Overview
Users may configure the Portal to enable default Auditing; this allows the System to audit transactions involving all Entities, such as Folders, Assets, and Tasks.
A user can view the an Audit Report by selecting an Entity and viewing the Audit History. In regards to the types of changes used for auditing, we use MERGE SQL commands whenever entities are saved to the database. The following list are changes used for auditing: Inserted, Updated, Deleted, Merge for data, Viewed for reports, Activity for logins/logouts, AD sync, module installation, password changes, import/export, and failed login attempts.
The examples below details how to enable Auditing in the Portal and within Custom Data Structures.
System Settings
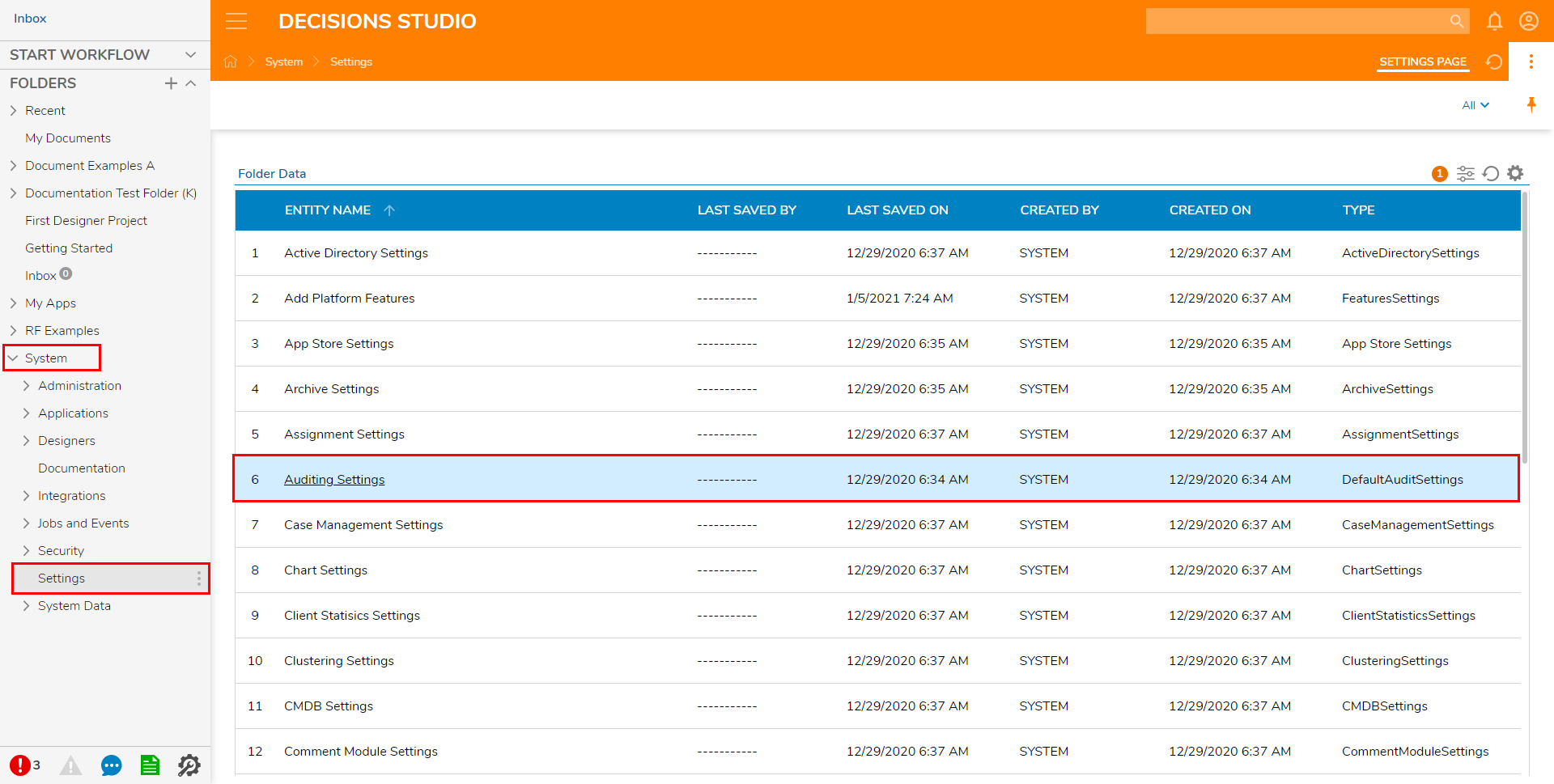
- From the Designer Studio, navigate to System > Settings.
- Click Auditing Settings.
- From the Edit Default Auditing window, toggle the checkboxes for each desired Audit type under Activity Auditing and/or Data Auditing. Data and Activity AuditingWhen enabling Data auditing, this will not enable auditing at the system level and is required for the audit change feature to apply for a data structure. However, enabling any auditing action under Activity Auditing will enable auditing at the system level. This can lead to the audit_entity table to fill rapidly and may lead to performance issues.
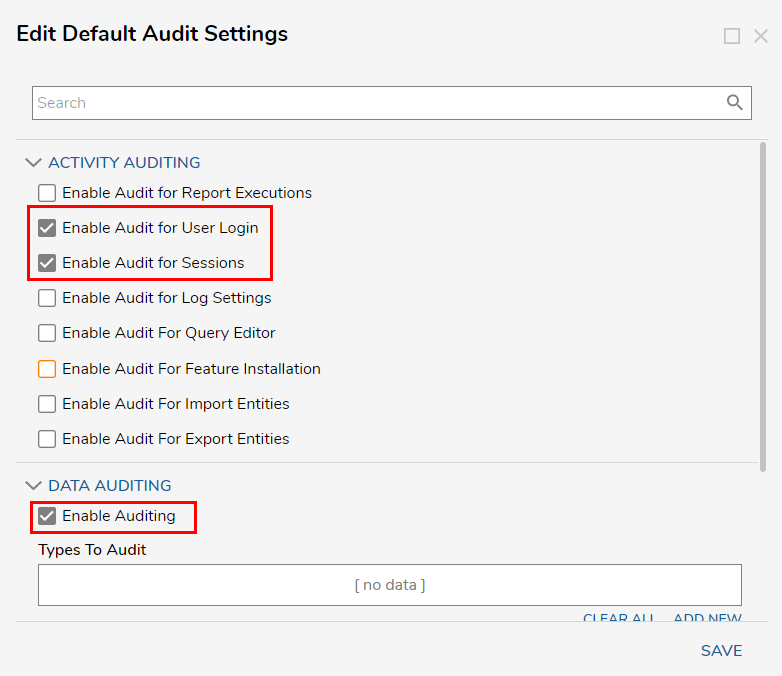 If Enable Auditing is selected under Data Auditing, an Audit Type will need to be determined.
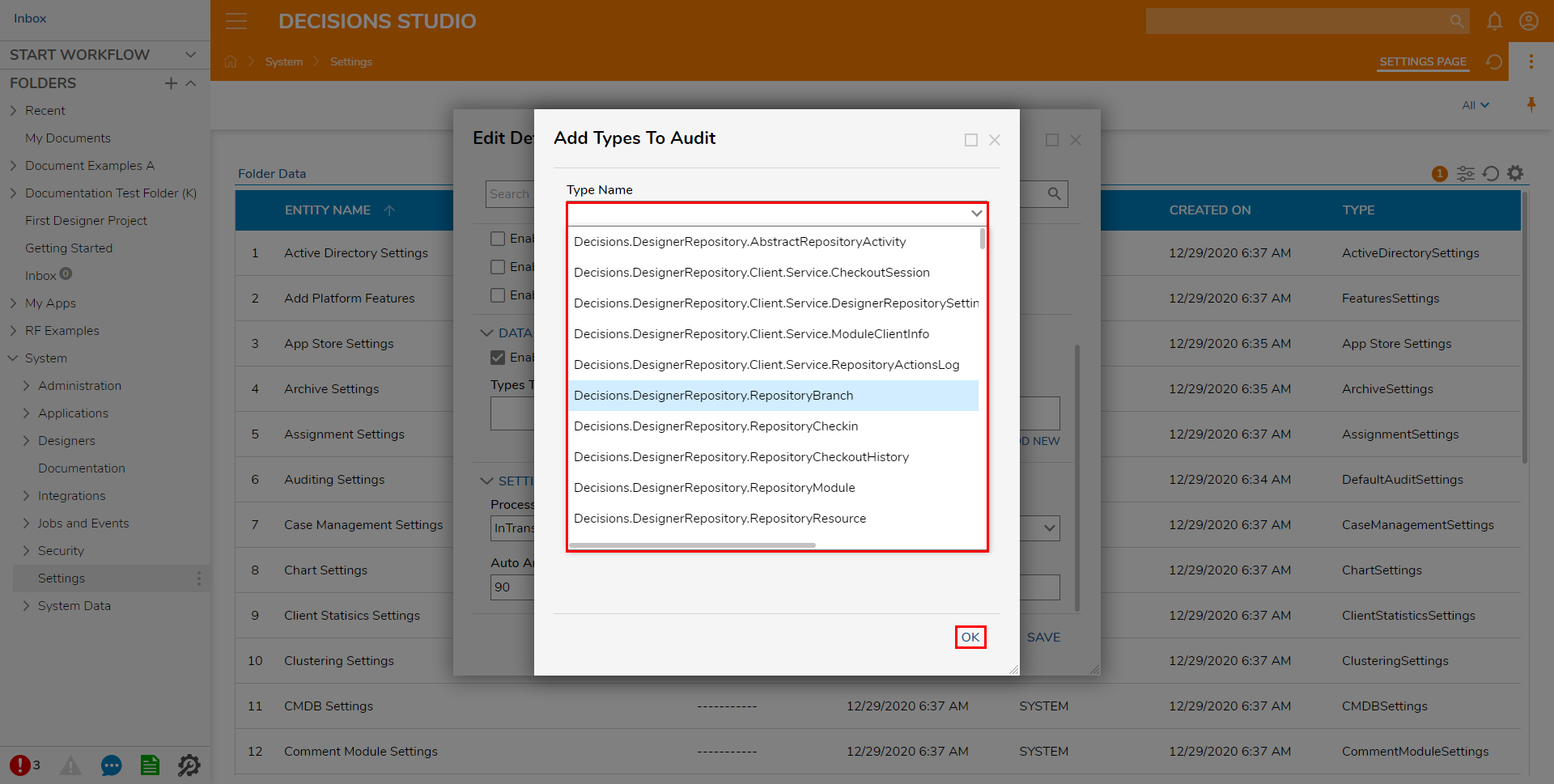
If Enable Auditing is selected under Data Auditing, an Audit Type will need to be determined. Under Types To Audit, click ADD NEW. Then, either search for the type of Data or find it via the dropdown menu under Type Name. Click OK to save this choice.
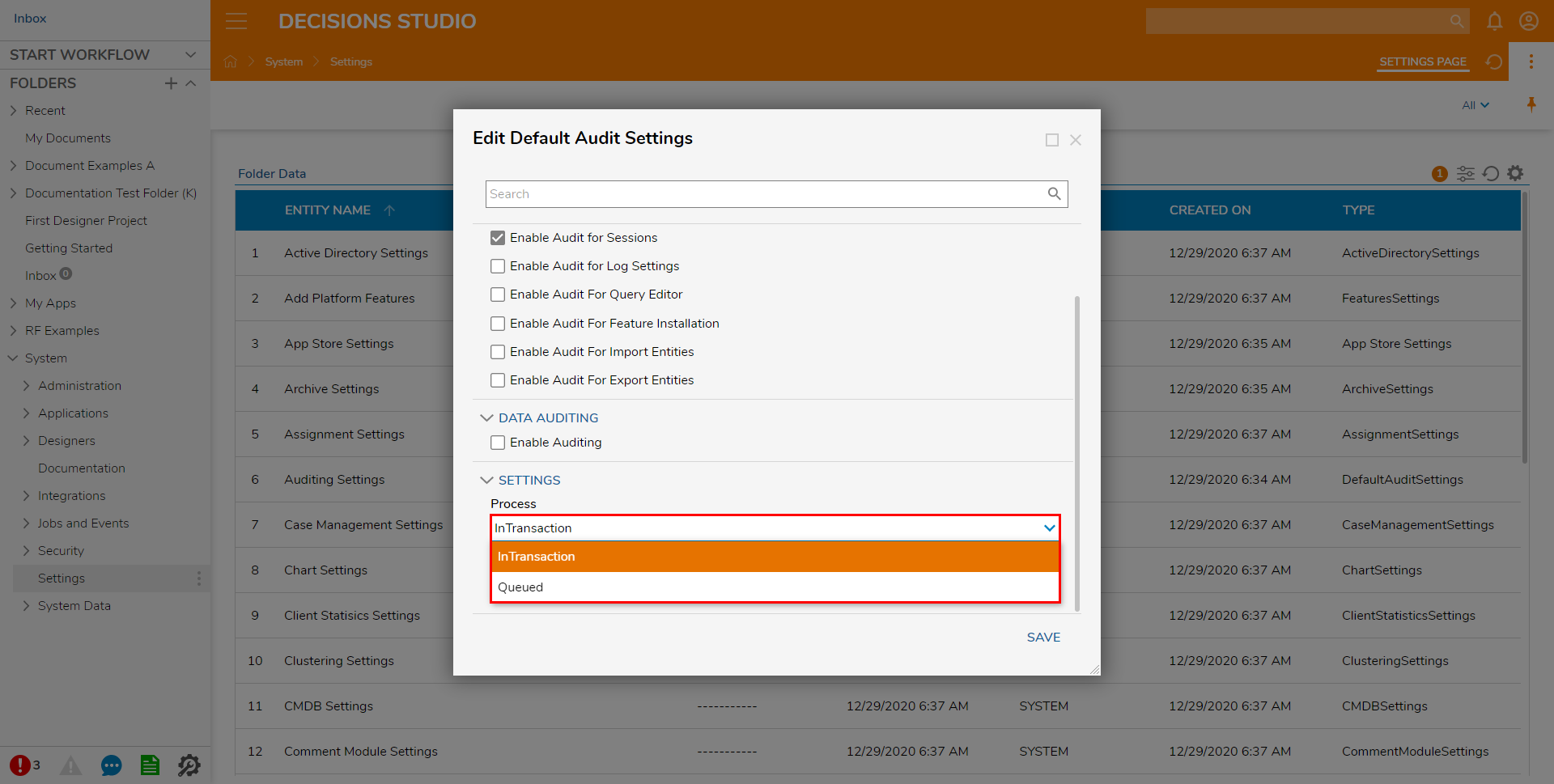
Under SETTINGS, select the desired Process setting.
The Process settings are as follows:- InTransaction - All the updates are stored in the same transaction.
- Queued - The updates do not share the Transaction of the main update; they are updated very quickly, but in a different transaction. (If data integrity is primary, then doing InTransaction is best.)
- If desired, users may set the number of days that the Auditing Session's History Data is archived via the Auto Archive History after Days box.

Click SAVE to save the Default Audit Settings.
The System will now Audit the set Entity transactions automatically. Audited Data can be viewed by creating a Report that uses Audited Entities as its Data Source.
Custom Data Structures
Custom Data Structures can also be configured for Auditing. To do so, follow these steps:
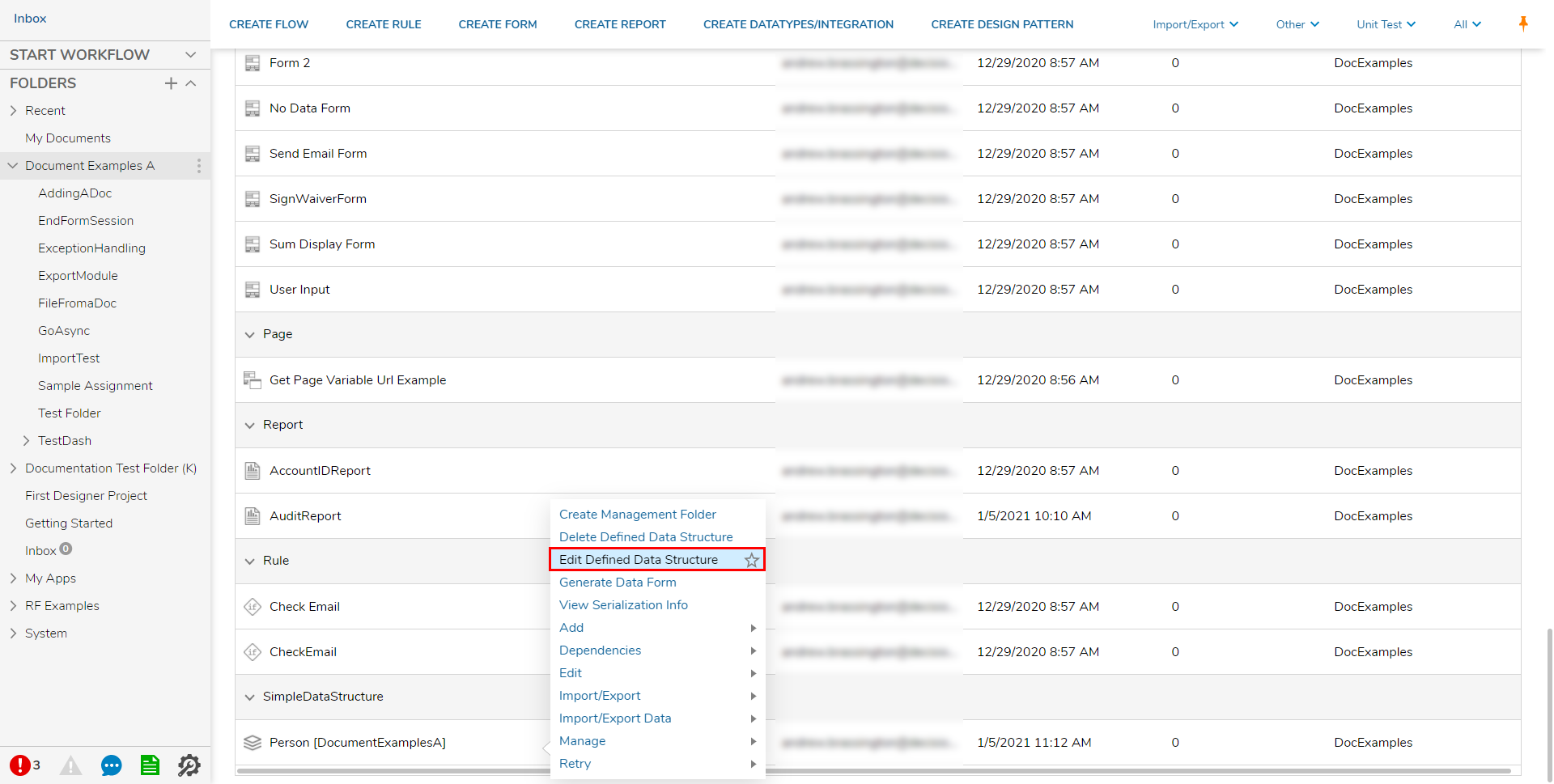
- From a Designer Project, right-click a pre-existing Custom Data Structure (or create a new one).
- Select Edit [Type of Custom Data Structure].
- From the ADVANCED category in the Data Structure's Properties panel on the right, check the Audit Changes box.
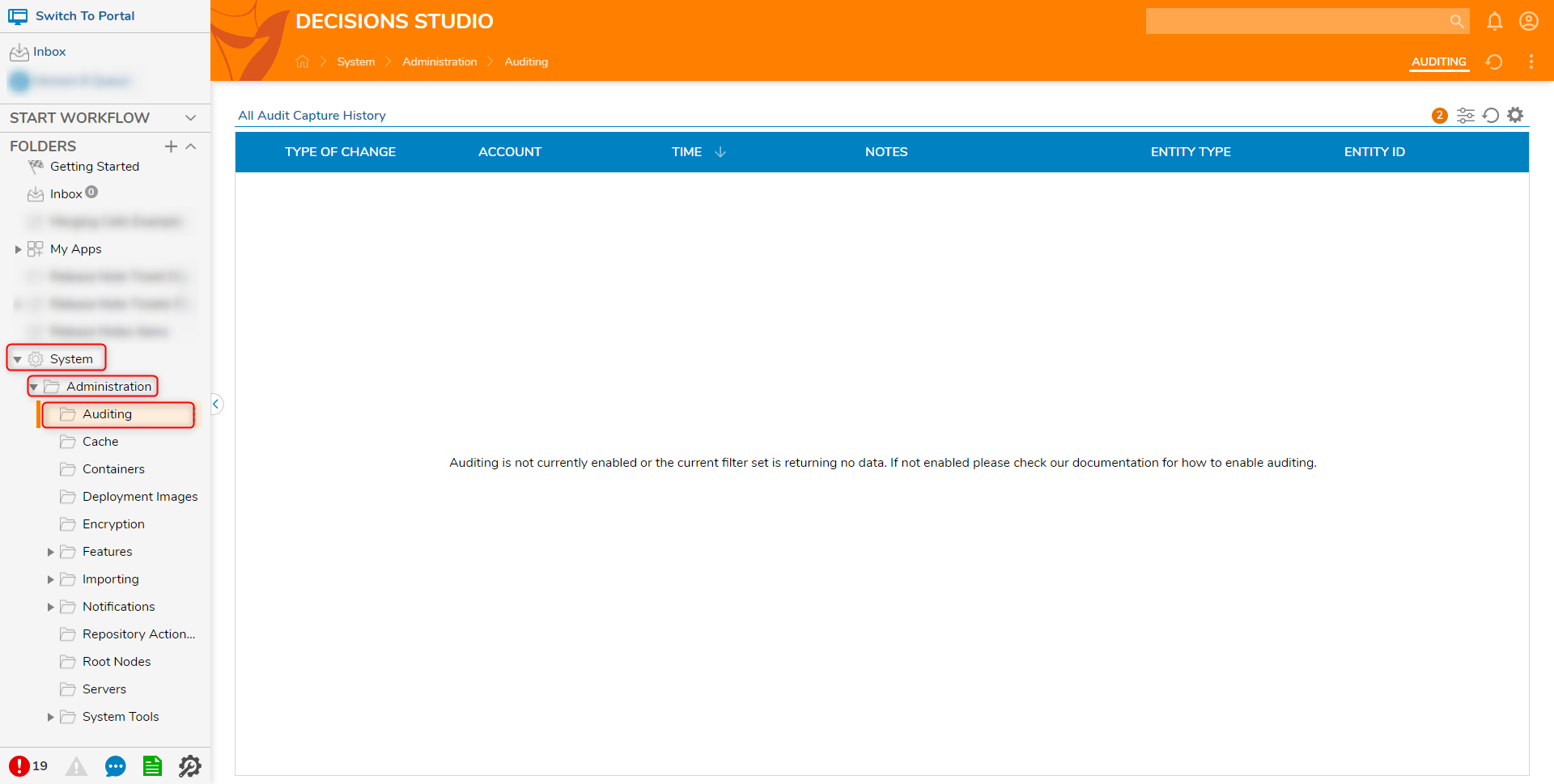
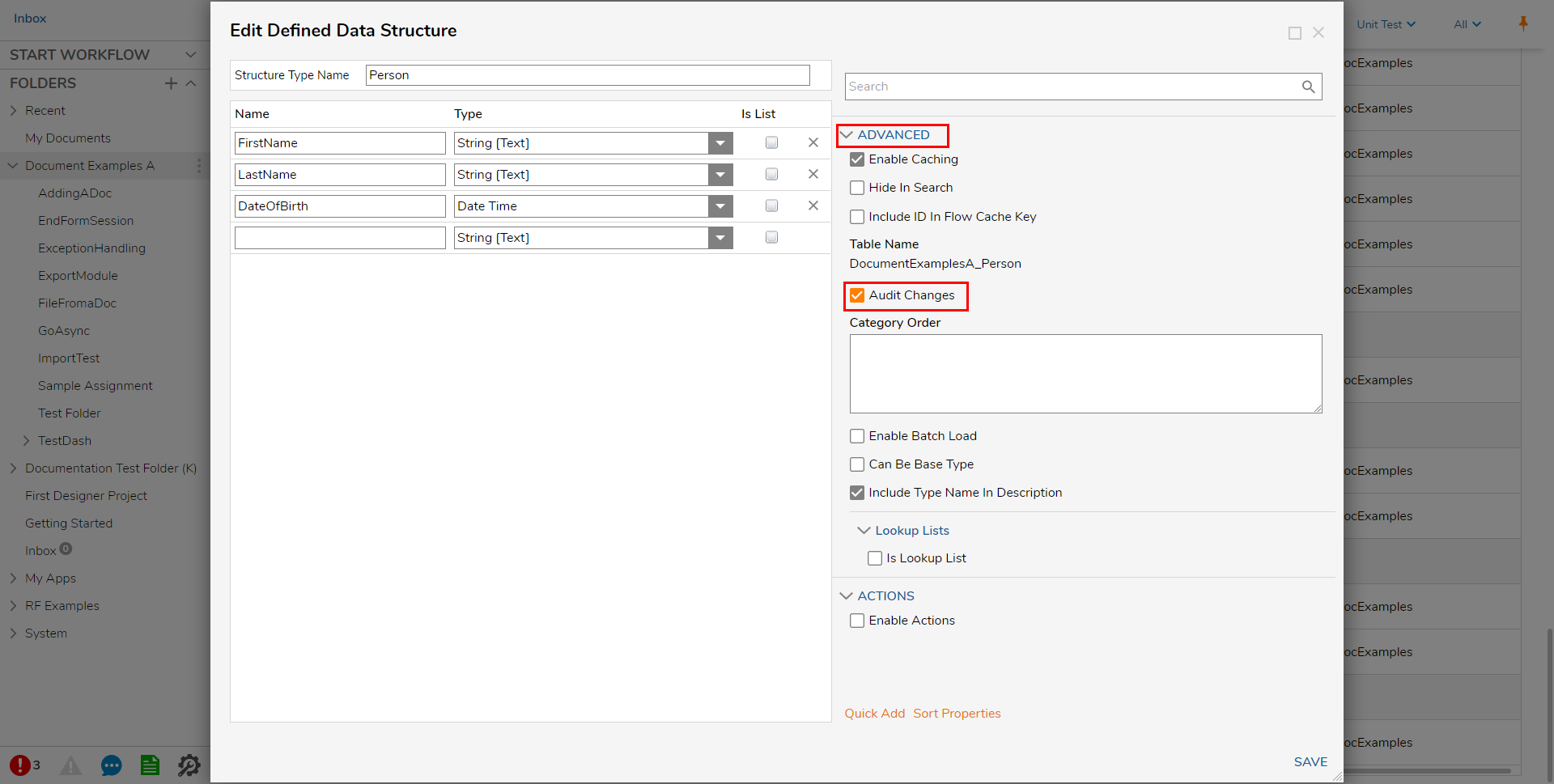 Any Create, Update, or Delete action taken against this Data Structure will now be recorded. A default Audit Report is made available to users under System > Administration > Auditing. The same information can also be accessed by querying the audit_entity table on the Decisions database.
Any Create, Update, or Delete action taken against this Data Structure will now be recorded. A default Audit Report is made available to users under System > Administration > Auditing. The same information can also be accessed by querying the audit_entity table on the Decisions database.
Activity Auditing
The below table covers the settings found when editing default audit settings.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Enable Audit for Report Executions | Viewing a Report will be recorded in the audit logs. |
| Enable Audit for User Login | User Logins will be recorded in the audit logs. |
| Enable Audit For Sessions | User Session creation and timeouts will be recorded in the audit logs. |
| Enable Audit for Log Settings | Any changes made to Log Settings from the portal will be recorded. |
| Enable Audit for Query Editor | Queries executed in the Query Editor will be recorded in the audit logs. |
| Enable Audit for Feature Installation | Installing features/modules will be recorded in the audit logs. |
| Enable Audit for Import Entities | Importing entities will be recorded in the audit logs. |
| Enable Audit for Export Entities | Exporting entities will be recorded in the audit logs. |
Global Audit Report
The Global Audit Report can be found under System -> Administration-> Auditing. This report shows all the audit records that have been captured across the system.