| Data Structure Quick Summary | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Complexity? | Performance Impact? | Saves to Database? | Configuration Folder? | Entity Framework? | Folder Behavior? | Process Tracking? |
| High | Low | Can decide if stored or not | Yes | No | No | No |
A Defined Data Structure (DDS) allows users to define another data type as a Superclass. This causes the DDS to inherit fields from the Superclass.
Example
- In a Designer Project, click CREATE DATATYPES/INTEGRATION on the top Action Bar.
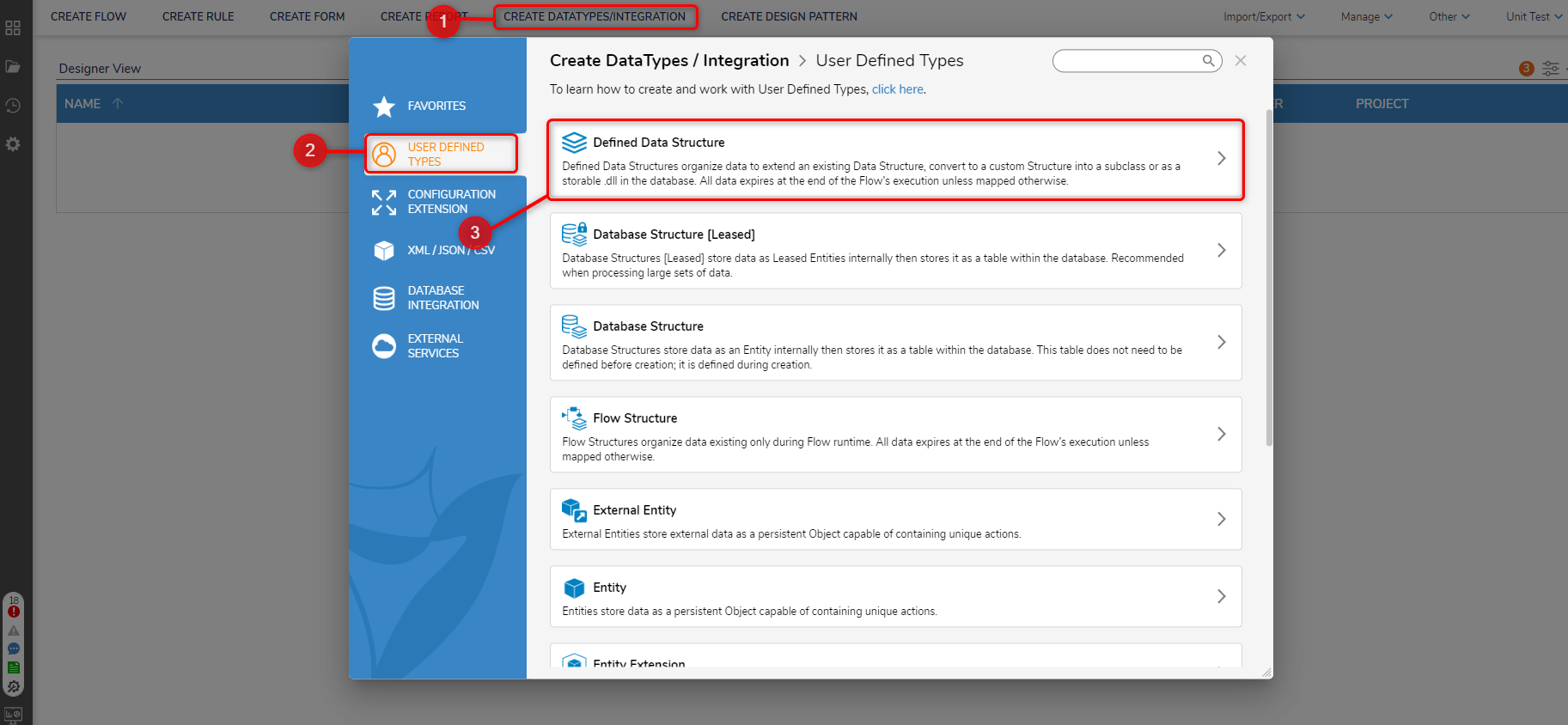
- In the Defined Data Structure window, enter a name for the structure and defined the data fields for the data structure. The Defined Data Structure can be configured to be database stored by configuring the Storage Option setting. This would cause Decisions to generate Flow steps under the USER DEFINED TYPES category in the ToolBox panel.
- Click on the name of the structure to view the Defined Data Structure's settings. Set the Storage Option field to DatabaseStored. Saving and Deleting Database Stored DDSIf deleting a database stored DDS, ensure to delete its table as well in the database to prevent clutter. If wishing to create another databased stored DDS of the same name without deleting this table, a validation error will occur to prevent creation since the same-named table already exists.
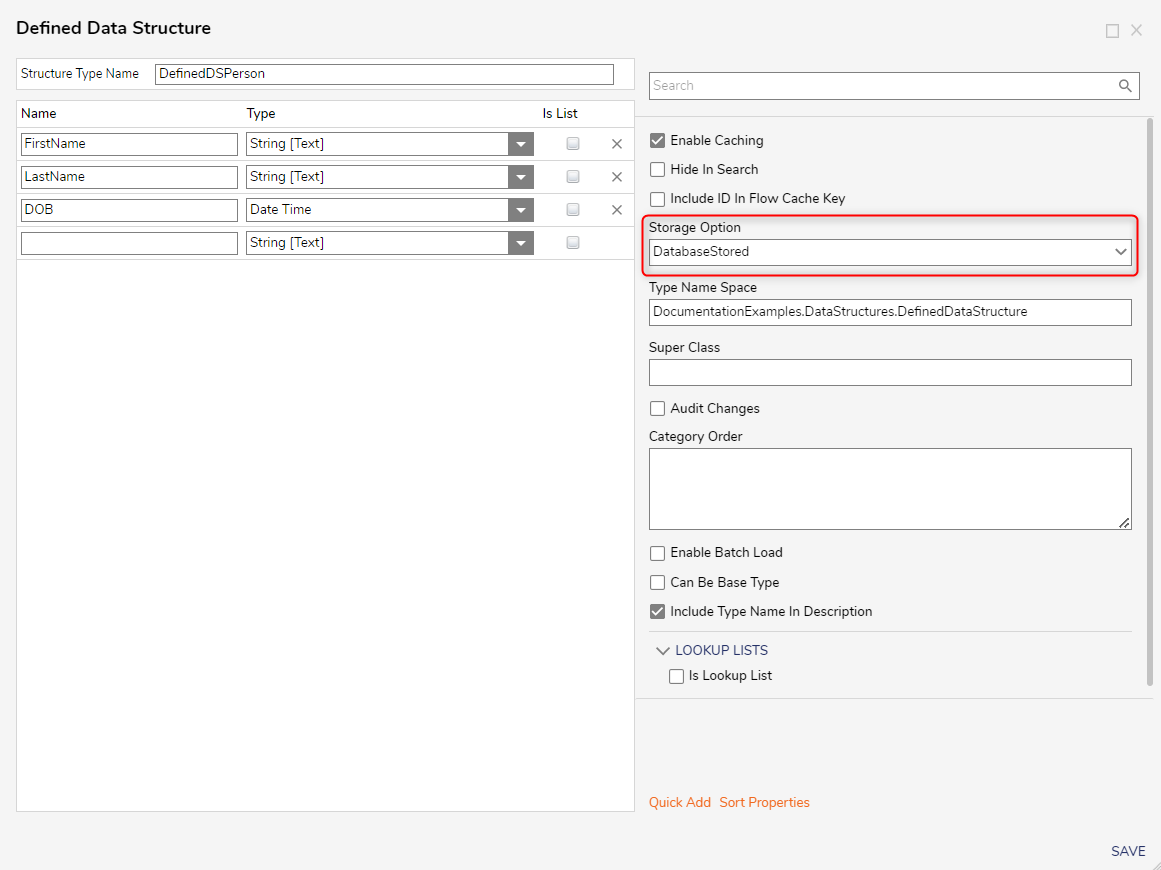
Create Defined Data Structure Settings
| Setting Name | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Hide In Search | Hides the data type from appearing when being searched | |
| Storage Option | Specifies where the data structure will be stored | |
| Type Name Space | Creates the unique identifier for the Entity (namespace.typename) to generate the SQL table name for the Entity (namespace_typename) | |
| Super Class | Specifies the class to inherit traits from. The input is case sensitive and is formatted as [Type Name Space].[Struture Type Name] | |
| Category Order | Allows data field categories to be organized in a certain way. For example, grouping required data fields together | |
| Can Be Base Type | Allows the created type to be used as a super-class for sub-classes | |
| Include Type Name In Description | This enables or disables the visibility of the Type namespace | |
| Is Lookup List | Specifies if the data will be a Lookup List | |
| Lookup List Category | Specifies the category for the Lookup List | |
For further information on Data Structures, visit the Decisions Forum.