Overview
Rule Chains are a set of Rules combined in a sequence that generate Facts (outcomes). They add more context to the process that can be used. Rule Chains be used in any kind of business Process where dynamic decisions making is necessary. Two possible options for Rule Chaining are Forward Rule Chains and Backward Rule Chains.
What is Forward Rule Chain?
Forward Chaining is the ability to take Inputs, generate Outputs and consume those Outputs as Inputs later in the Process.
What is Backward Rule Chain?
Backward Chaining is the ability to select an outcome and only require Inputs that are necessary to reach that outcome. When Outputs are selected, this narrows down the Inputs only for that Output. This process limits the number of Inputs that are brought into the Rule Chain.
Example
Below is an image representing how the Rule Chain is built.
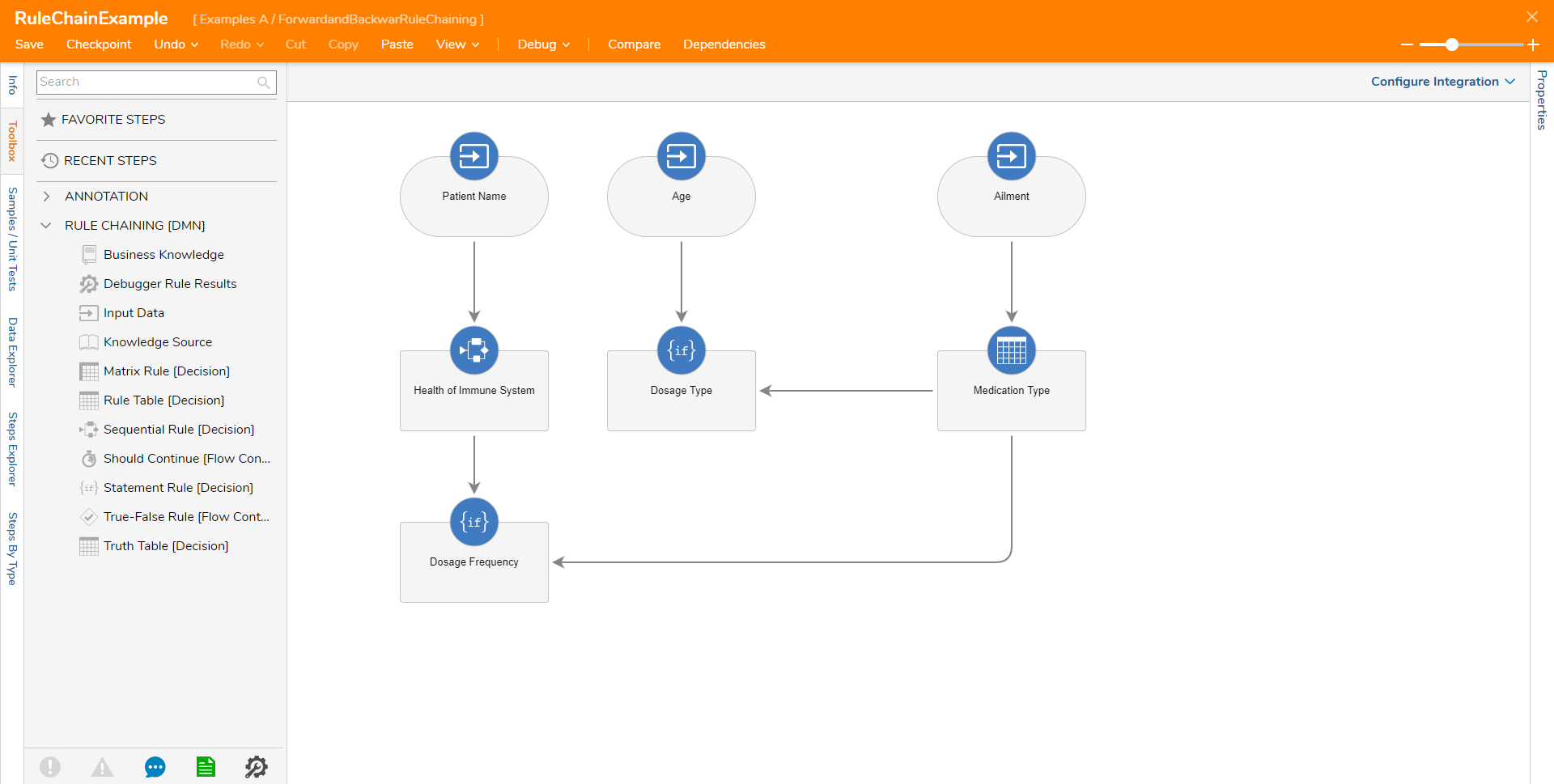
Forward Rule Chain
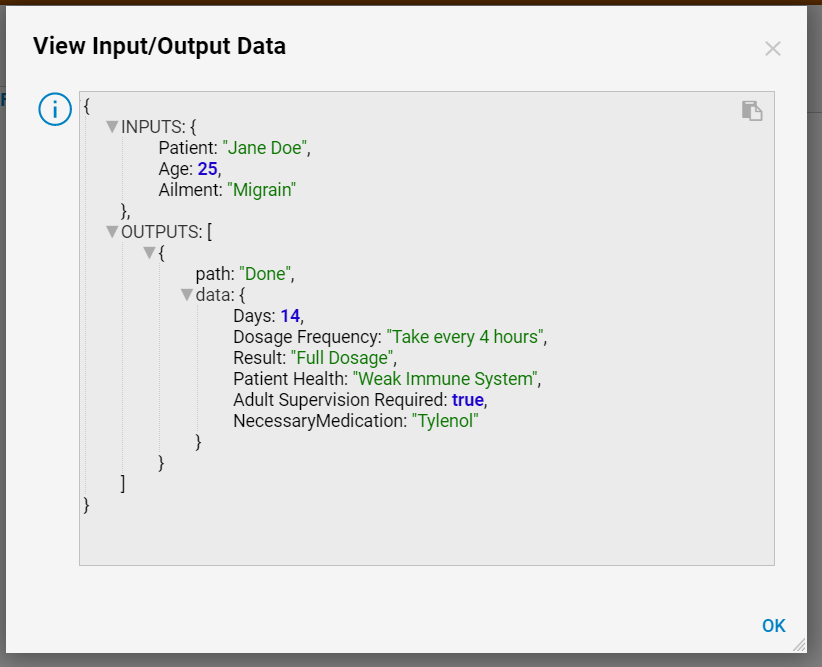
By default, the example Rule Chain is Forward Chaining since all the outcomes/Inputs are used through the process. When this Rule Chain is run (in this example from a Flow) it will display all the Inputs: Age, Ailment, Patient, as well as the Outputs: Days, Result, Patient Health, Adult Supervision, NecessaryMedication.
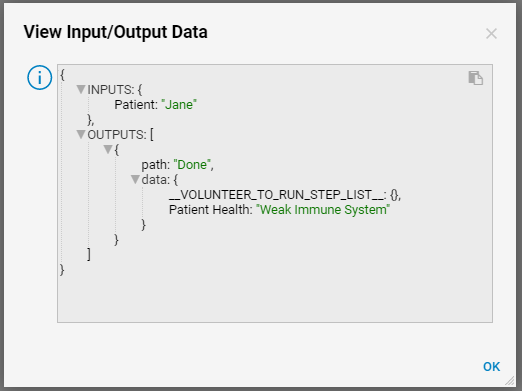
Backward Rule Chain
For Backward Rule Chaining, some outcomes will be deselected from the Properties tab of the Step.
In the example below, the user only wants the Patient Health outcome so only that outcome is selected. This reduced the Input values to only Patient value.
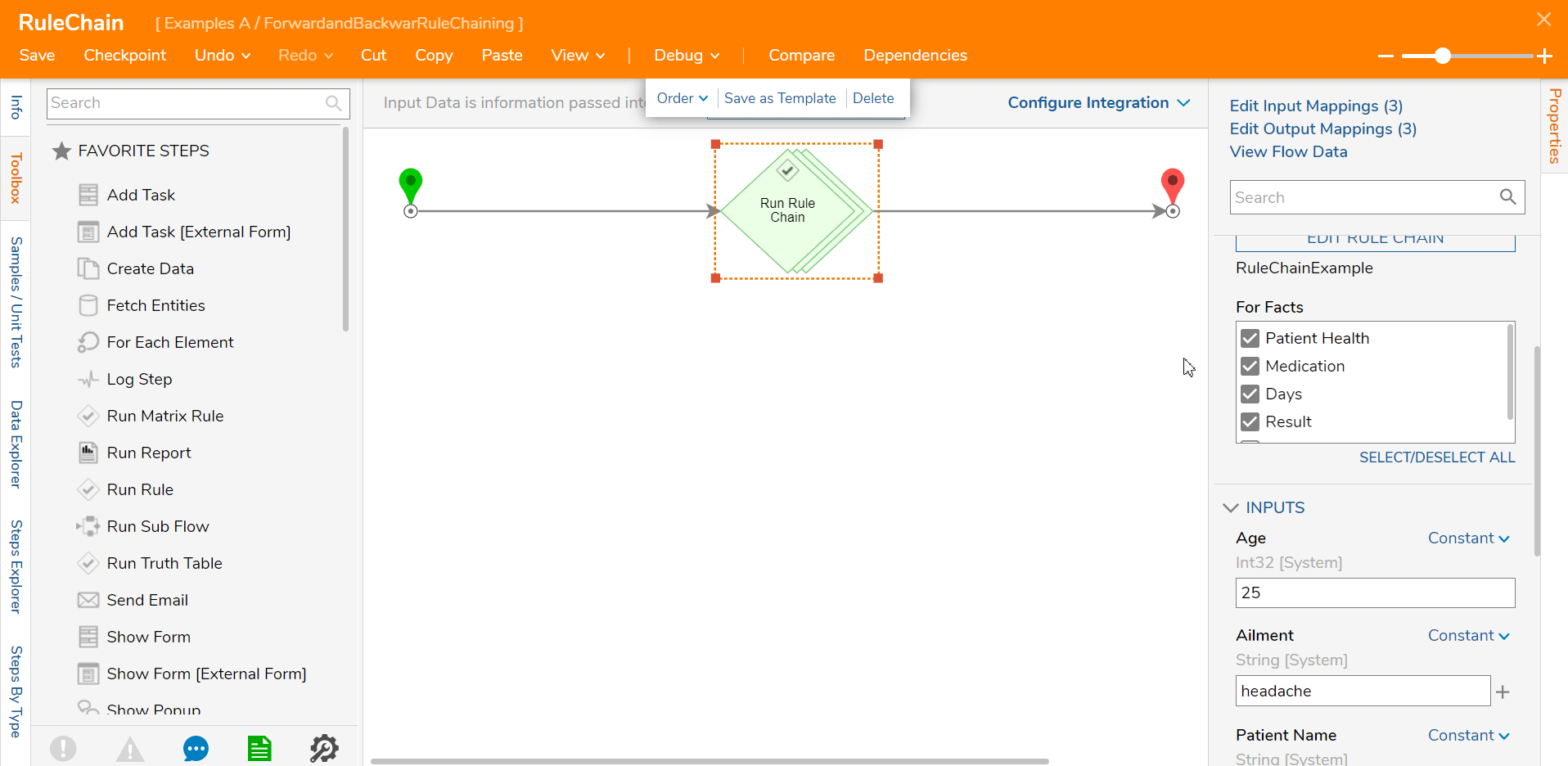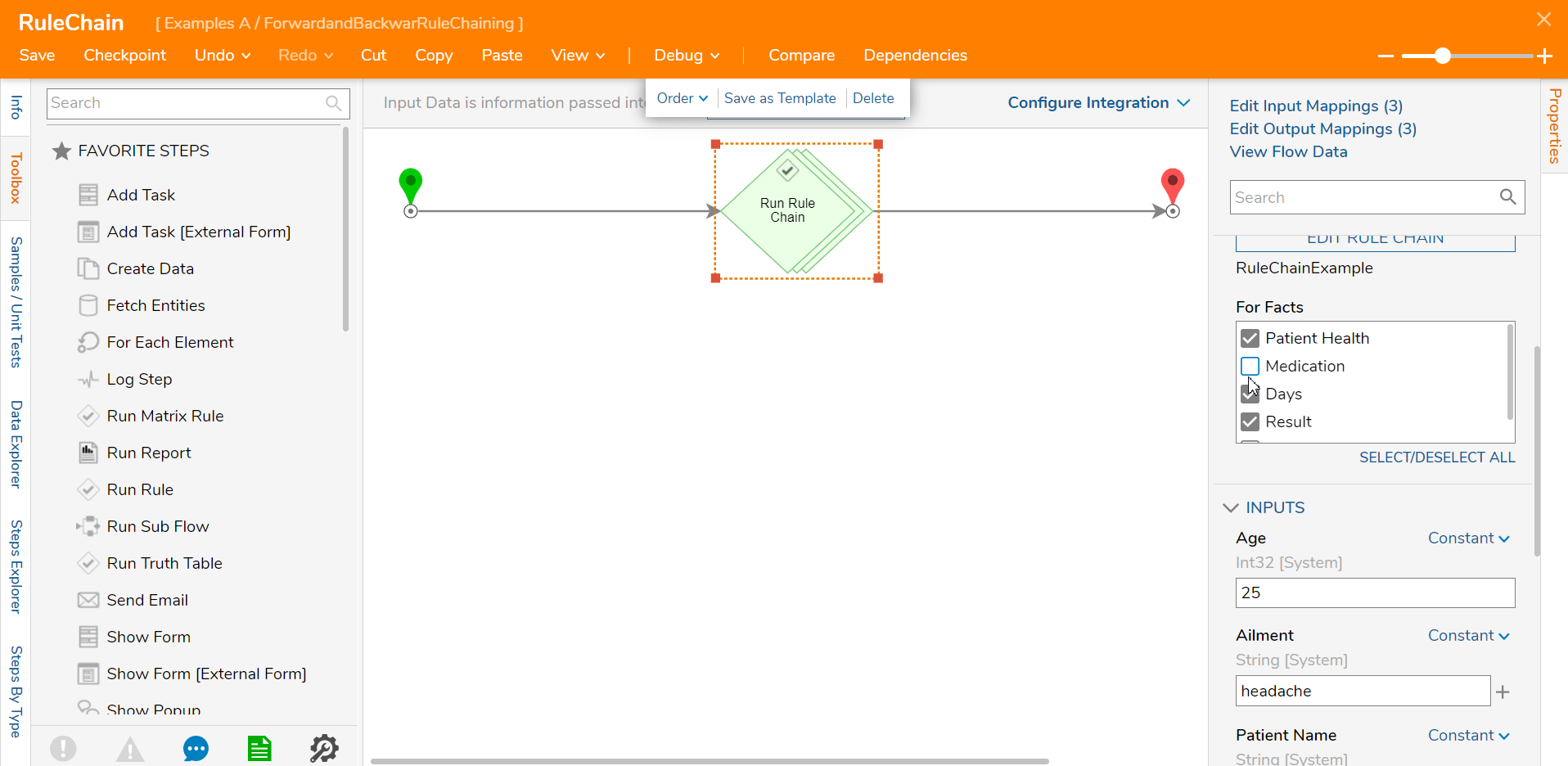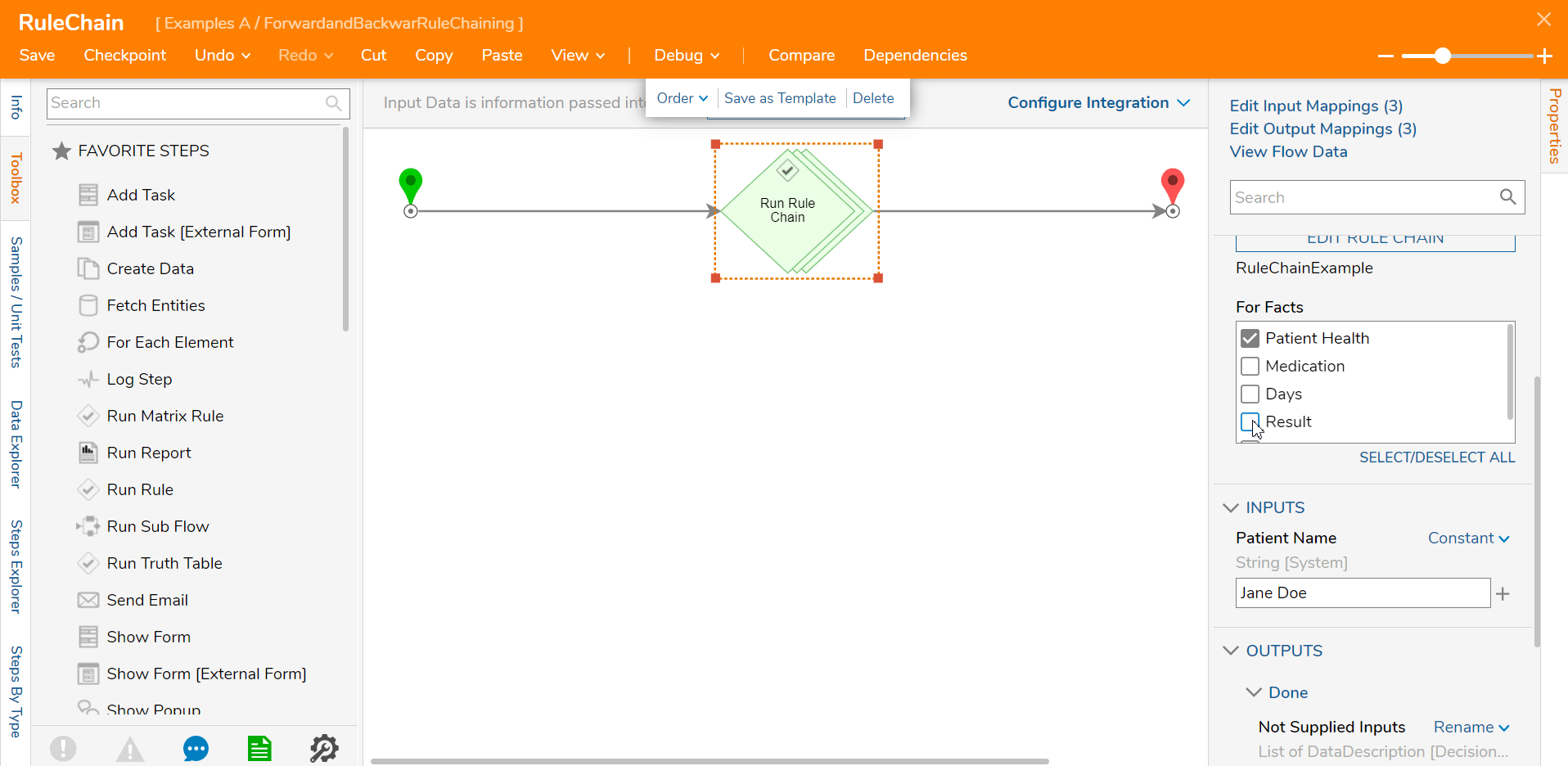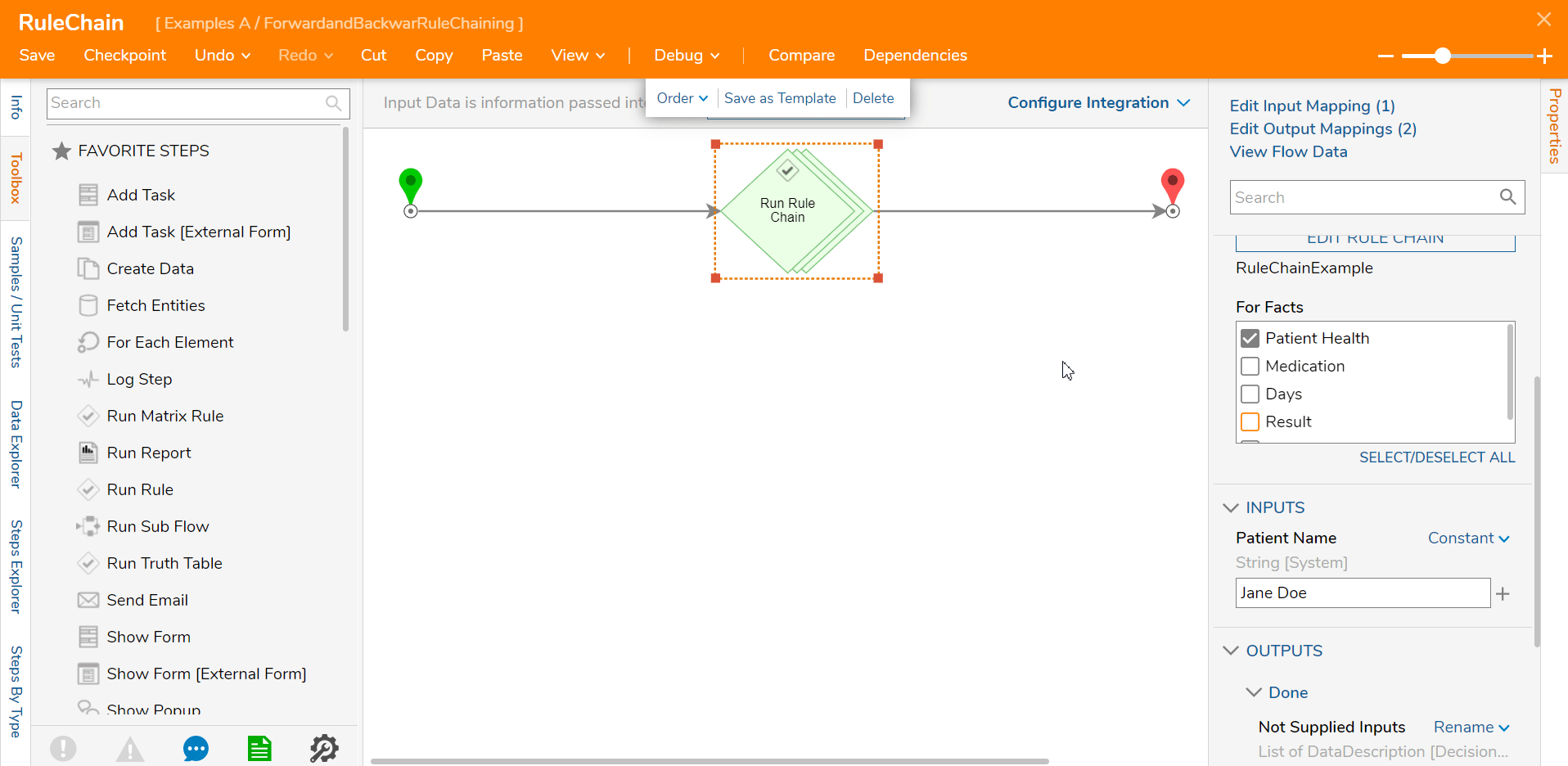
When this Rule chain is run with the modifications, the Input and Outputs are limited compared to the results of the Forward Rule Chain.