Overview
Decisions allow users to integrate with external databases. The workflow engine doesn't mandate storing any of its data locally. Instead, it can be integrated with existing databases to enable reading and writing data. This flexibility helps to use the data within Designer Elements (Flow, Forms, Rules, Reports, etc.) to perform CRUD(Create, Read, Update, and Delete) actions on the connected database. The following document explains the various options and settings involved in configuring a connection to an existing database.
Following are types of Database that can be integrated:
- MSSQL
- MySQL
- Oracle
- Azure
- Postgres
- ODBC
- Azure Synapse
- Mongo DB - Users must install the Mongo DB Module.
Configuration
- In Decisions Studio, navigate to System > Integrations > Databases and click CREATE CONNECTION.
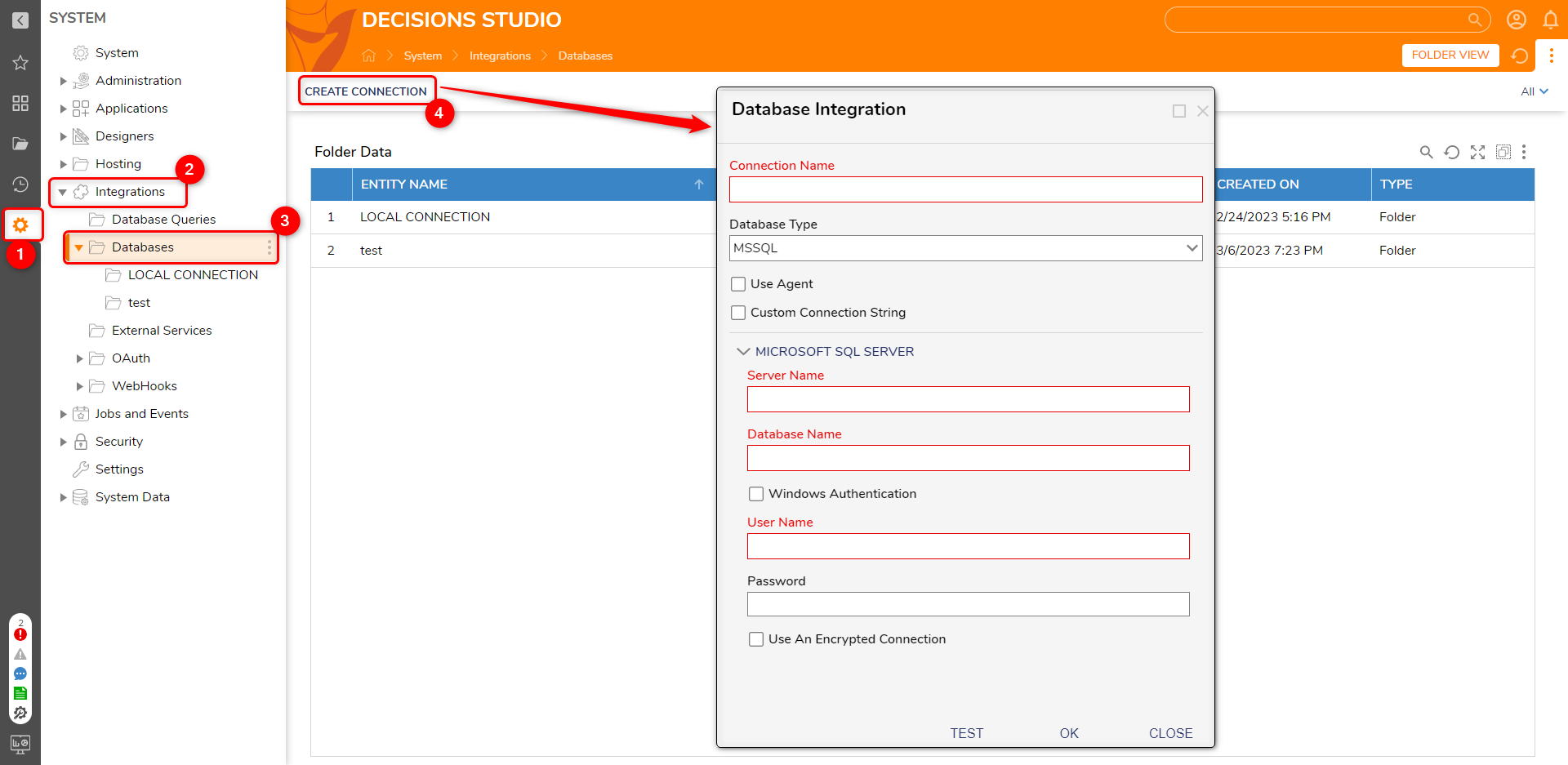
- In the Database Integration window, complete the fields required for integrating with the desired external database type.
Configuration Option Description Connection NameThis will be the name of the ConnectionDatabase TypeThe type of database that will be integrated with (MSSQL, MYSQL, ORACLE, AZURE (SQL), POSTGRES, ODBC, AZURESYNAPSE)Use AgentCheck this setting to get Decisions' integration settings from a database Agent. For more information, refer to Database Integration via Agent.Use Custom Connection StringAllows users to connect to a database via a custom connection string.Server NameThe DNS name or IP of the server running the database.Database Name Name of the database Windows AuthenticationChecking this box will use the windows logon to access the database.SQL Authentication - User Name
Username of the SQL account used to access the database.- Password
The password of the SQL account access the database.- Use an Encrypted Connection
When enabled, the connection between the client and server will be encrypted only if the Root SSL certificate is installed. For more information, refer to Microsoft's official document. - Trust Server Certificate
When enabled, the transport layer will use SSL to encrypt the channel and bypass walking the certificate chain to validate trust. For more information, refer to Microsoft's official document. Using Azure Service Principal Authentication - App ID
This is the Application (client) ID of the registered app under Entra ID (formerly known as Azure AD).- Client Secret
This is the value of the Secret ID generated for the registered App under Entra ID (formerly known as Azure AD).- Tenant ID
This is the Directory (tenant) ID of the registered app under Entra ID (formerly known as Azure AD). Refer to Installing Decisions "Using Azure Service Principal" for reference.Using SSL for Postgres - Disable, Allow, Prefer and Require
Refer to Postgres' official documentation for a description. Oracle - Use TNS
When enabled, the connection will follow the OCI(Oracle Call Interface) connection string. - Host Name
Host name of the Oracle server - Port
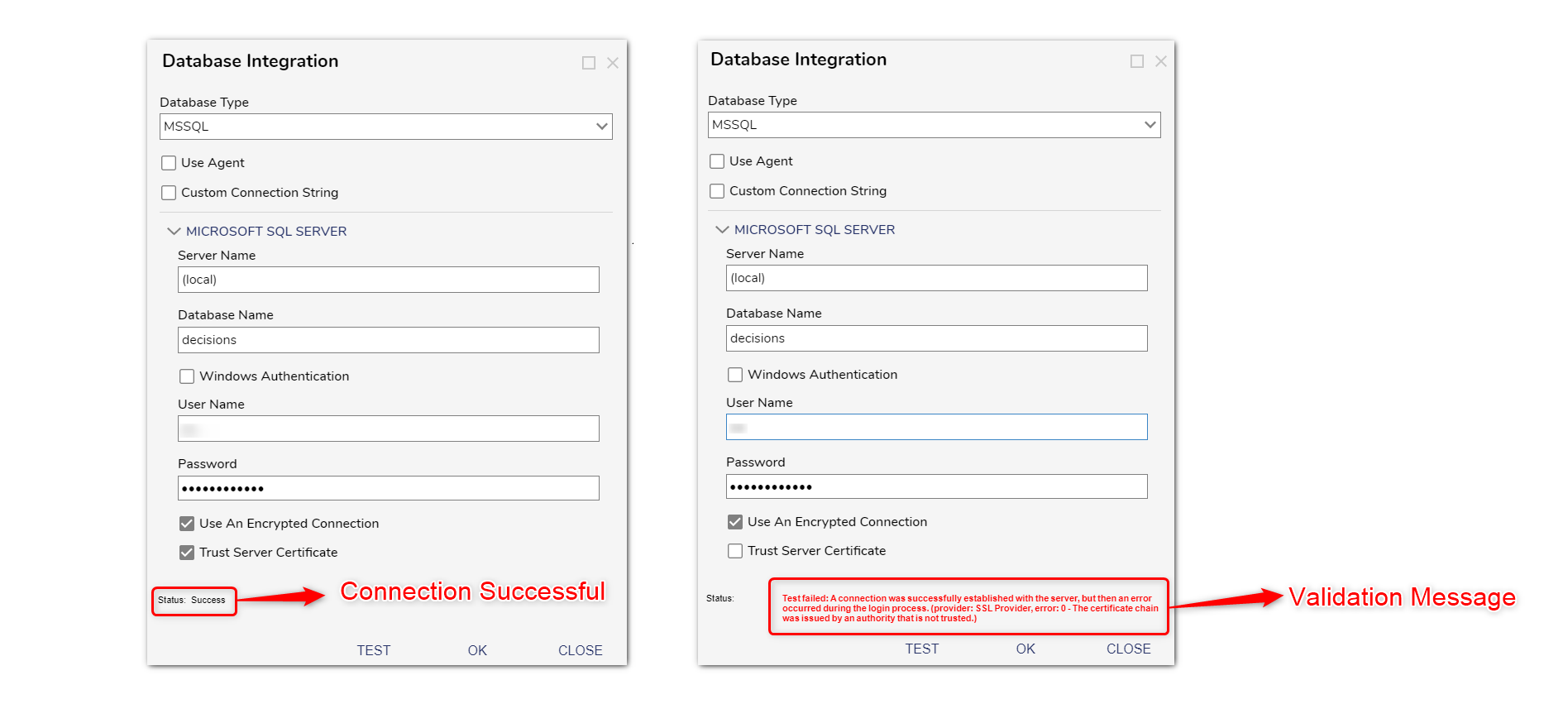
The port on which the server is running After filling in all the details. Click on Test to validate the connection to the Database. A Status field will appear in the bottom right corner.
Check for the Status. If the Status indicates 'success', it means that the connection was established successfully. In case of a failed connection, the Status will provide validation which can be used as a reference to troubleshoot the issue. Refer to the following image.
Updating External Connection String
Users can update the connection string of the already integrated external database. The primary use case of this might be to update the connection string of an external database when migrating from a development environment to a production environment.
- Navigate to System > Integrations > Databases. Right-click the desired entity and select Edit Database Definition [Advanced].
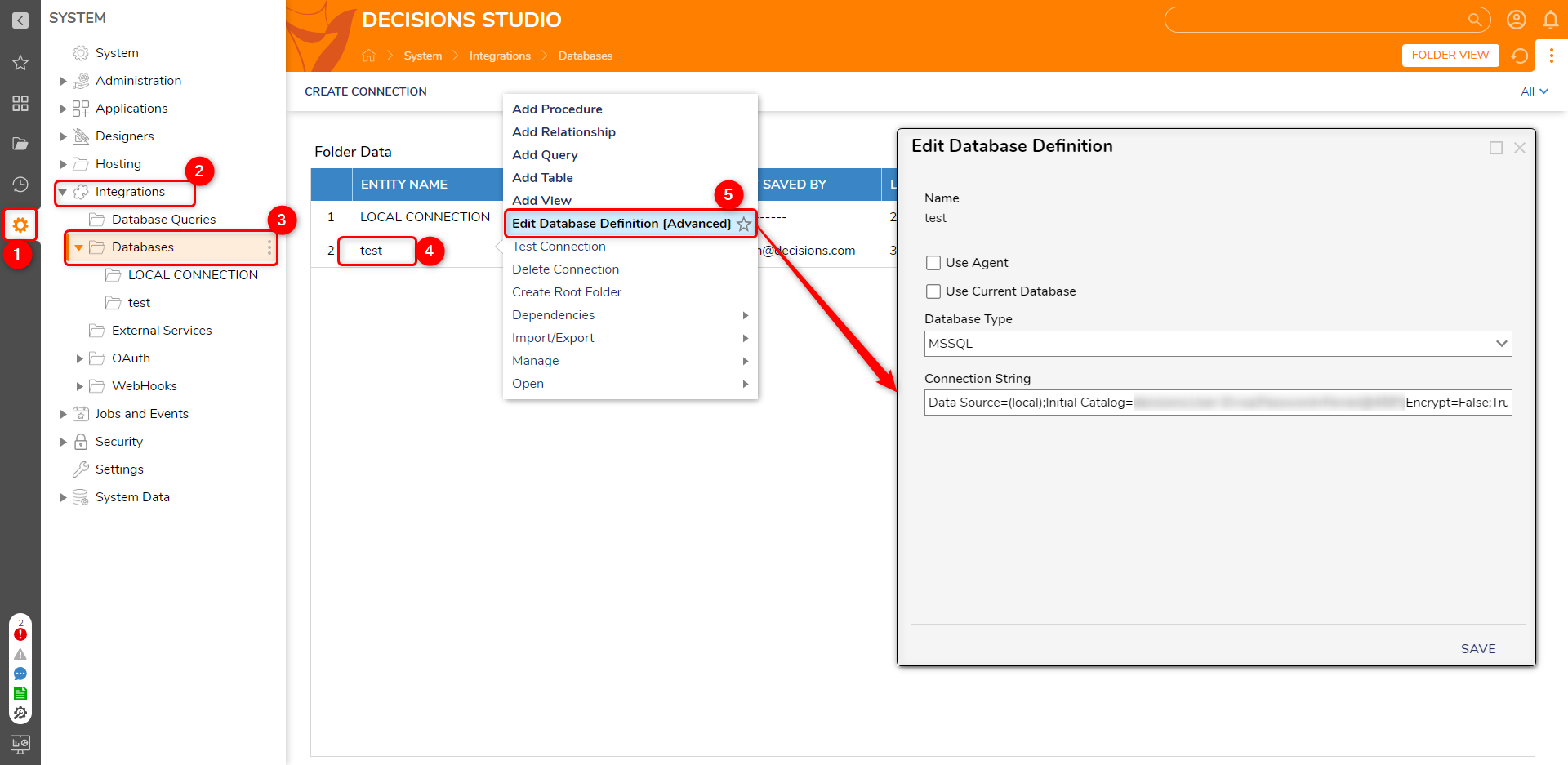
- Unselect Use Current Database and paste the updated connection string in the Connection String field.
- Click SAVE.