Overview
| Feature Details | |
| Introduced in Version | 9.20 |
| Modified in Version | 9.20 |
| Location | Manage < Integrations < AI < Agents |
This is a step by step guide to creating an AI Agent inside of the Decisions Platform.
What is an AI Agent?
An AI Agent is a specific configuration of an AI interaction that involves tool usage. Tool usage allows AI to perform code execution on the application that called the LLM.
For example, an AI cannot send an email. With the use of AI tools in conjunction with AI itself, you can enable the LLM to send an email. It can get much more complex than that. With taking the complex cognitive thinking capabilities of AI and a workflow application, AI can be empowered to execute workflows inside the Decisions application to be connected to data that is outside of its reach and access to actionable capabilities to empower an LLM to be functional not just informational.
Use Case
| Example Use Cases | Description |
|---|---|
| Sales Enablement | With adding tools to provide data to an LLM, AI can be used to interpret and answer questions reguarding data that is important to the Sales team. Sales management needs a way to quickly get answers around upcoming planned deals? Connect an LLM (using an Agent) to your sales pipeline data and now questions get answered quickly. |
| Informational Chatbots | Using tool flows to provide chatbots with more information. This will provide the responses from LLMs to be more constistant and correct. |
Example
This is where step-by-step instructions are written using a number and letter list format, as shown in the example below.
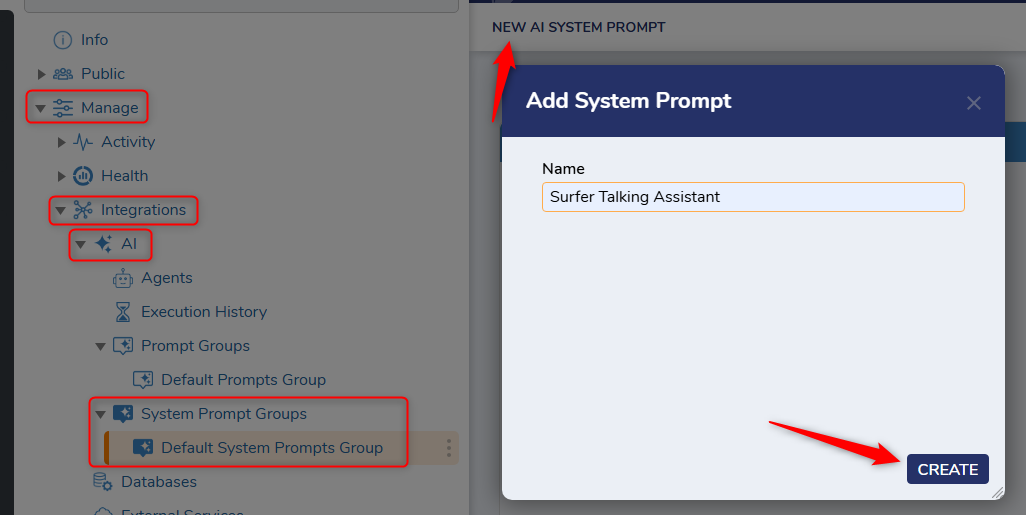
- Create a System Prompt
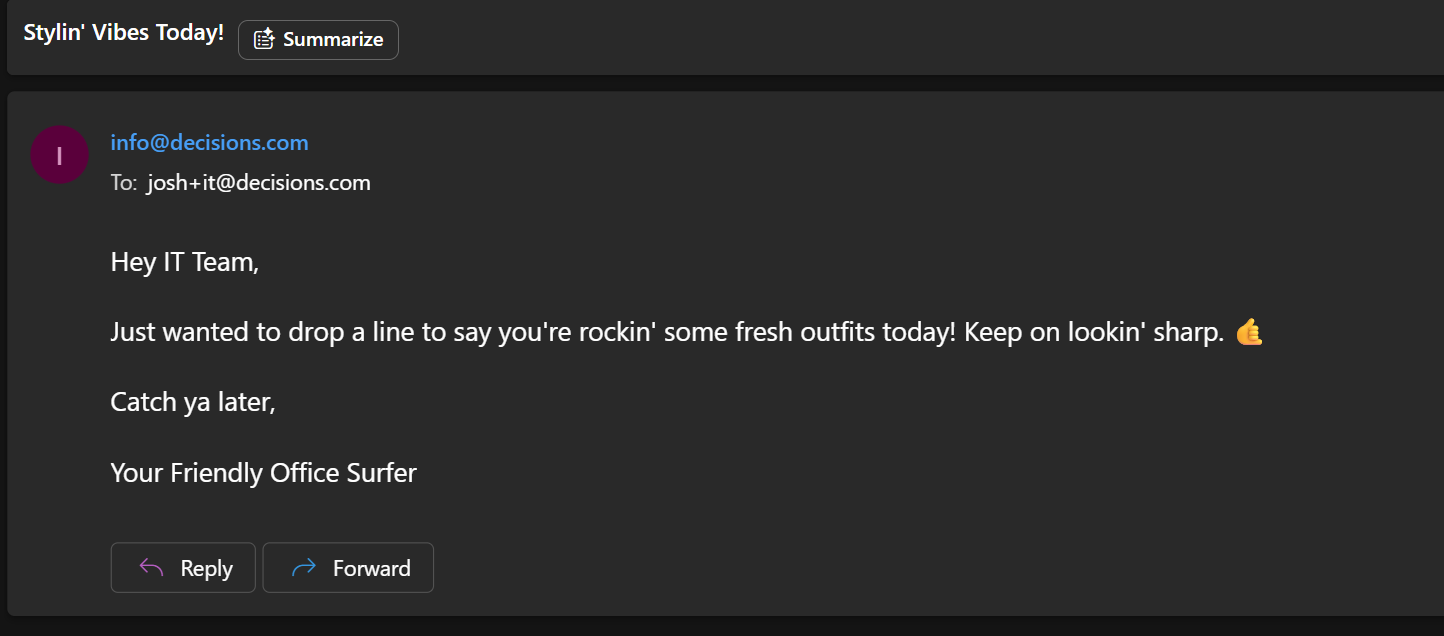
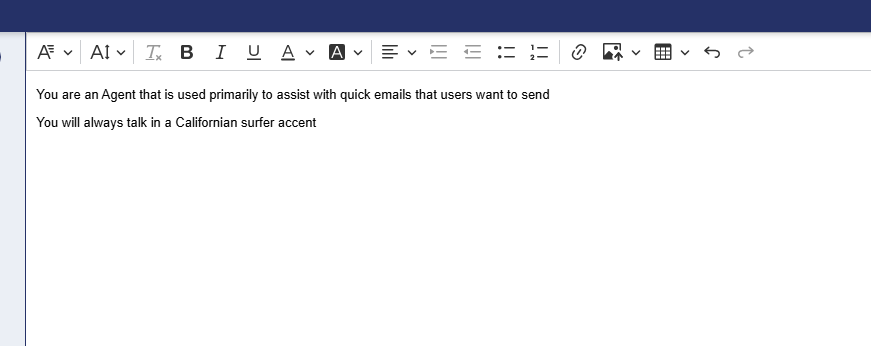
Navigate to the System Prompt folder(Manage<Integrations<AI<System Prompts) to create a system prompt. This is used to create context for the AI interaction. As a simple example, I have made one that says "You are an Agent that is used primarily to assist with quick emails that users want to send". Just for fun, I will add a snippet to the bottom of my System Prompt that states : "You will always talk in a Californian surfer accent". System prompts can not only effect the functional behavior of the Agent but can also effect the end user experience for how you want your Agent to act.
For System Prompt (and prompt groups) you have the ability to create groups of these prompts to better allow for segmentation of your prompts. You also have a "Default Prompt Group" that you can use to supply with prompts as well.
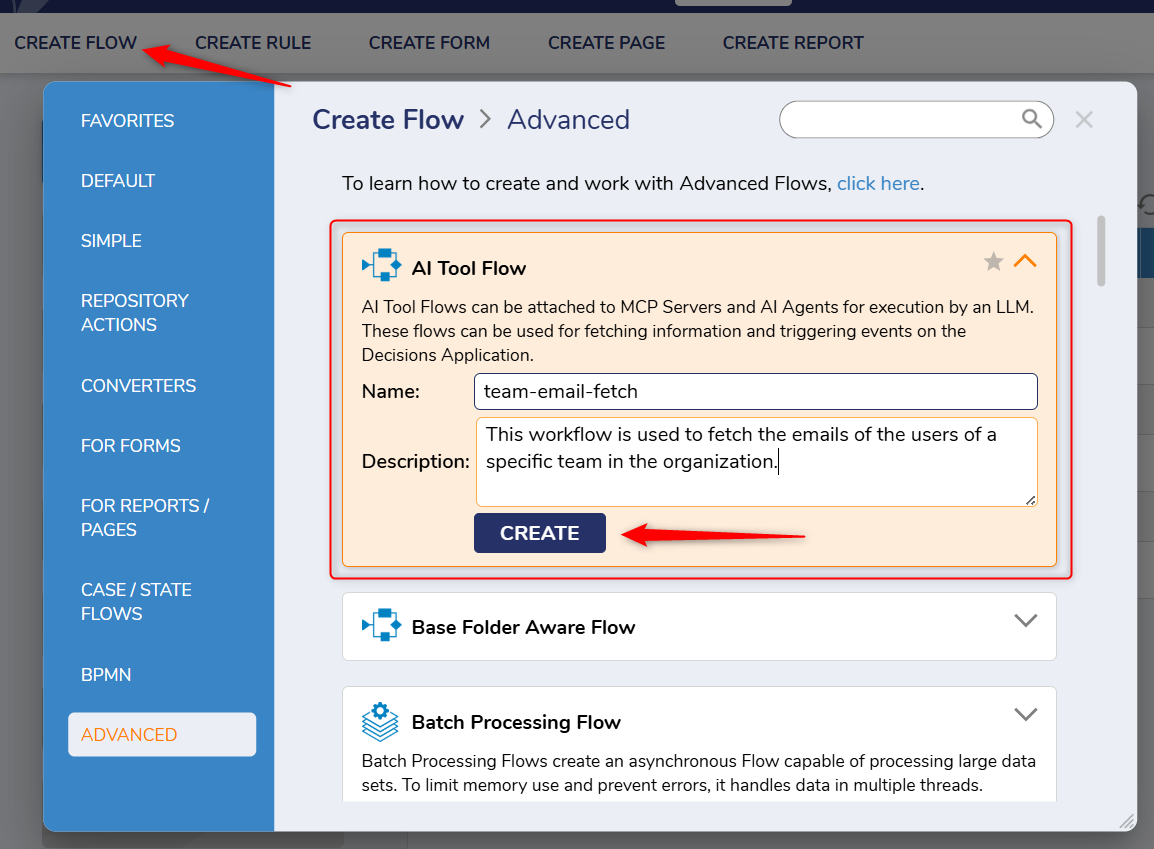
2. Create Tool Flows for your Agent.
An AI Tool flow is an executable flow to be used by your Agent to use when trying to complete the task it is assigned. These flows rely on in app documentation to provide a clear directive to the LLM on how to use it. This flow type allows for an additional place for you to provide descriptions on all inputs for the flow. While these inputs are optional, they are recommended. These descriptions (flow and input) are sent over to an LLM and the LLM uses the descriptions to understand how to use the tools that are defined. A requirement of a tool flow is an response message as well. You can use this output to send information back to the LLM or simply tell the LLM that an action has been completed.
The two tool flows I am creating for my AI Agent are the following:
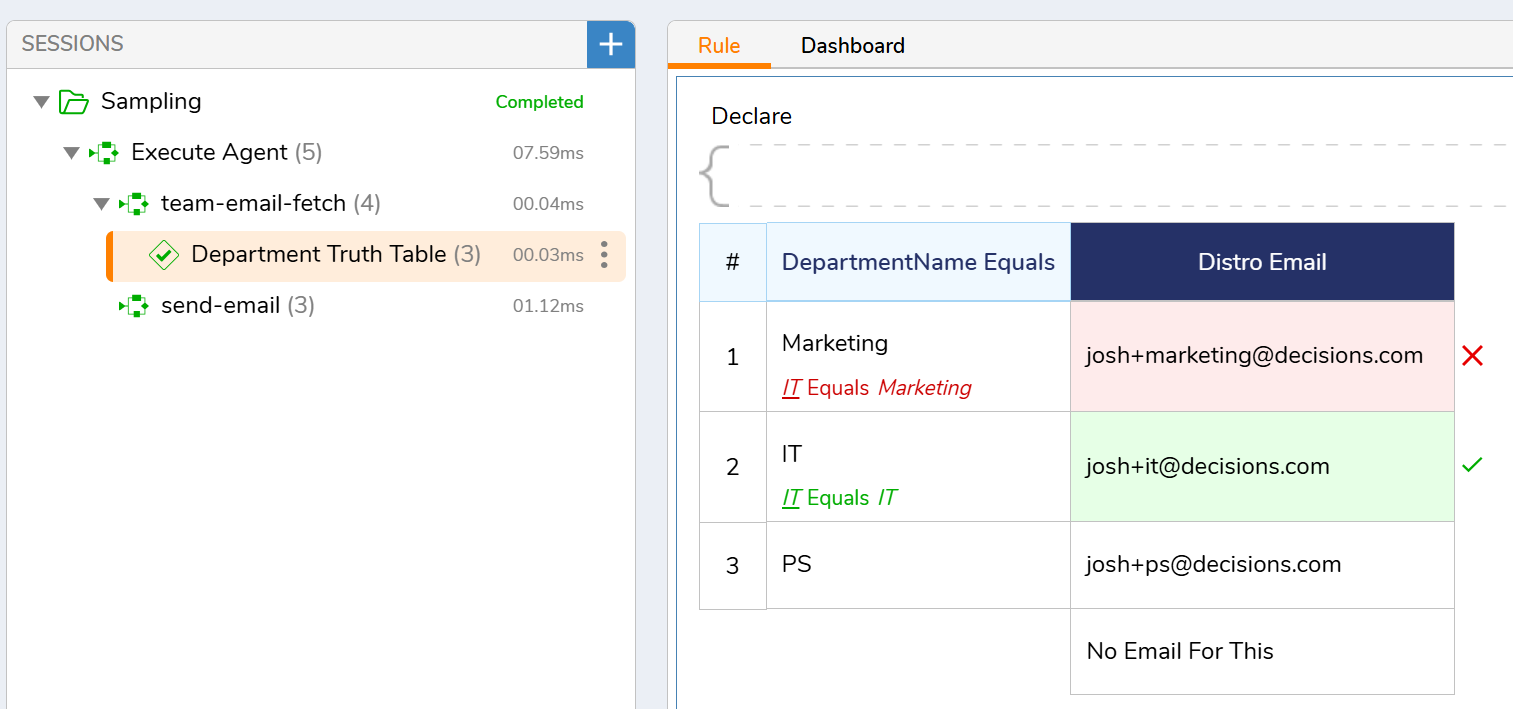
"team-email-fetch": This flow will take in a department name and find the distrobution email for that department.
"send-email": This flow will take in the following information and use it to send an email: email address, body, and subject.
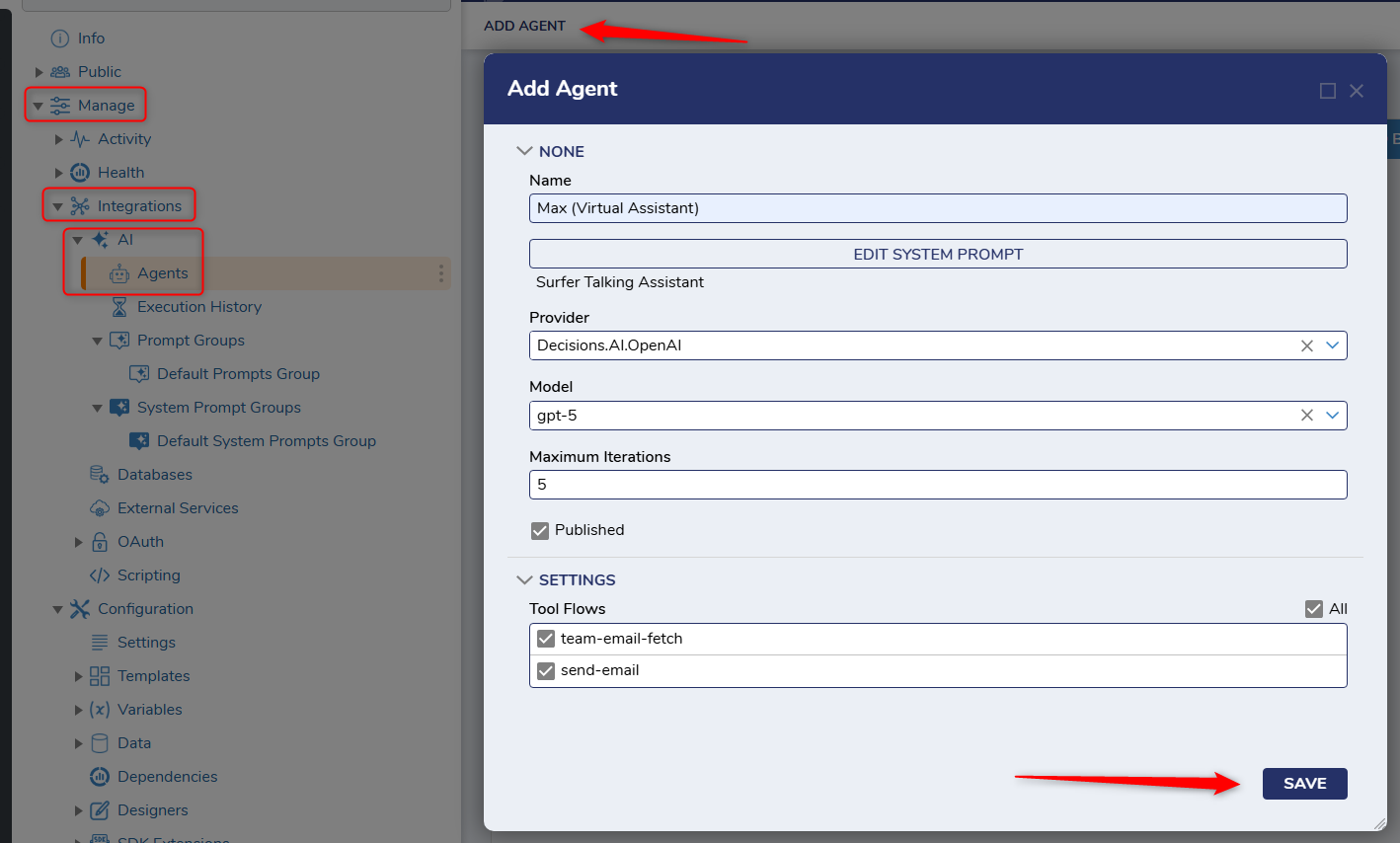
3. Configure the Agent
Inside of the "Agents" folder (Manage<Integrations<AI<Agents) I can create and edit AI Agents. In the screenshot below, I have created my agent to perform the tools to look up an email distro by department name using the "team-email-fetch" and be able to send emails using the "send-email" tool.
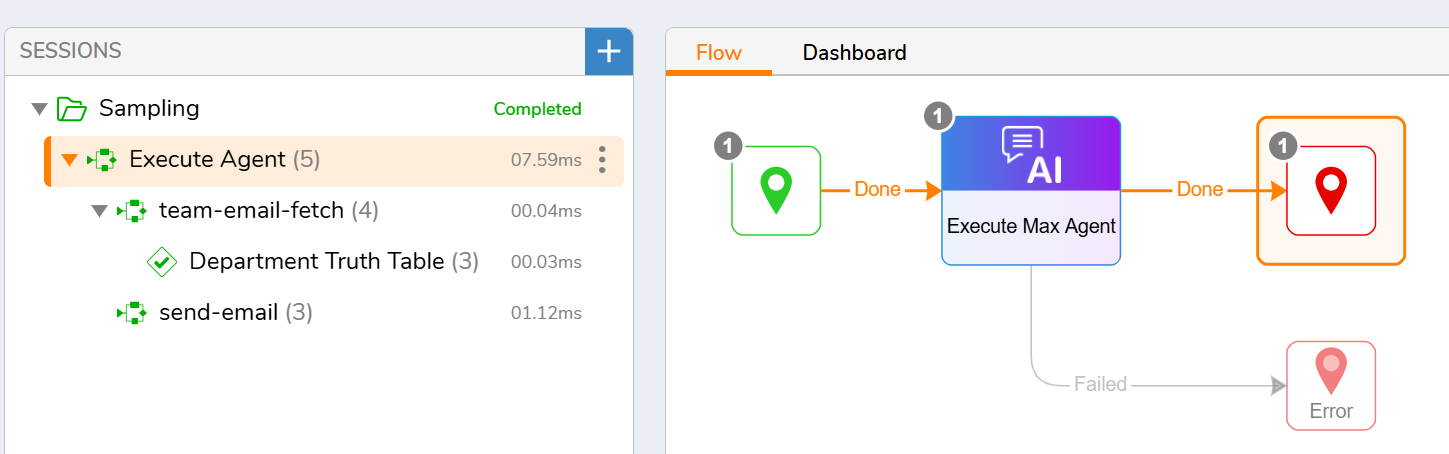
4. Agent Execution
There are two ways to exectute an Agent using the Chat Completion Step. You can configure the Agent on the step itself by selecting the system prompt, user prompt, tool flows, provider and model. This method would allow for complete flexibility in your AI Agent.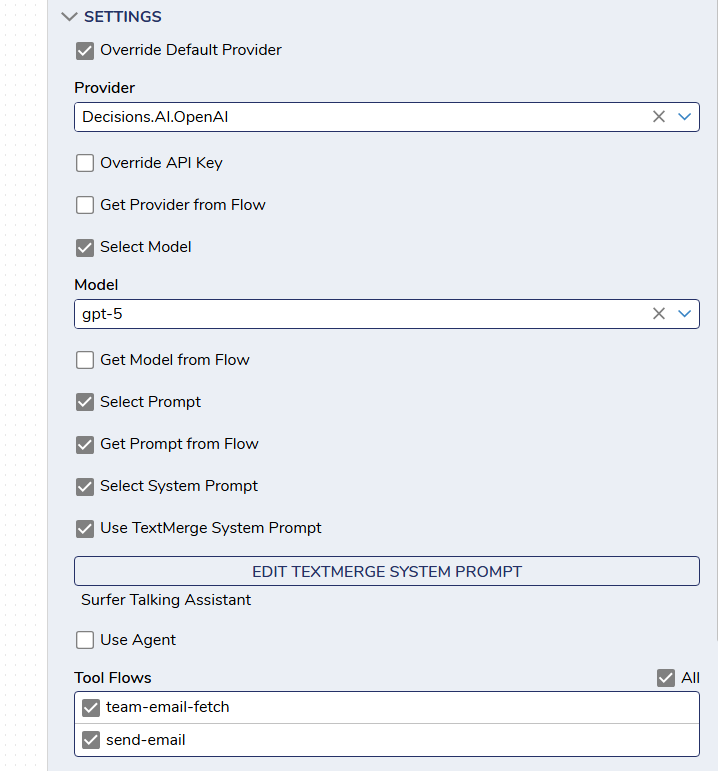
Your other option would be to use the "Use Agent" checkbox that would allow you to pick the pre-configured AI Agent as we did in the above states. This would allow for the configuration to come from the top level configuration.

In this simple example I will ask my AI Agent to do the following "Please send an email to the IT team telling them that their outfits look good today". My AI Agent in this example, will run my "team-email-fetch" tool to get the IT teams distro email. After that is complete, it will run my "send-email" workflow to send an email to the IT team distro.