Overview
Filters may be applied to a process map to exclude certain activities, events, or executions from analysis. To create a filter, select the filter icon located above the primary and secondary drop down menus on the right and then select Add Filter. The Filter Log Selector can also be accessed in the Log Animation settings when animating multiple variants to apply filters onto specific variants. After creating a filter, users may toggle their appear or delete them when hovering over a filter in the Filter Log Selector.
Editing the Filter Log
The icons at the bottom of the Filter Log Selector allow users to edit any created filters. Users may also rename filters once they have been created.

From left to right:
| Icon | Function |
|---|---|
| Up and Down Arrows | Moves the filter up/down in the Filter Log order. |
| Trashcan | Deletes all filters in the Filter Log. To remove a specific filter, hover of it and select the trashcan icon there. |
| Outlined Save | Saves the filters currently in the Filter Log. |
| Filled Save | Save the current filters as a new file in the Process Miner. |
| Open Folder | Loads existing filter files within the Process Miner. |
| Duplicate Filter | Allows the user to duplicate preexisting filters. |
Filters Available
The following filter typologies are available:
| Filter Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Attribute Filter | Filters out events or executions based on attributes contained in the event log. |
| Duration Filter | Filters out activities, handover, or executions based on their duration. |
| Endpoints Filter | Filters out executions where start and end events do not have specific attribute values. |
| Frequency Filter | Filters out activities or handover based on the number of items they are performed and executions based on the number of activities performed as part of the process instance. |
| Order Filter | Filters out executions based on the presence of particular order dependencies among activities. |
| Timeframe Filter | Filters out executions which do not fall within a specific timeframe. |
| Variant Filter | Filters out executions belonging to specific execution variants. |
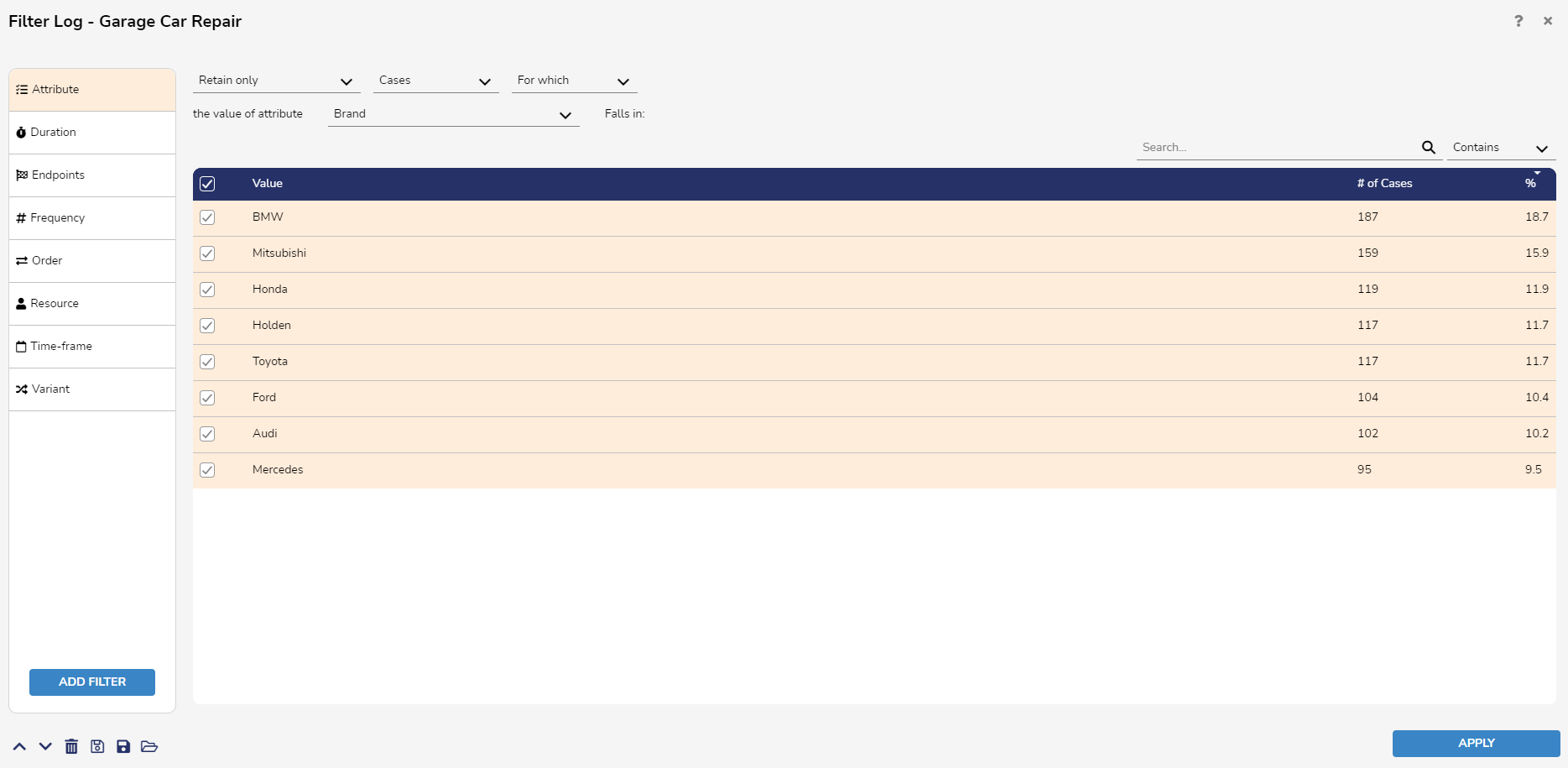
Attribute Filter
Generally used to select executions containing common properties, the Attribute Filter is the most commonly used filter. Users may configure this filter further by retaining/removing executions or events possessing certain attribute values. Acceptable values are defined by changing the specific attributes and phrases from the logic statement above the filter view:
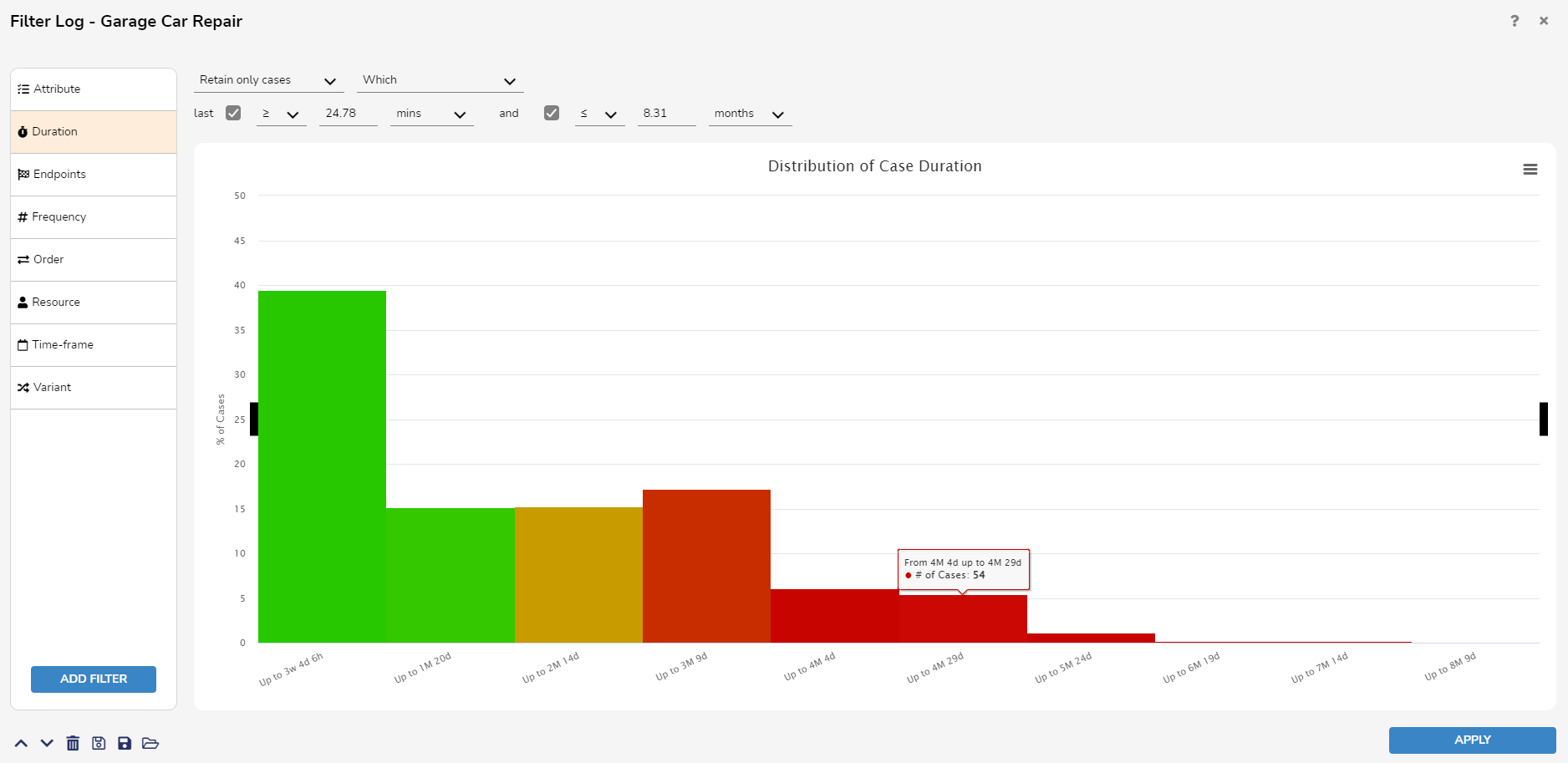
Duration Filter
The Duration Filter allows users to retain or remove cases with durations or total waiting times i.e. the sum of the durations of the handovers occurring in an execution within a certain range. Additionally, it also allows to define filters based on the duration of activities or handovers.
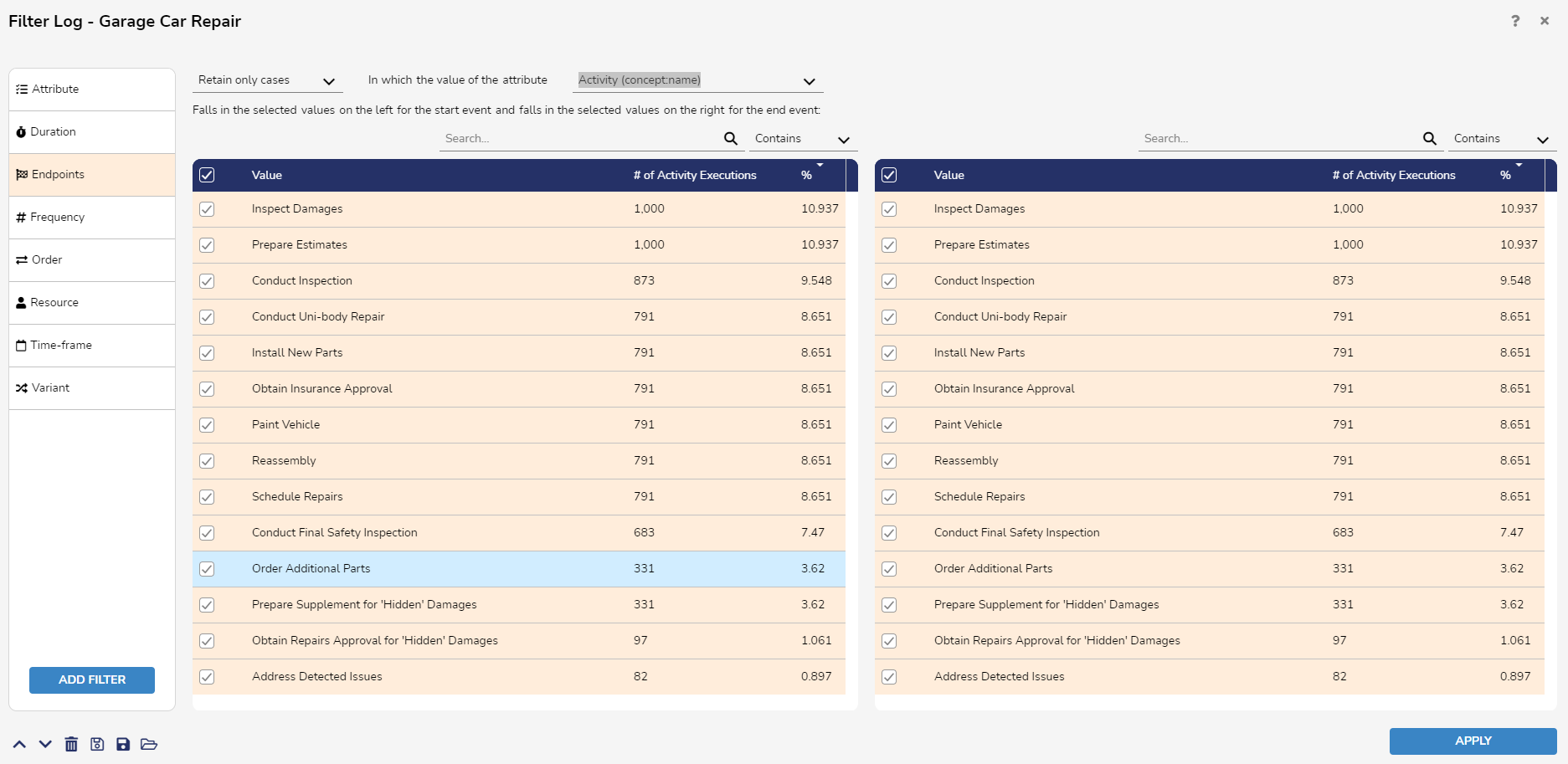
Endpoints Filter
The Endpoints Filter allows users to retains or remove cases in which the start and end events have certain attribute values. The filter searches for the start event in the left column and searches the right column for the end event.
Frequency Filter
The Frequency Filter allows users to retains or remove cases in which a certain number of activities are performed. The required number of activity executions is specified in the form of a range. Additionally, it is also possible to define filters based on the number of occurrences of a specific activity or handover.
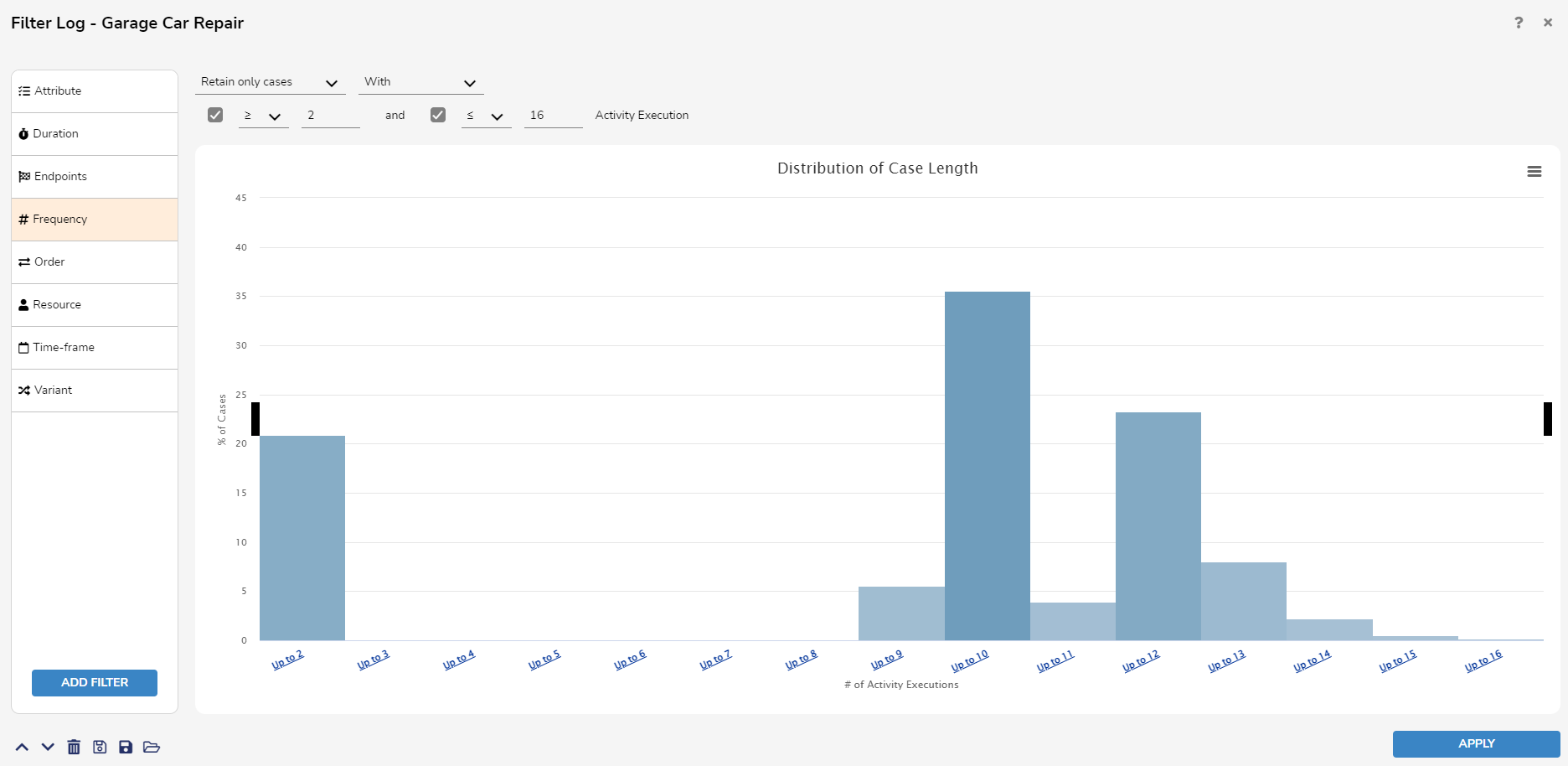
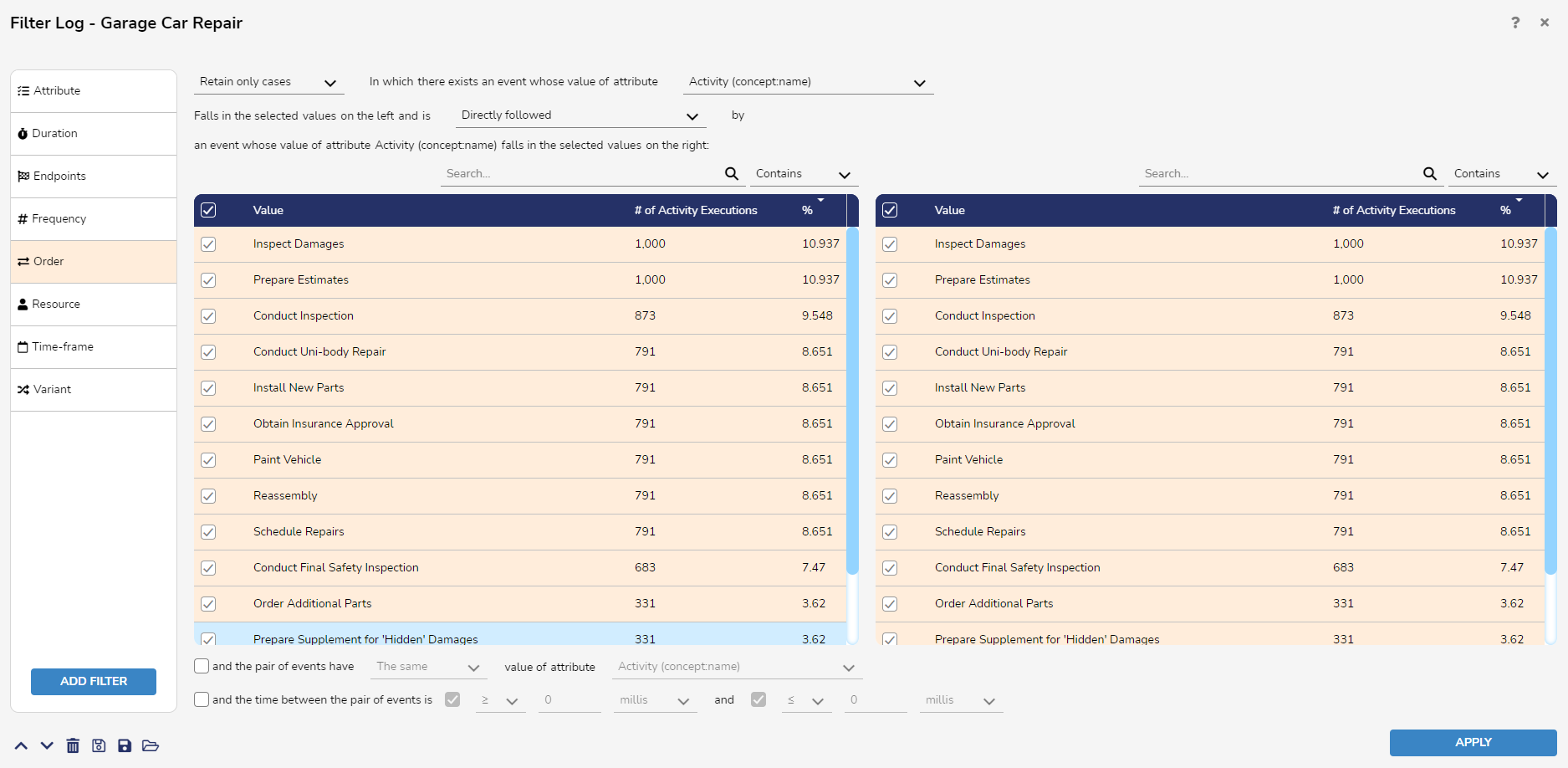
Order Filter
- The Order Filter allows users to remove or retain cases in which there exists two events with certain property that are in a specific order relationship. There are four possible relationships: Directly Follow, Never Directly Follow, Eventually Follow, and Never Eventually Follow.
- Directly Follow: Of attributes A and B, B directly follows A in an execution if at least one event with attribute value A which is immediately followed by an event with attribute value B.
- Never Directly Follow: B directly follows A in an execution if there exists no event where attribute value A is immediately followed by an event with attribute value B.
- Eventually Follow: B eventually follows A in a given execution if there exists at least one event with attribute value A that is followed by an event with attribute value B after an unspecified number of events.
- Never Eventually Follow: B never eventually follows A in an execution if there exists no event with attribute A that is followed by an event with attribute value B after an unspecified number of events.
- There are four possible time frame relationships that the Order Filter can maintain: Started Within, Completed Within, Started and Completed Within, and Active Within.
- The two checkbox filter statements further orders with the following statements:
- The first statement checks other attributes for similar or different values for ordering.
- The second statement checks if the pair of events occurred within, started by, or ended by a certain timeframe for ordering.
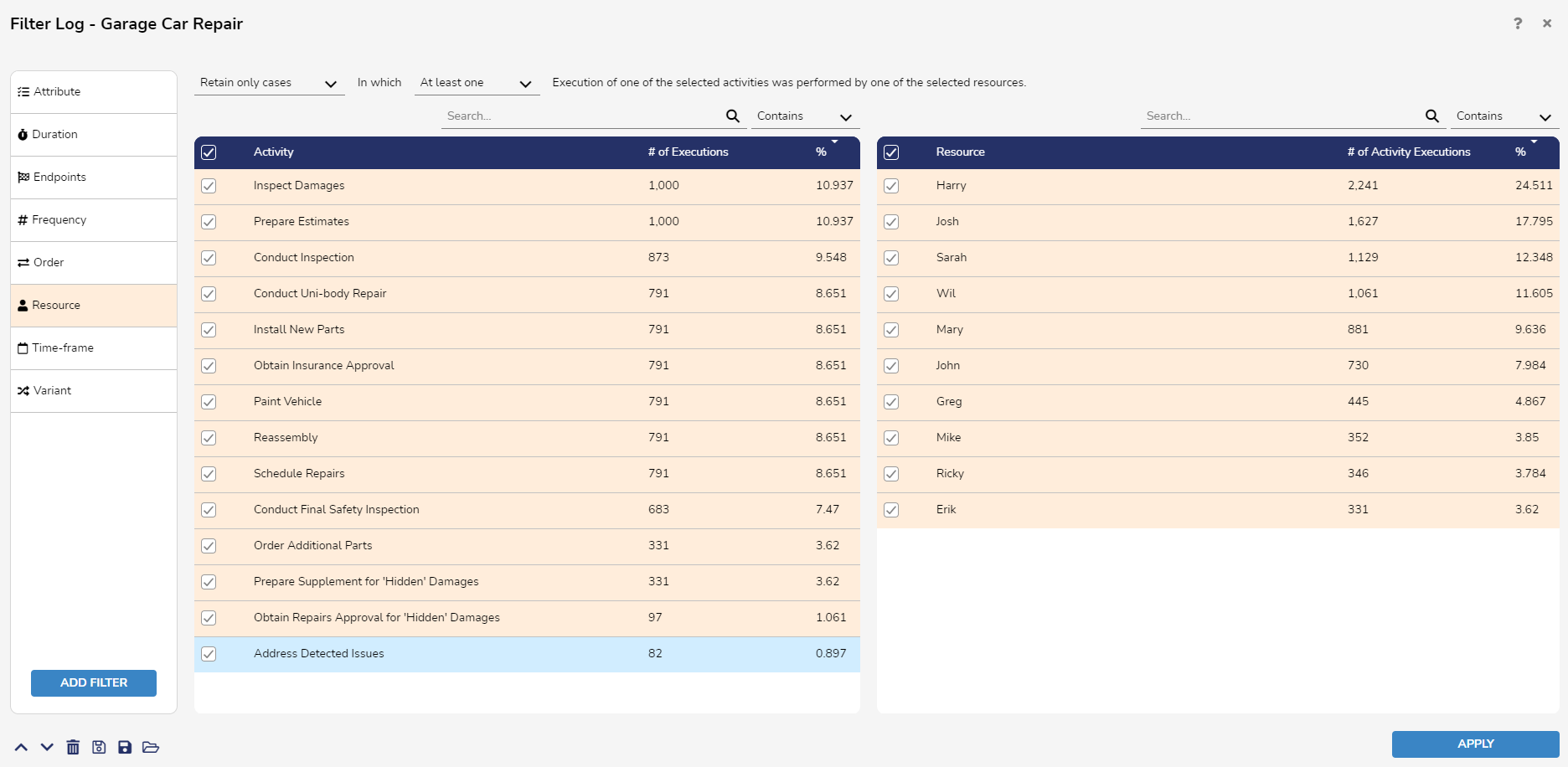
Resource Filter
The Resource Filter allows users to remove or retain cases in which certain activities are performed by certain resources.
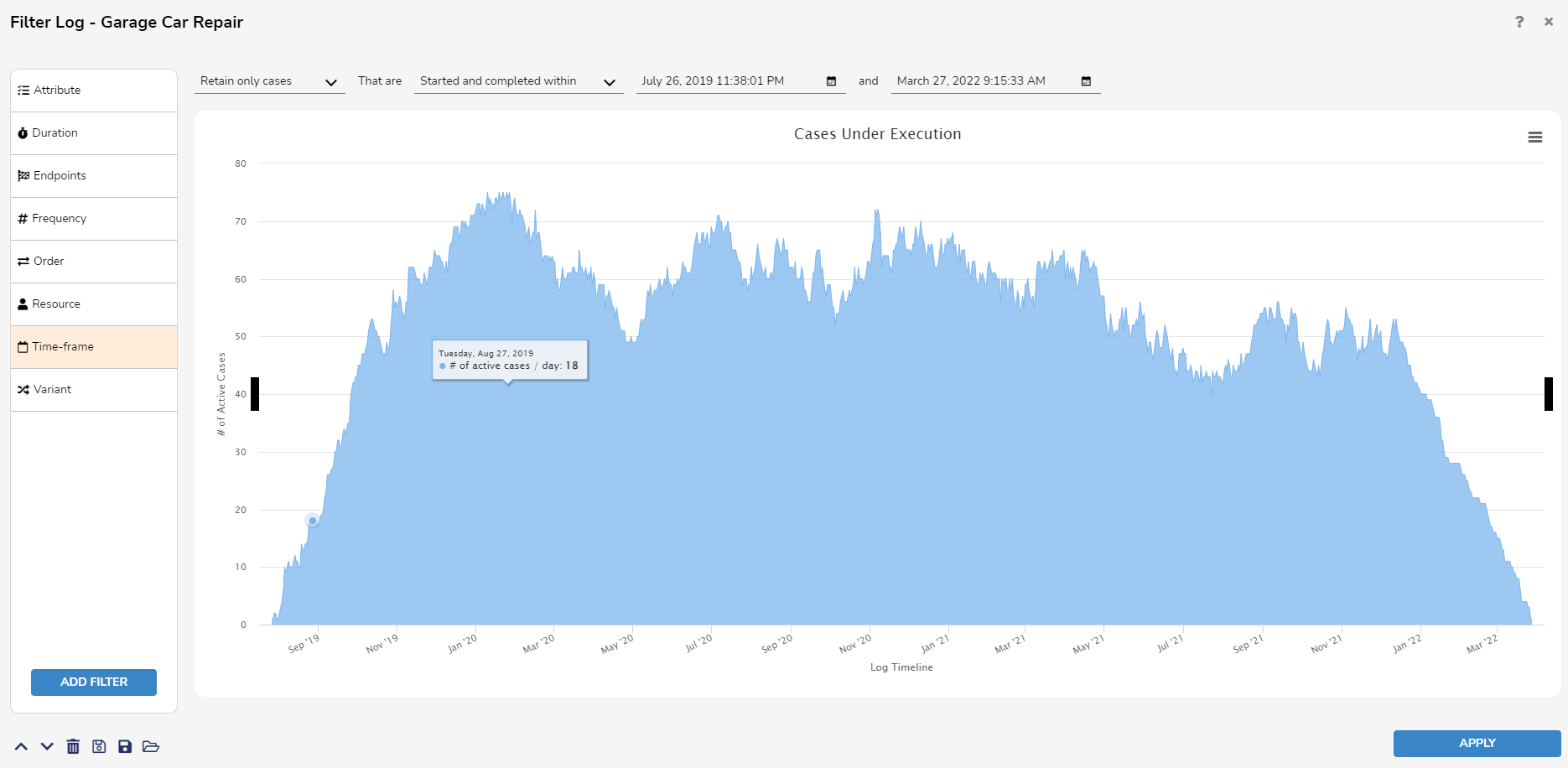
Timeframe Filter
The Timeframe Filter allows users to remove or retain cases occurring within a specific timeframe. The Timeframe Filter supports four potential ranges:
- Started and Completed Within: Considers only executions with first activity performed after the start date and the last activity performed before the complete date.
- Started within: Considers executions with their first activity performed after the start date.
- Completed within: Considers executions with their last activity performed before the complete date.
- Active within: Considers executions with at least one event performed after the start date but before the completed date.
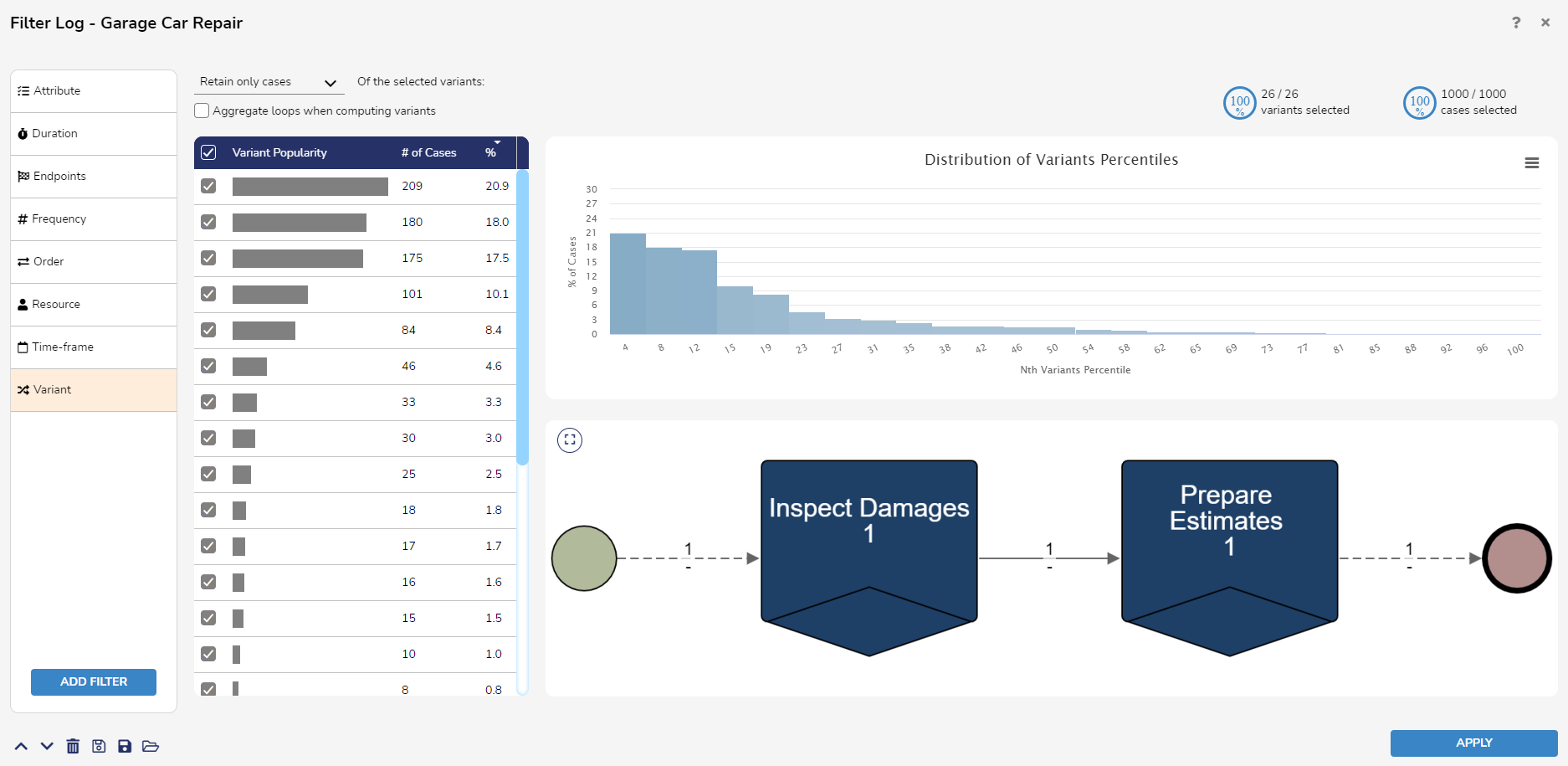
Variant Filter
The Variant Filter allows users to remove or retain cases which follow a specific execution variant. When hovering over a variant in the chart, the Variant Filter shows the number of executions it appears within.