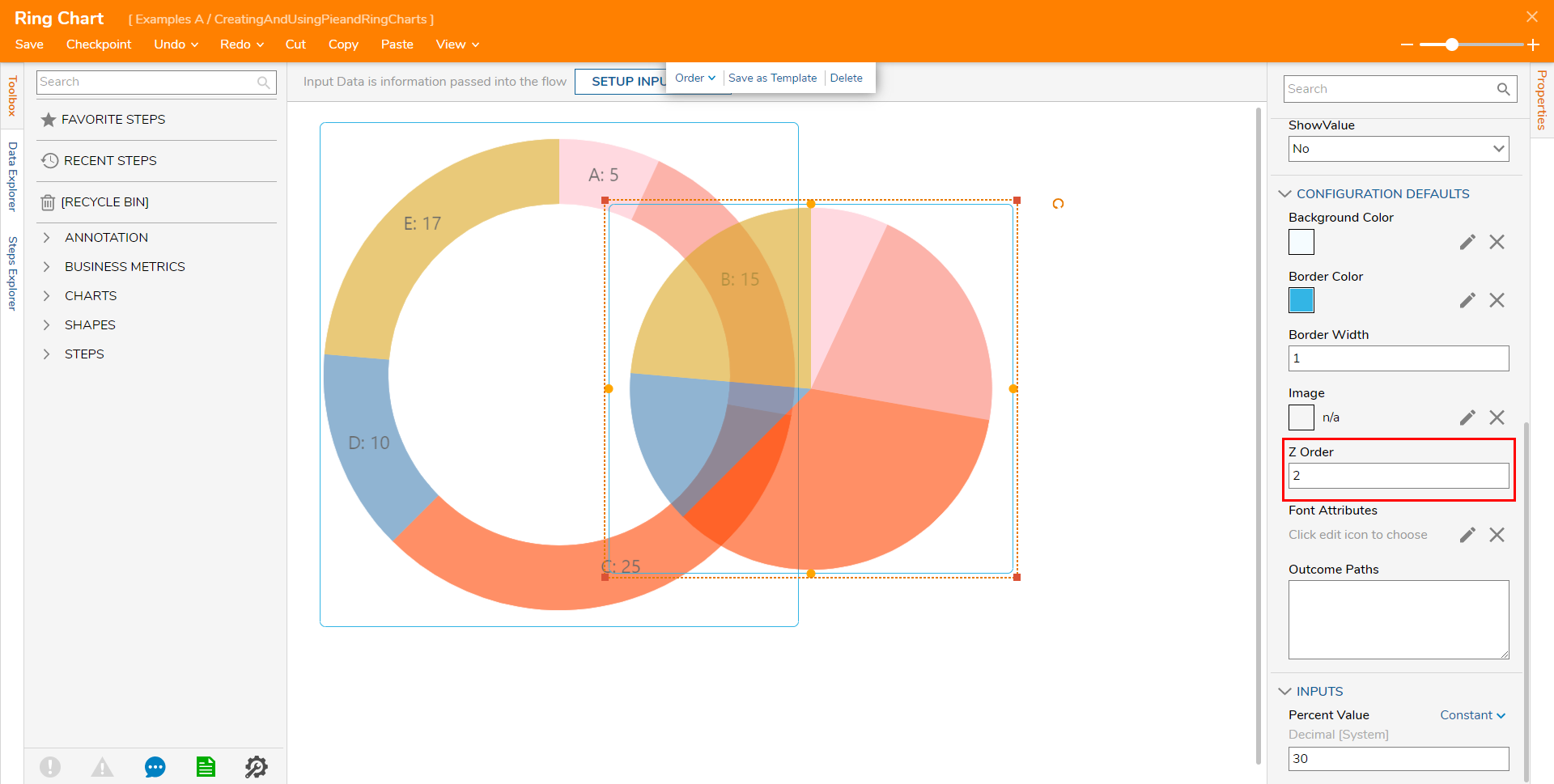
or overlapping: 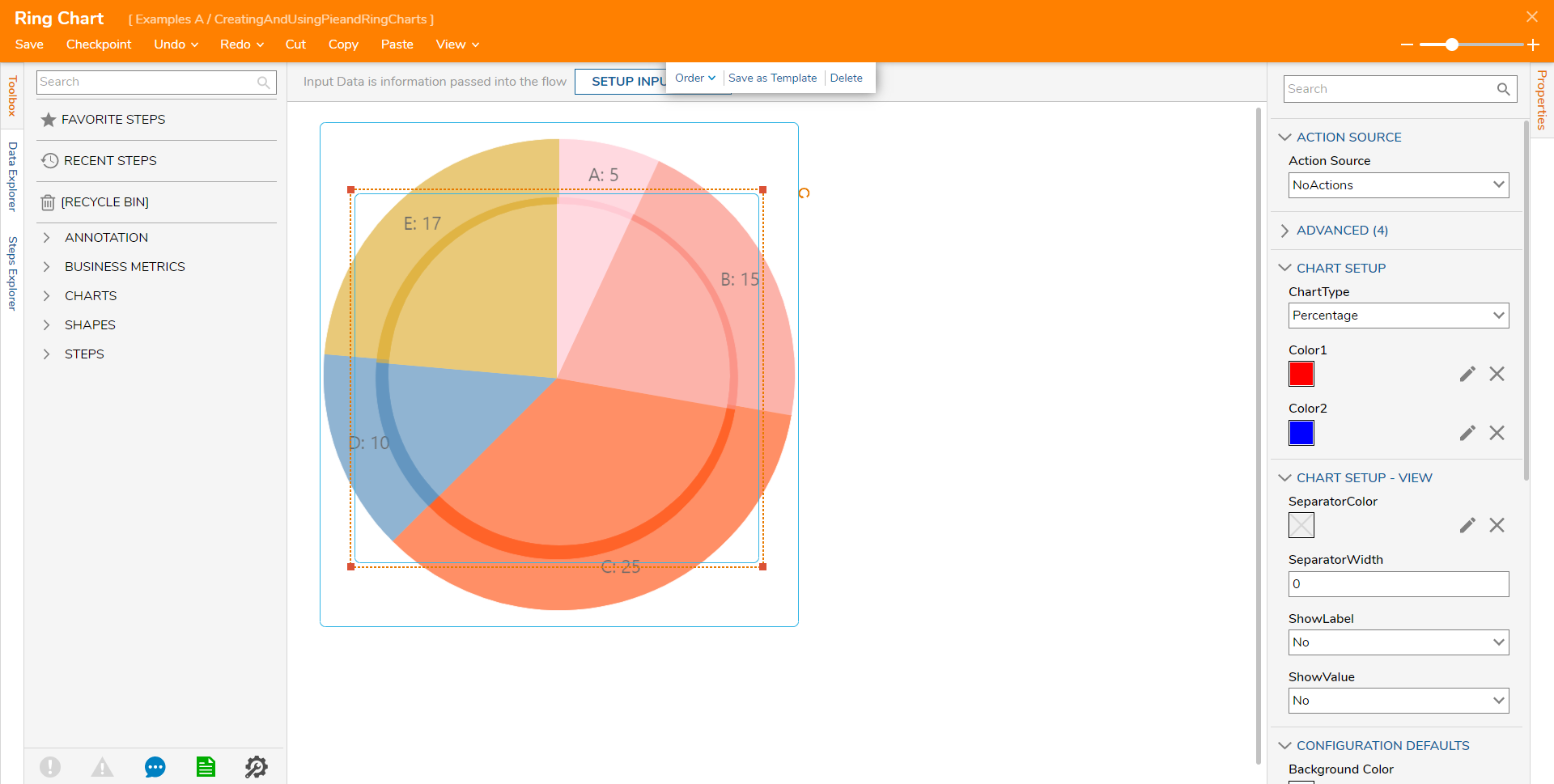
To adjust the overlap settings, enter a numerical value into the Property Z-Order; overlap is determined by which object has the higher Z-Order value.