Overview
Decisions offers many JSON steps that enable users to manipulate JSON, such as through a data pair, without specifying a particular JSON data type. Utilizing these steps permits users to handle different instances of JSON regardless of the JSON datatype. When using other datatypes, users need to work solely within them, whereas Dynamic JSON can handle different JSON Datatypes because it is not associated with a specific one.
Users can utilize different types of JSON and create a process that dynamically retrieves desired values regardless of the original datatype. This article describes use cases that demonstrate how the Decisions platform handles Dynamic JSON.
Handling Dynamic JSON Structures with JSON Deserialization
Users can utilize the "Waterfall Method' using JSON Deserialization as another way to handle Dynamic JSON structures. The following image utilizes the JSON Deserialize and Create Data steps. Each error path should be connected the the following JSON Deserialize step.
This example only utilizes three possible Datatypes. Users who require additional Datatypes can attach additional JSON Deserialize steps to the error path of the previous JSON Deserialize step. Users may also add a Throw Exception step although is not required.
.png)
The "Waterfall" structure of the Flow allows Users to run the Flow in the debugger and simultaneously handle errors, if any should occur. The following example shows the first JSON Deserialize step in the Flow hitting an Error. Instead of ending the entire Flow, the waterfall structure allows the next step in the process to continue. Once an error is identified, Users can address it in the Flow and run the Debugger again to review any changes made.
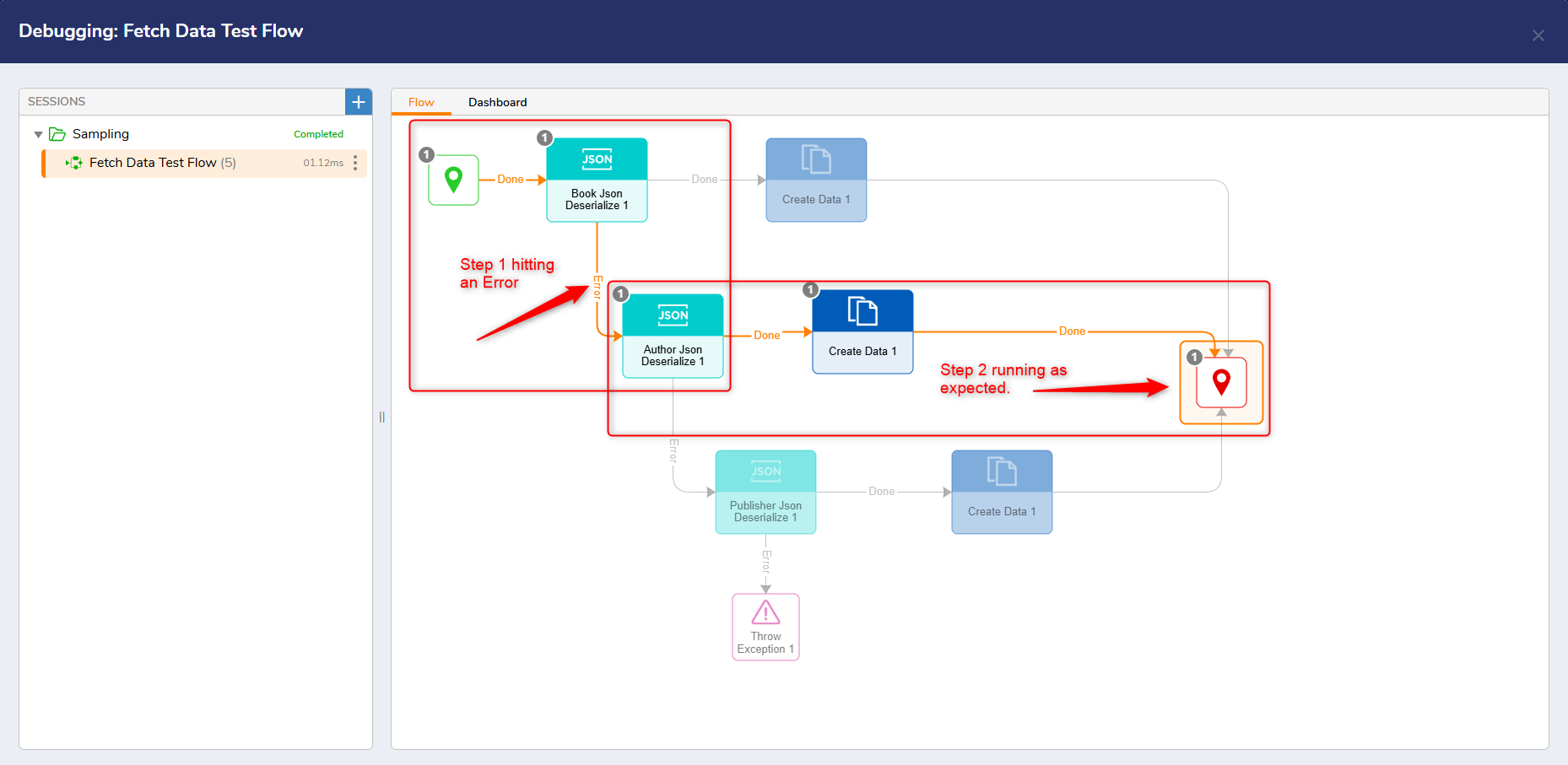
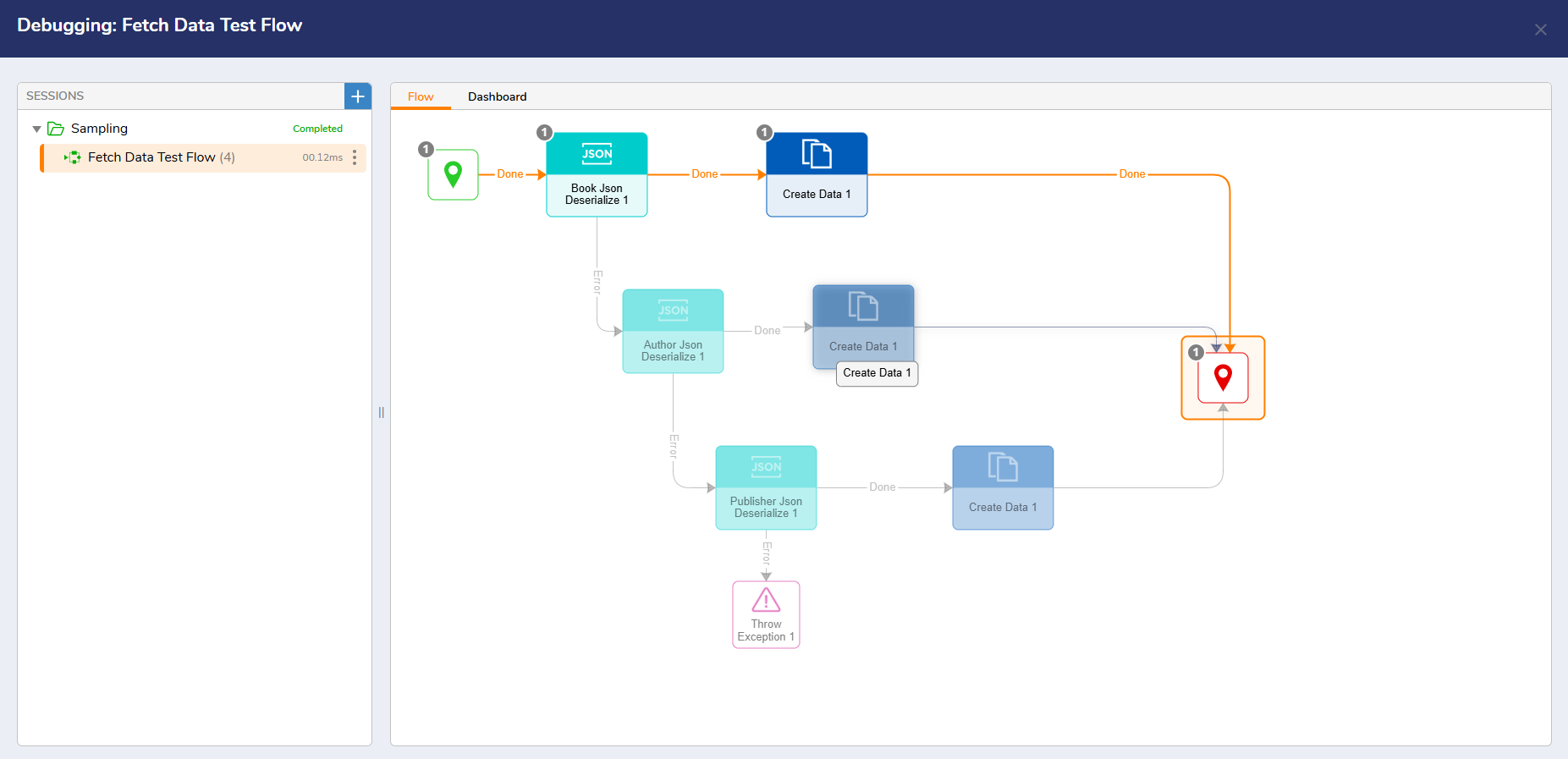
If no errors occur, the Flow will run as expected.
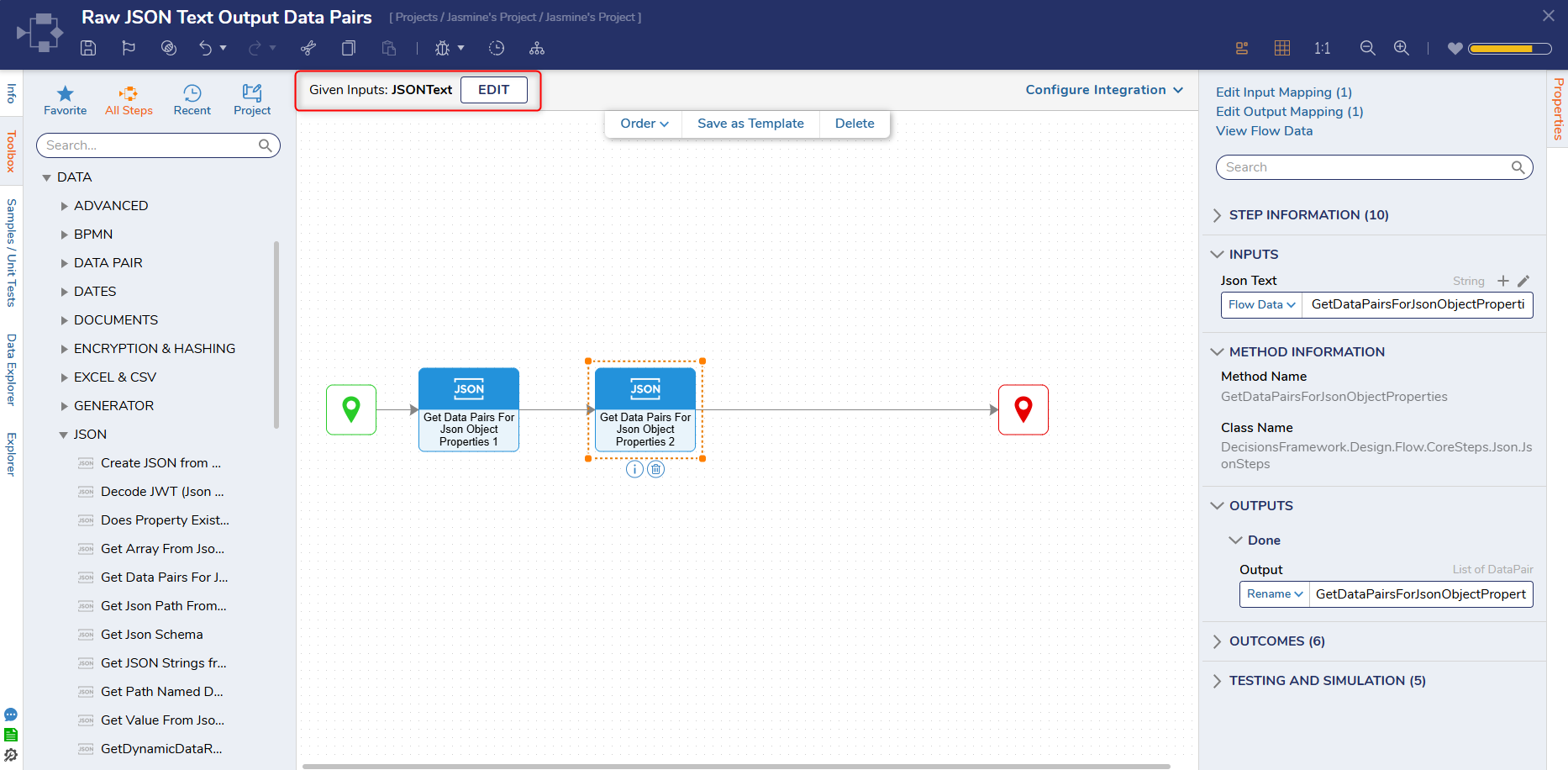
Analyzing Data Properties with Data Pairs
Data pairs are essentially made up of two values: Name and the corresponding Value.
Using the Get Data Pairs for JSON Object Properties Step, Users can input a string of JSON to review all data properties, without the need for a composite type.
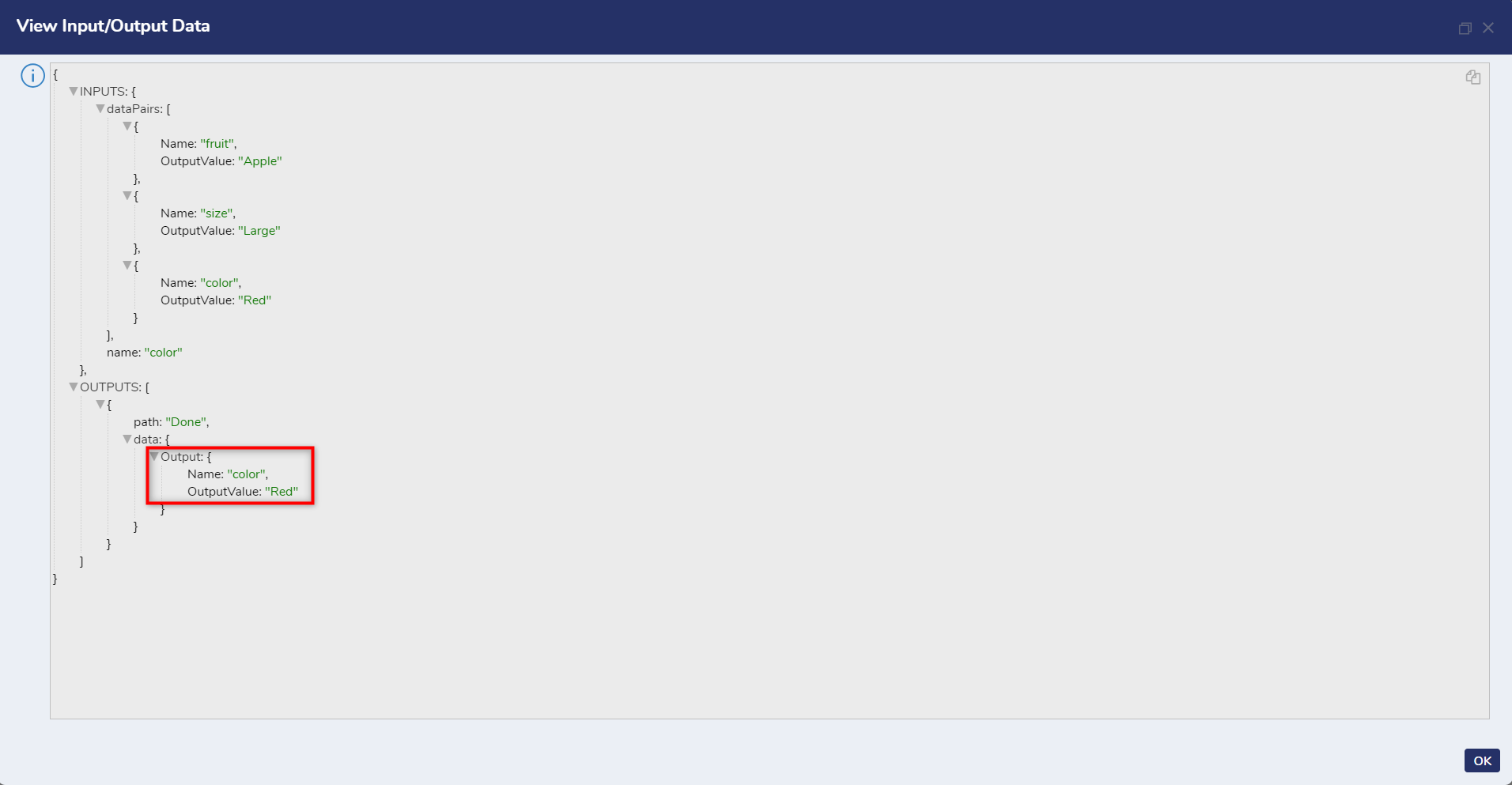
Evaluating Data by Searching for Specific Properties
Users who have a list of JSON but want to search for a specific property like color, for example, can use the Does Property Exist in JSON step.
{
"fruit": "Apple",
"size": "Large",
"color": "Red"
}This step utilized with Dynamic JSON analyzes all properties within a string of JSON text and highlights a specific property in the Output Data.
Steps for these examples can be found by navigating to Data > JSON in the Toolbox.