- 09 Jul 2024
- 2 Minutes to read
- Print
- DarkLight
HTTP and Response Code Error Handling
- Updated on 09 Jul 2024
- 2 Minutes to read
- Print
- DarkLight
Overview
Decisions Flows, Rules, and Reports can be called as REST APIs using most typical REST Method such as Get, Post, and Put. Given that the Workflows in Decisions are highly configurable by the Designer, it is not always possible to return standard HTTP codes. The following document describes how Decisions handles certain types of Error conditions and how the Designer can configure the Flows to throw specific codes and Error Messages when required.
Expected API Exception Return
Unless otherwise specified in the Flow designs covered below, Decisions returns two things when an Exception occurs while calling a Flow as an API.
- HTTP Status Code
- A Plain Text Error Message to the Calling System.
The screenshot below displays a typical Error Message in Postman.
Standard HTTP Code Patterns: Succesful Calls
200 Success
Successful calls into the Workflow Engine will return a 200 Response. This means that the Flow Diagram was able to make its way from the Start step to the End step without encountering an uncaught Exception. Steps in Flows can have Outcomes for Errors/No Data Return that can be Error Conditions. If the Flow is built to incorrectly handle these scenarios Flow design can inadvertently appear to succeed to the Calling System.
Standard HTTP Code Patterns: Failed Calls
403 Forbidden
Requests missing Authentication or having invalid Authentication will return HTTP Error Code 403.
500 Internal Server Errors
Almost all other Exception events occurring during the calling or execution of a Flow will return a 500 Internal Server Error to the Calling System. Below are a few examples:
- Step hits an uncaught Exception that causes the Flow to Fail to continue to its End step.
- A malformed Request Body is sent; this would typically be a 400 Error in other Web Applications.
Examples of Malformed Request Responses
- Input Property Misnamed: “Input parameter [Property Name] is missing.”
- Input Property Missing: “Input parameter [Property Name] is missing.”
- Invalid DataType: “Input string was not in a correct format.”
- Malformed JSON: “There is an error in XML document (1, 1).”
Throwing Explicit Errors to Calling Systems
The Flow Designer allows users to throw specific Error Messages and Codes to Calling Systems at any time using the Throw API Exception step. This allows a Designer to handle any Runtime Event as an Error alerting the Calling System of something adverse occurring.
.png)
.png)
Upon reaching this step, the Flow will direct to the End step of the Flow.
Serializing Error Messages
Because the Error Message is just a Plain String [Text] input users may leverage the ability to Serialize Data into JSON/XML as means of returning Data in a configurable format.
To do so:
- From the Flow Designer, add a Catch Exception step from Toolbox > FLOW MANAGEMENT > ERROR HANDLING to the Flow structure.
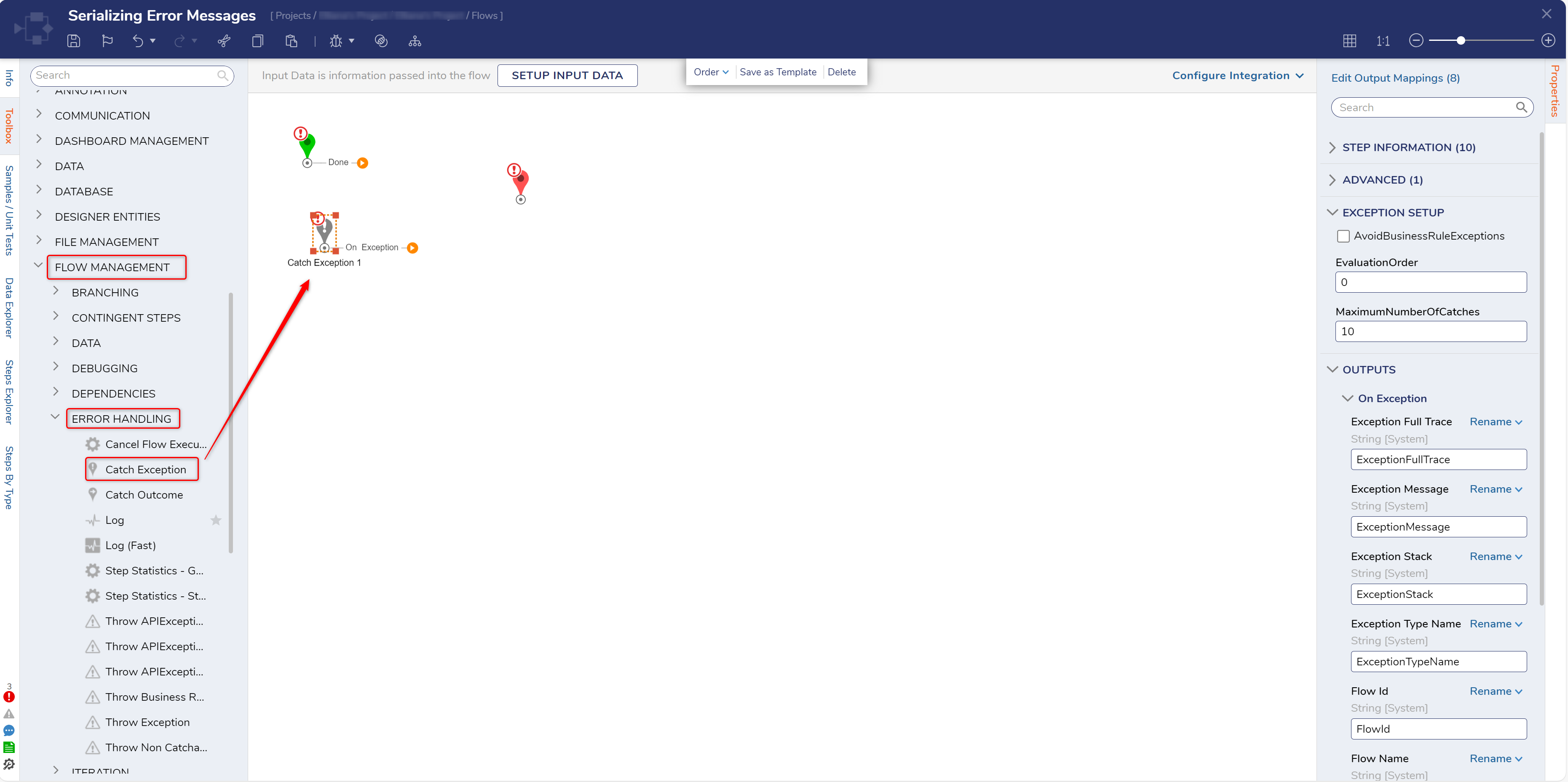
- From the Toolbox > DATA > JSON category, attach a JSON Serialize step to the On Exception path of the Catch Exception step.
- From the Properties tab of the JSON Serialize step, select String [Text] from Type, then Select From Flow map ExceptionMessage to the Object to Serialize Input.
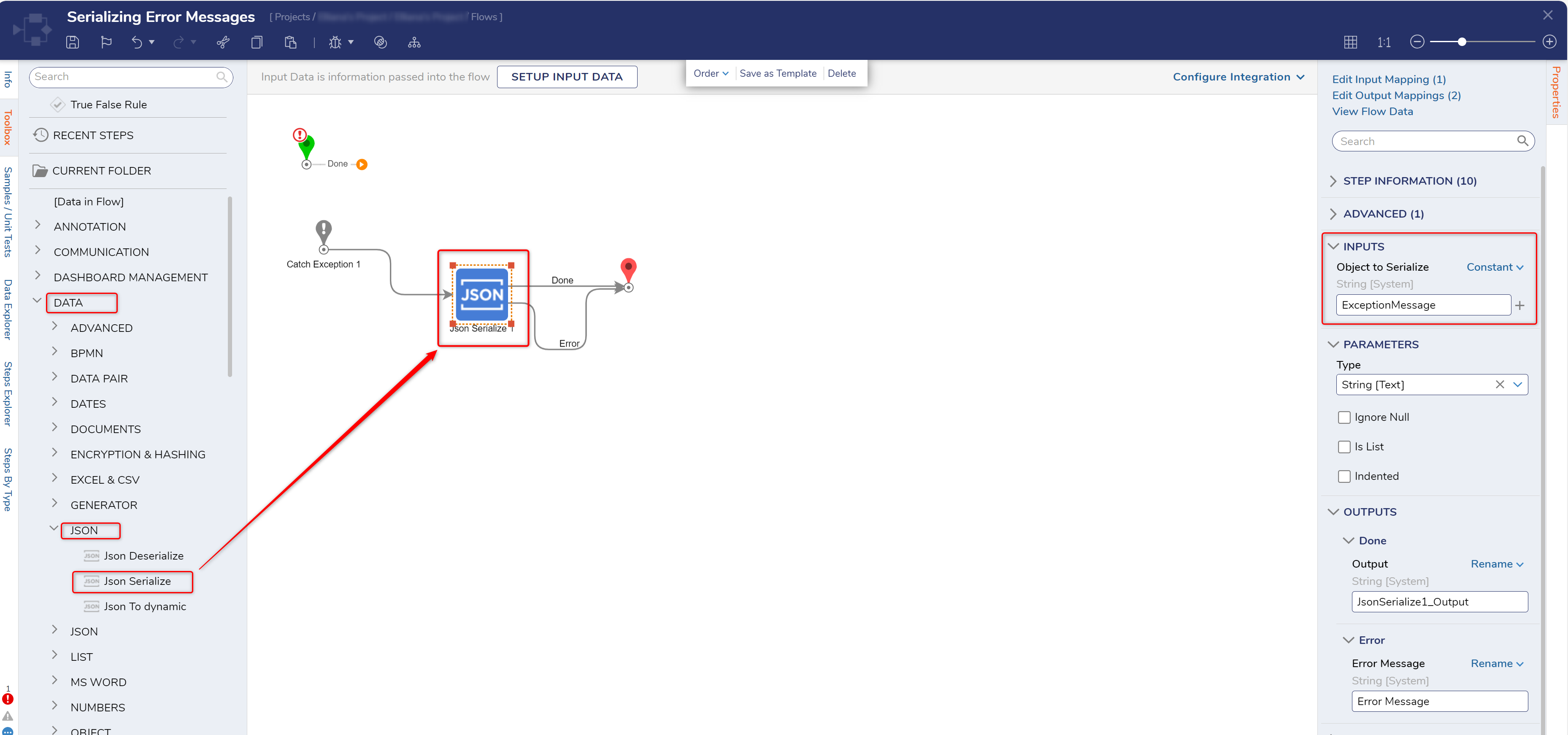
- From the same ERROR HANDLING category of the Toolbox tab that the Catch Exception step came from, attach a Throw Exception step to the Done and Error paths of the JSON Serialize step.
- From the Properties of the Throw Exception step, map JsonSerialize1_Output to the Message Input.
.png)




.png)

