- 07 Mar 2022
- 3 Minutes to read
- Print
- DarkLight
Configuring the Root-Cause Analyzer
- Updated on 07 Mar 2022
- 3 Minutes to read
- Print
- DarkLight
Overview
The Root-Cause Analyzer of the Diagnoser visualizes the root-case of the selected attribute to identify underlying issues and where they originate. This information then aids users to create potential solutions.

Nodes and Edges
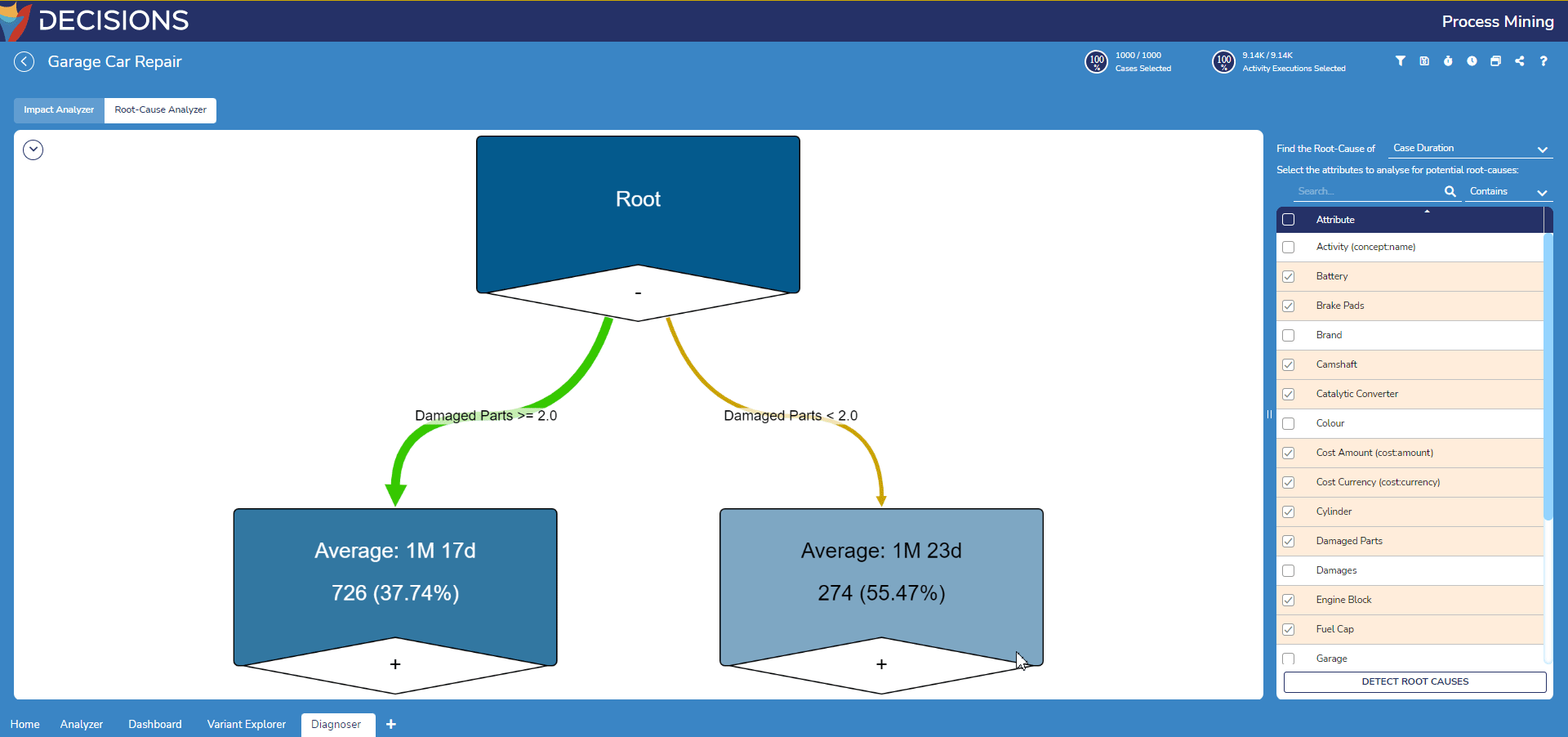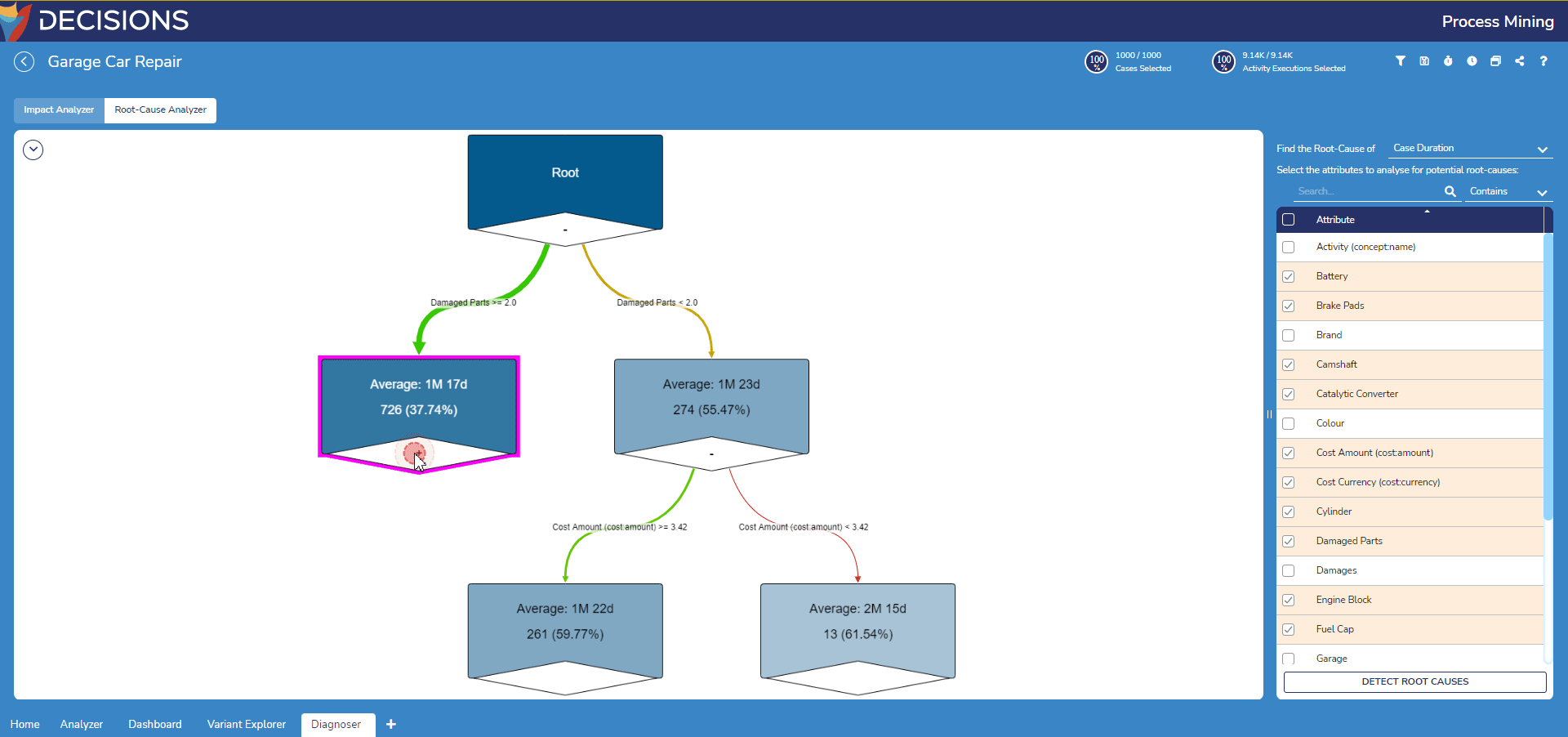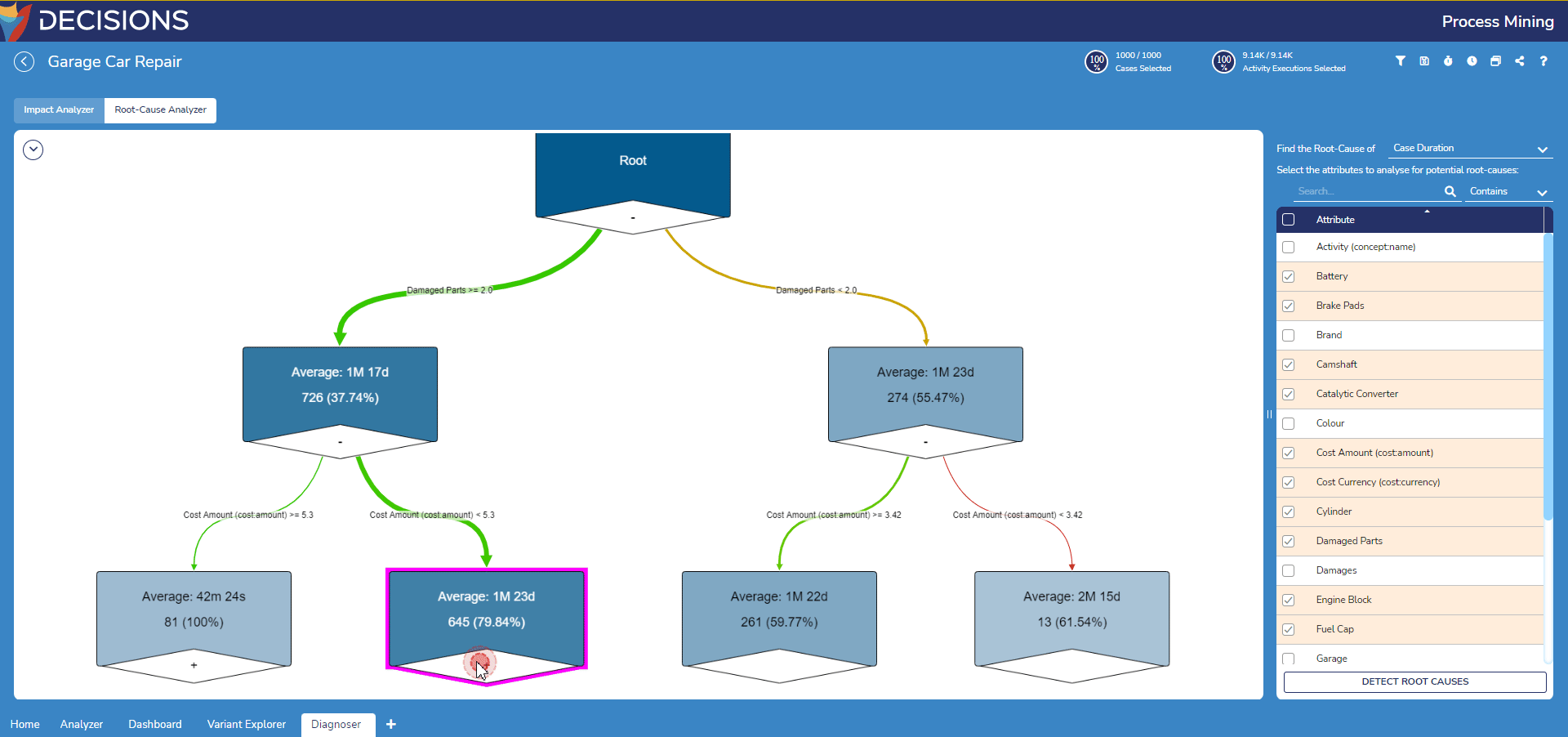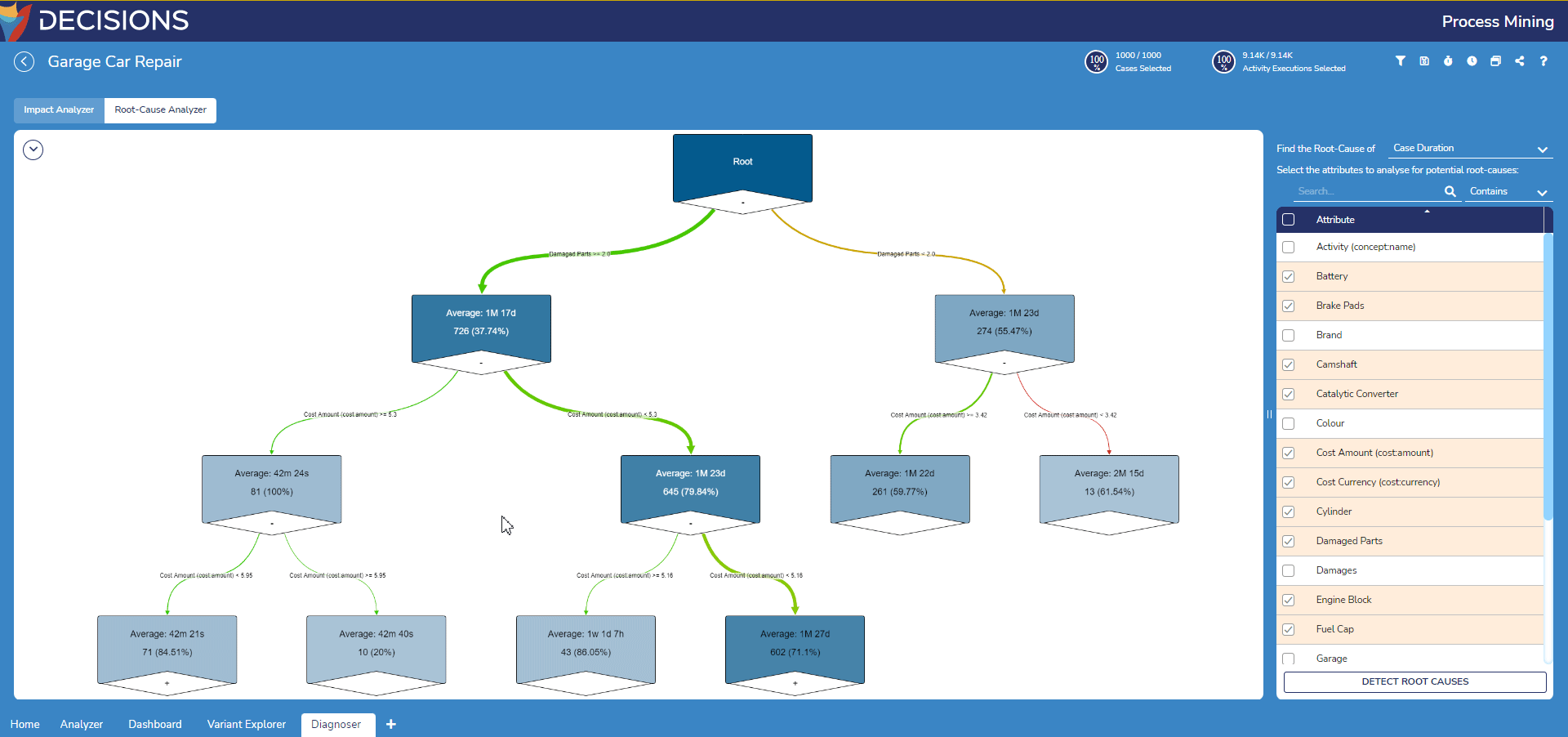
The Root-Case Analyzer's diagram comprises a root node, several intermediate leaf nodes and edges.
Nodes
The root node represents all cases within the event log. From here, edges connect it to its leaf nodes.
Leaf nodes represent a group of similar cases and display the following information:
- The average value of the target parameter for the root-cause analysis e.g. duration.
- The number of cases within the group i.e. node
- The accuracy of the root-cause analysis for the given node
The number of cases effects the color of the node: darker colors denotes a larger group in the node and vice versa.
Double-clicking on a node opens additional information about the node such as the number of cases, root-cause analysis accuracy, and the average, minimum, and maximum values of the target parameter. Nodes with plus icons contain further leaf nodes.
Furthermore, users may filter the event log to retain only the cases included by the sequence of root causes leading to the specified node.
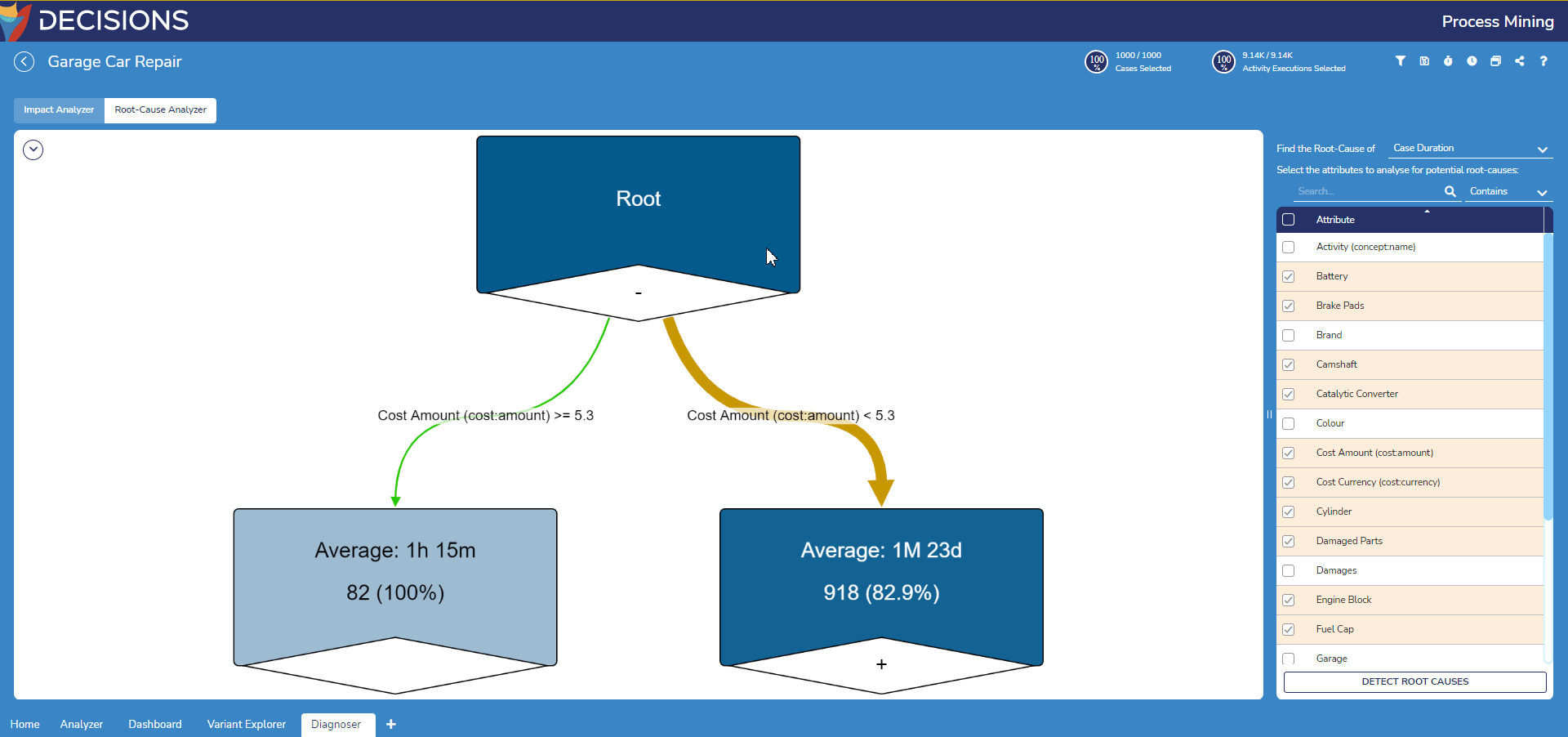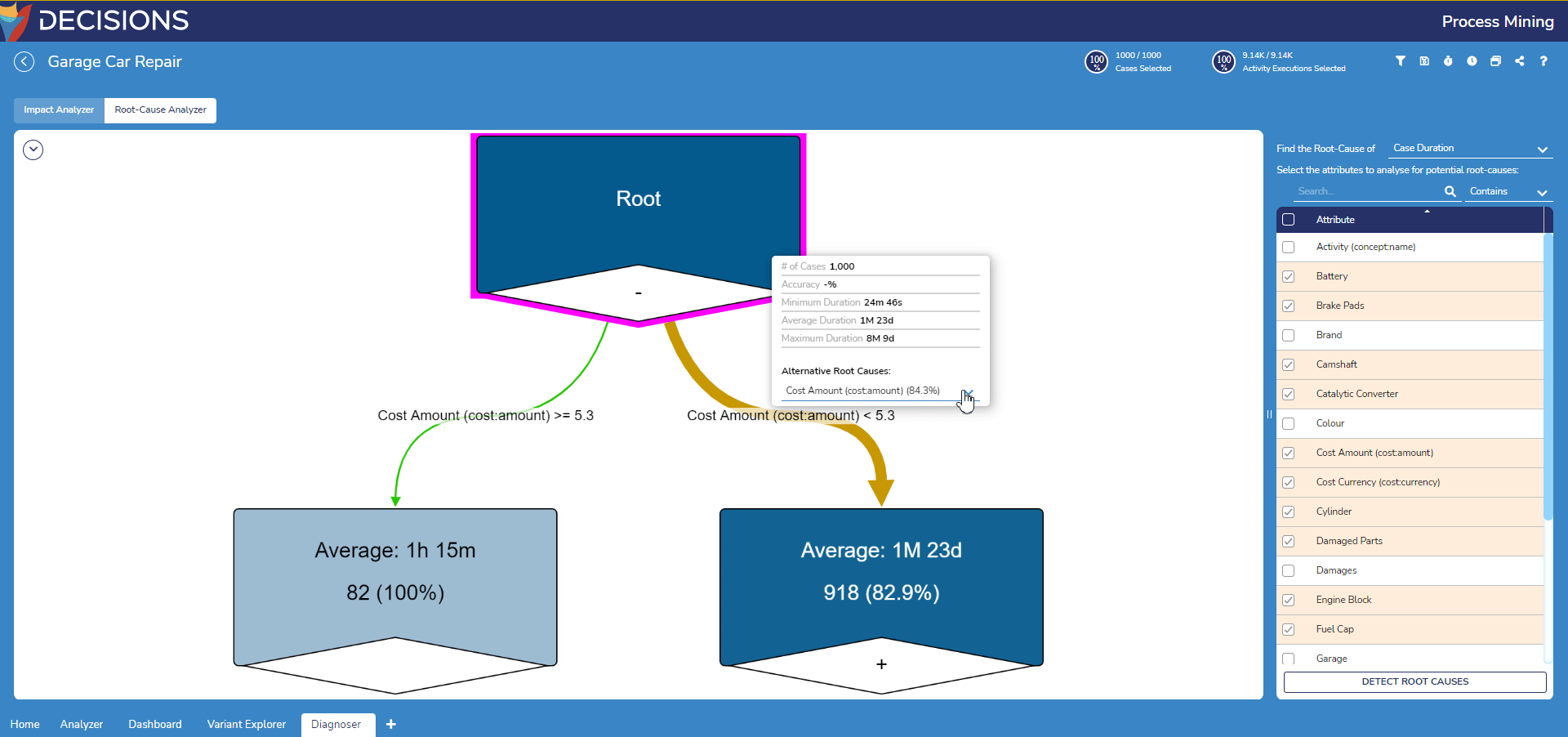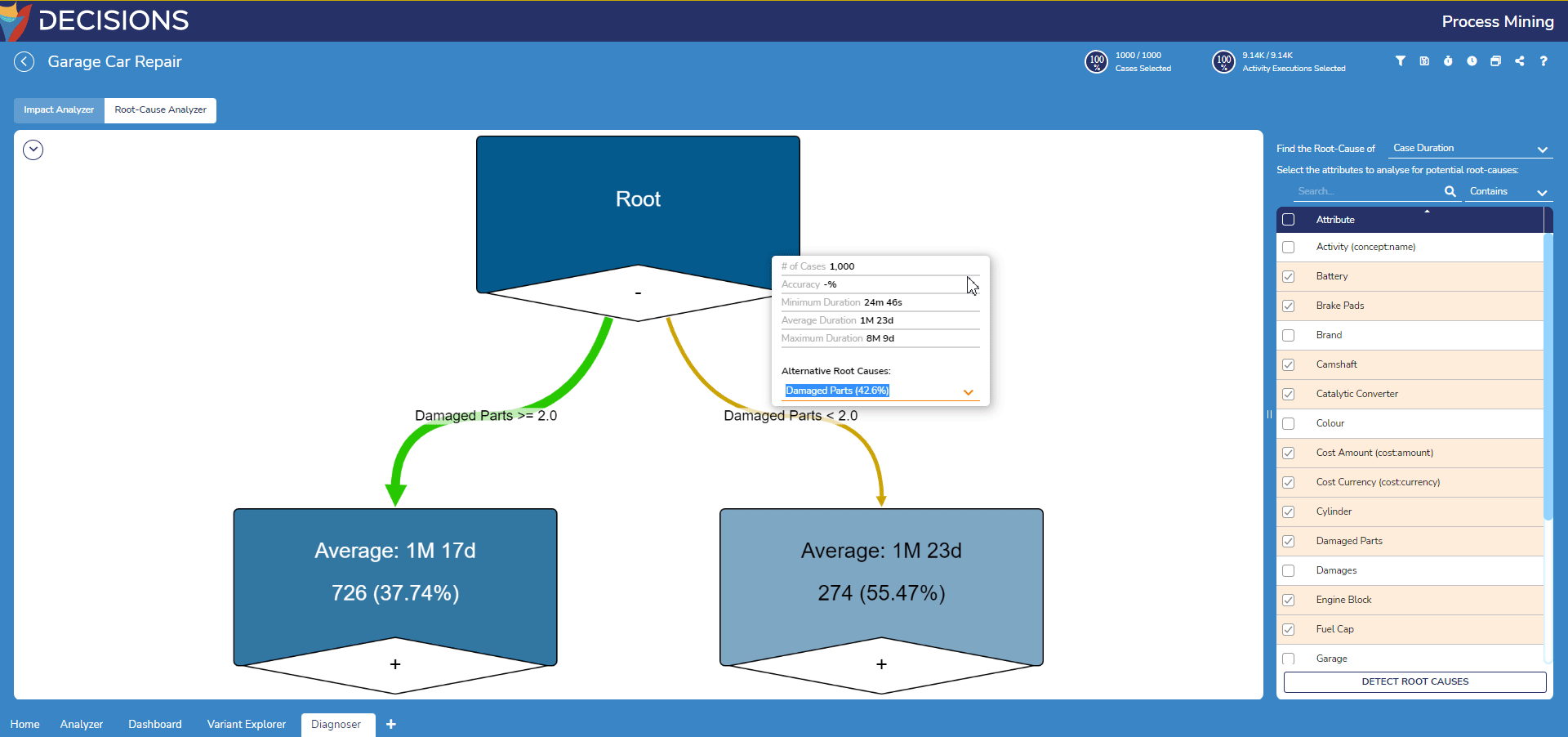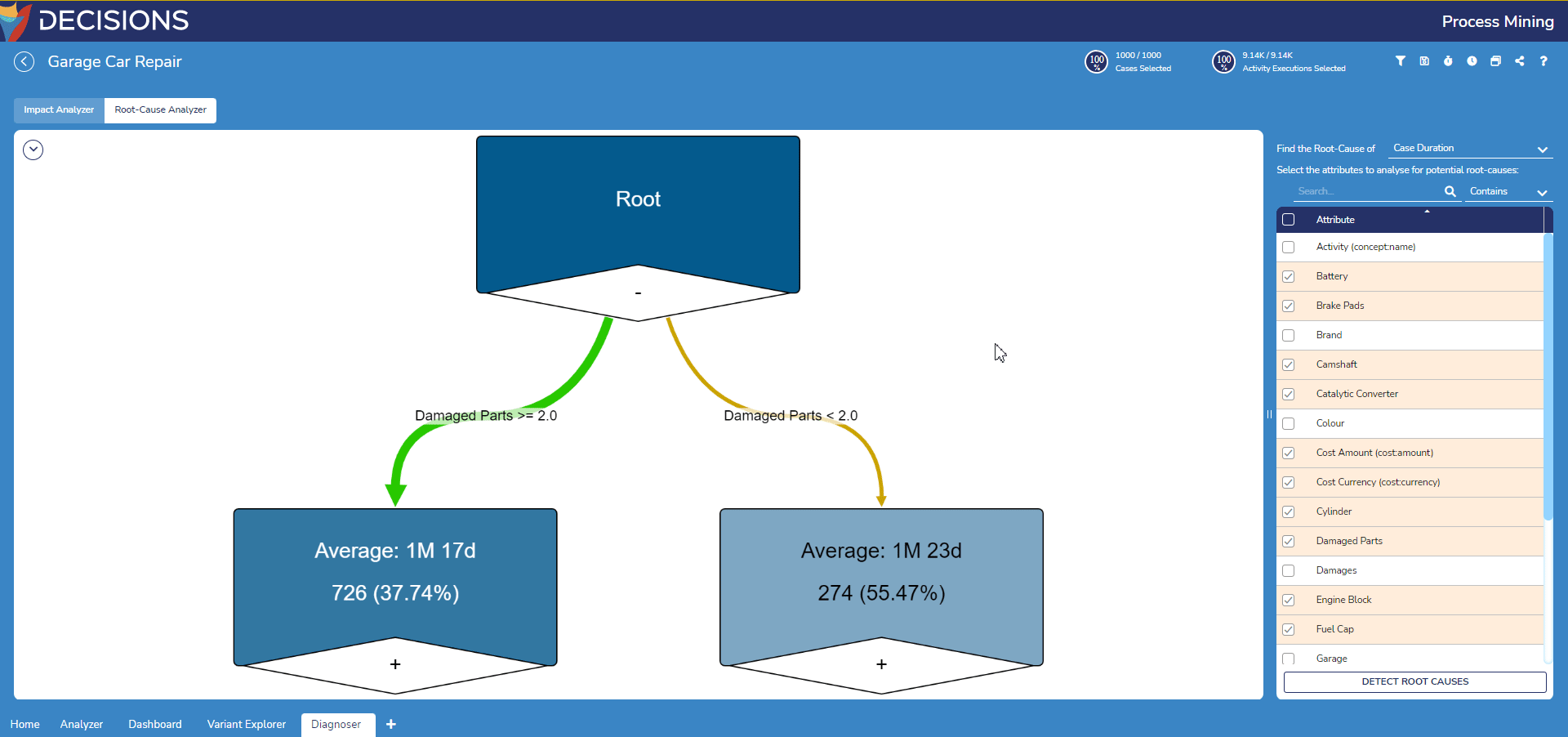
Finally, the Alternative Root Causes dropdown navigates users to other attributes to investigate, The default attribute here is the attribute with the highest relation to the node's value thus most likely the best option to explain its value.

Edges
An edge represents a root cause leading to a specific value for the target parameter and displays the following information:
- The root cause.
- The impact of the root cause.
- The number of cases influenced by the root cause.
The impact changes the color of the edge between gradient of green to red. Green details positive impact while red details negative impact. Impacts in between are represented with different shades of yellow depending on the level of neutrality of the node.
The number of cases effects the thickness of the edge: thicker edges denote a higher number of cases and vice versa.

Example
- Open an event log and select the plus icon at the bottom of the window. Select Diagnoser then OK to create a Diagnoser tab.
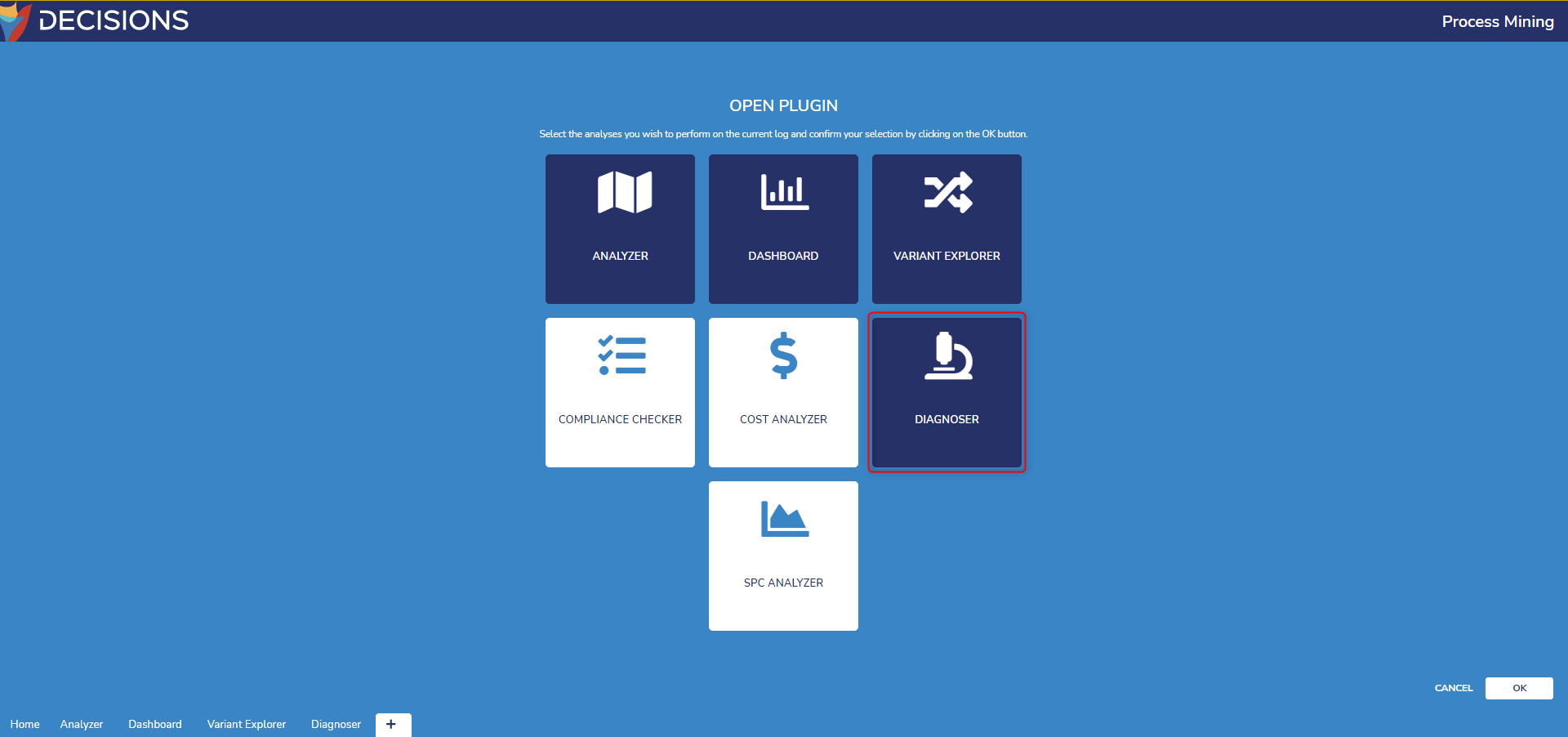
- Open the Diagnoser tab and change it from the default Impact Analyzer page to the Root-Cause Analyzer page by select its button above the center diagram.
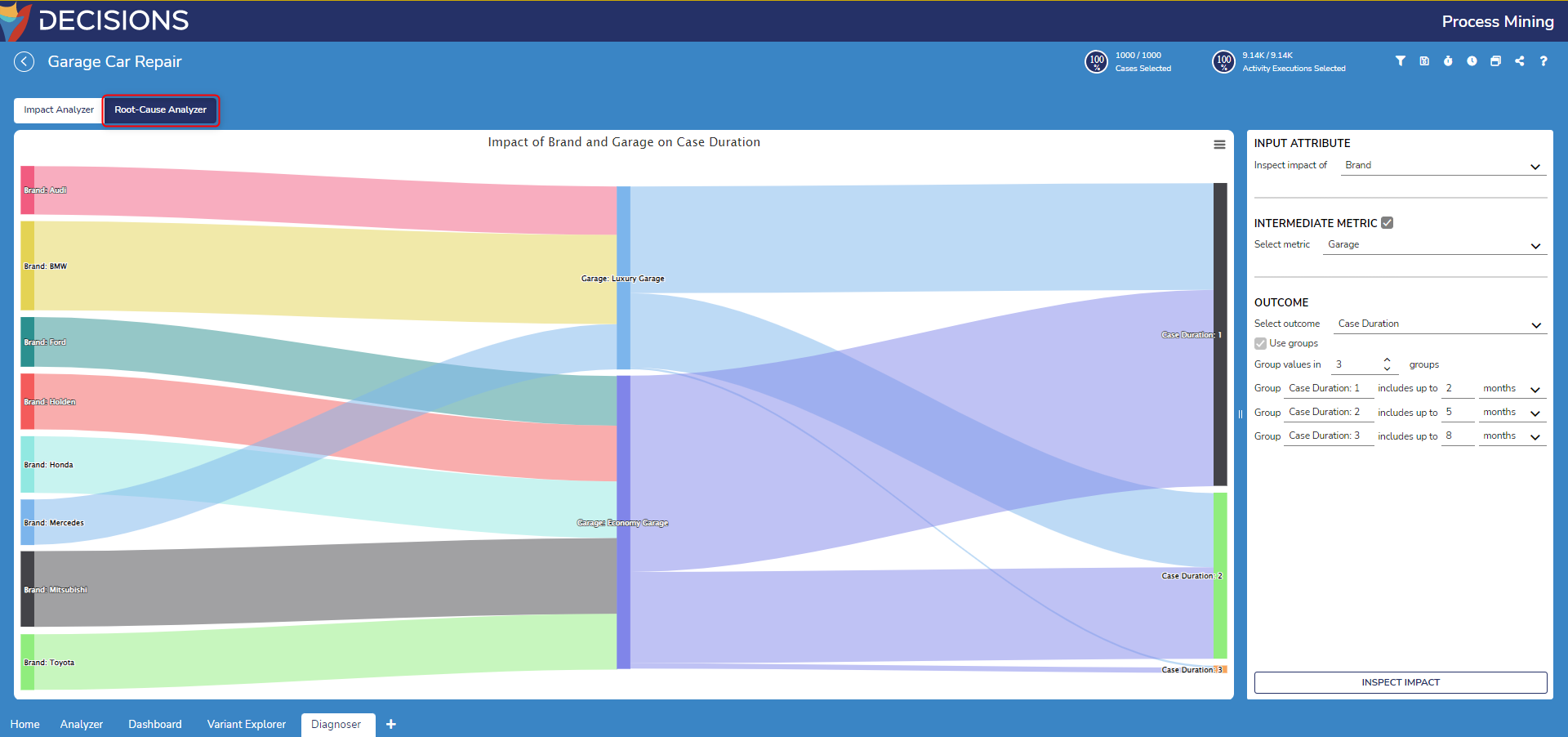
- In the Root-Cause Analyzer, navigate to the settings at the right of the diagram. For Find the Root-Cause of select a parameter to investigate. This example examines case duration.
- Underneath the prior setting, select the following attributes to analyze. This example selects every attribute representing a car part since the more part to repair typically leads to higher repair durations. Furthermore, Cost Amount and Cost Currency attributes are selected.
After selecting all desired attributes to examine, select Detect Root Causes to construct the diagram with the new settings.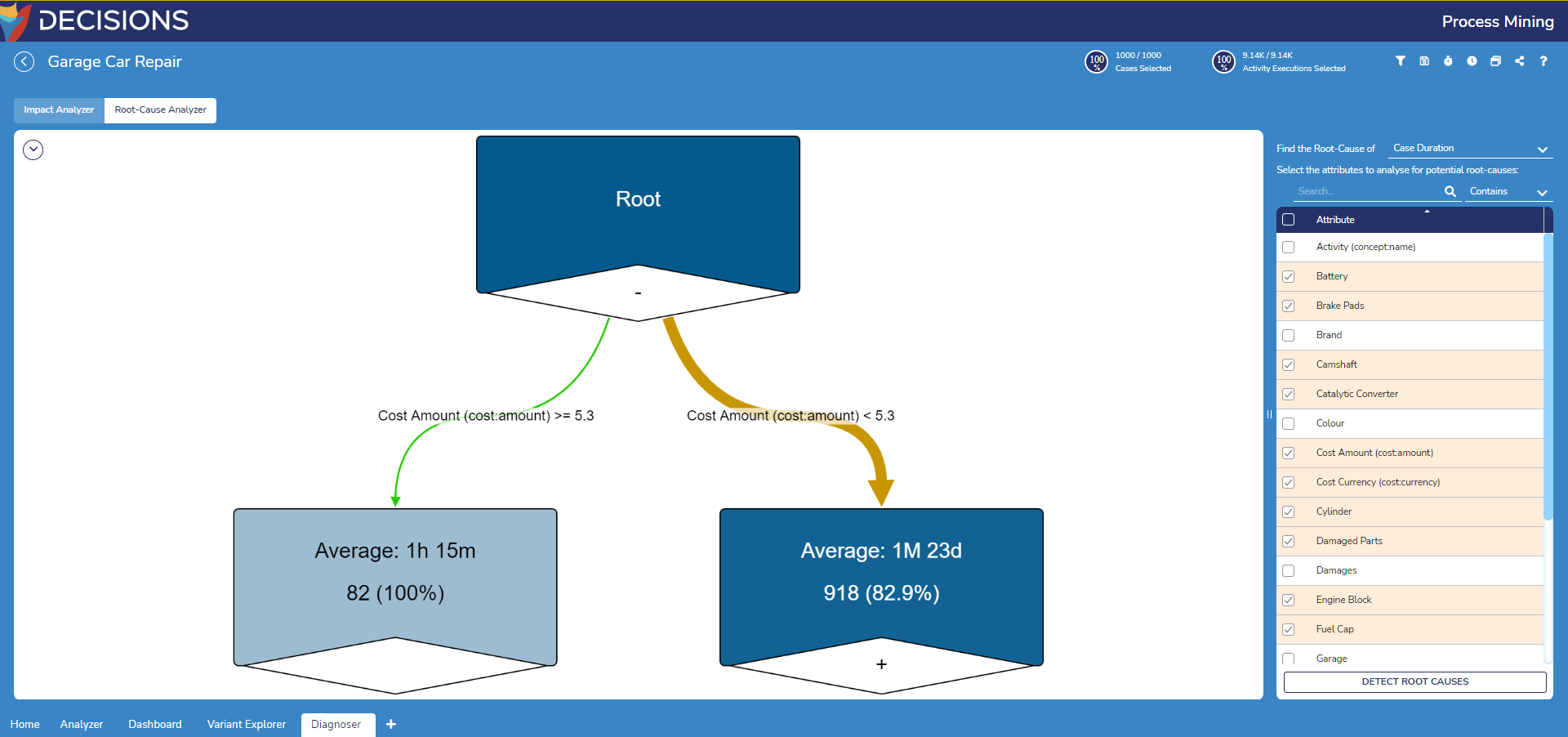
- Notice the root node now contains two edges splitting the log's cases between the default root cause on the root cause. To change this, click on the root node and select a new Alternative Root Cause to generate a root-cause analysis based on this attribute instead.
- To further examine the leaf nodes, double-click on leaf node with the plus icon to expand the leaf node to view its nested branch.
Filtering the Root-Cause Analyzer
Upon clicking on a node to view its further details, users may select Add Filter to automatically create a filter that retains only the cases influenced by the sequence of root causes leading to the selected node.
Nested leaf nodes generate a filter for each layer to capture this sequence. For example, a leaf node two layers down from the root node will generate two filters.
After selecting this button, the filter may be edited, disabled, or deleted by navigating to the filter window to the top right of the window.
Downloading the Root-Cause Diagram
At the top left of the diagram window, expanding the selection menu offers users the option to download the root-cause analysis diagram as either a PNG or JPG image file similar to a Process Map.







